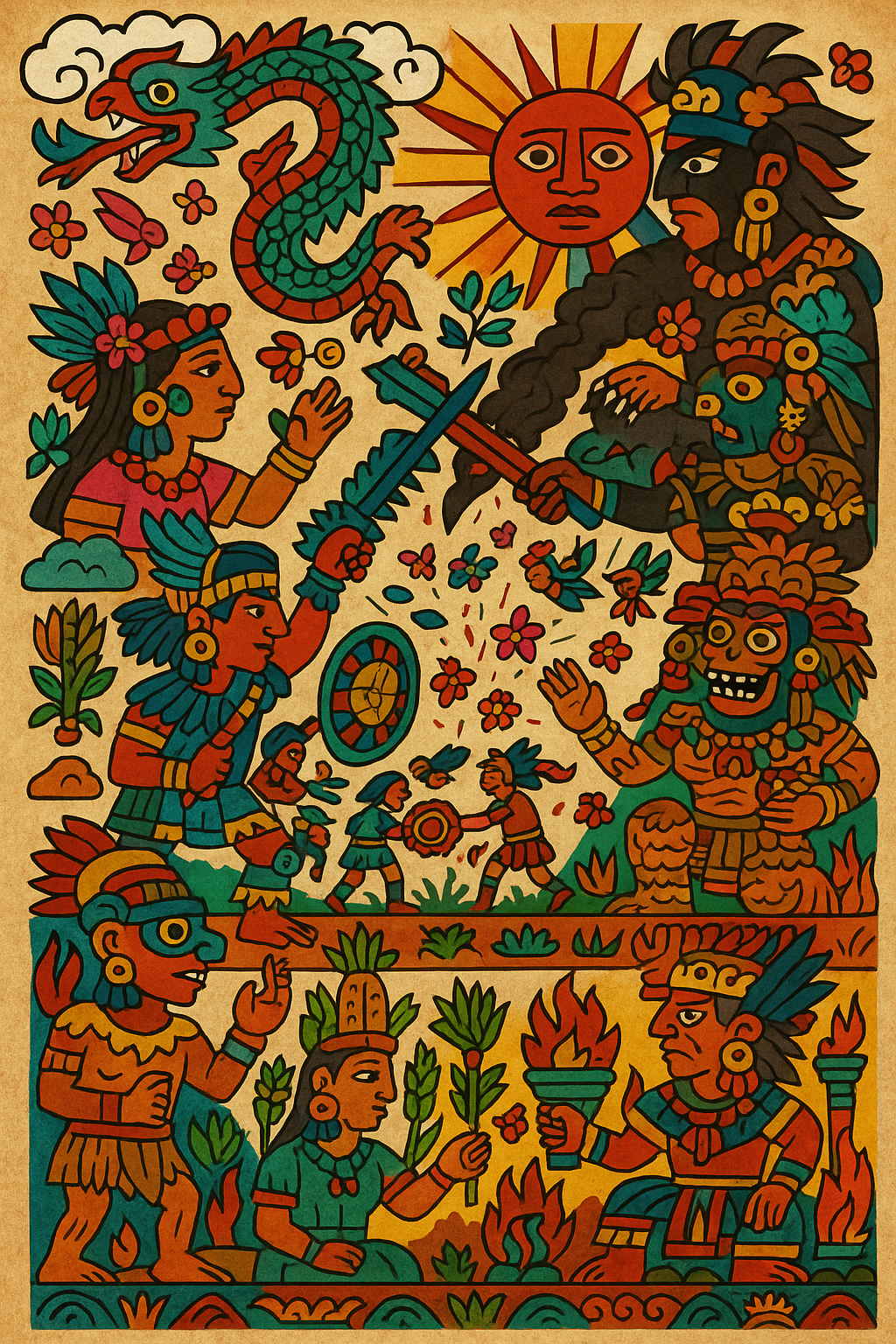
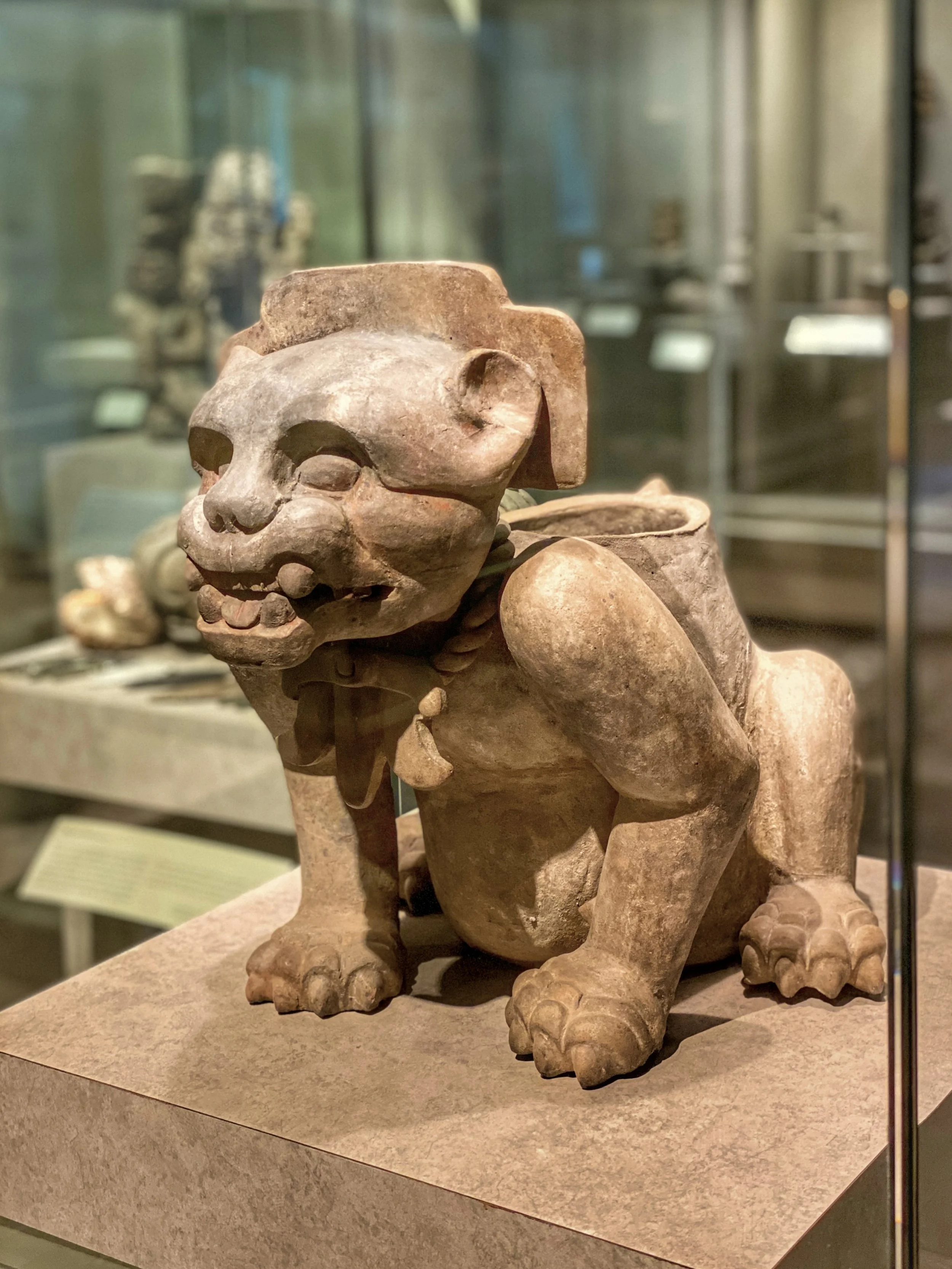
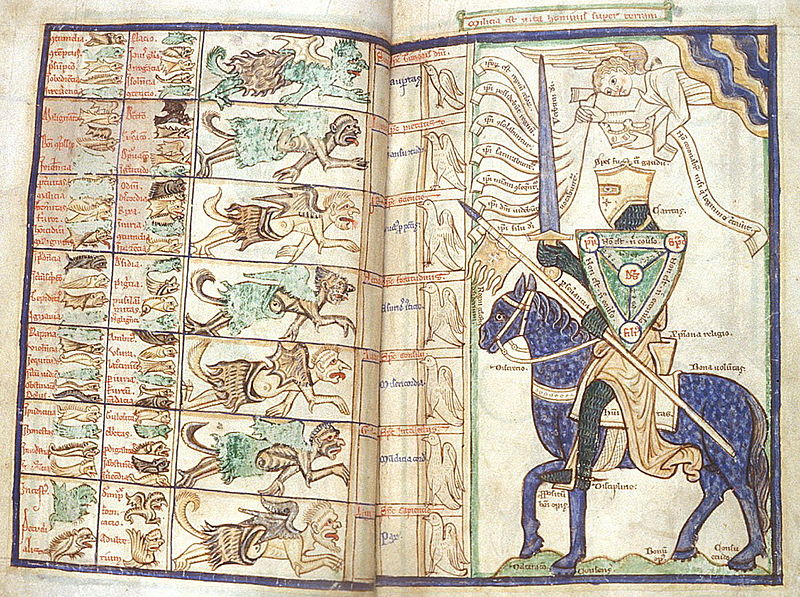
From Quetzalcoatl the Feathered Serpent to the bloodthirsty Huitzilopochtli, the Aztec pantheon was vast, violent and surprisingly flexible. Plus, learn how the Flower Wars provided (semi) willing fodder for human sacrifices.
The Mexica treated war as an opportunity for cultural accumulation, much like the Mongols did a few centuries earlier. Every conquest came with new foods, new customs, new technology and, often, new deities. If another city had a rain god who seemed to get better results, the Mesoamerican people didn’t see worshipping him as blasphemy — they saw it as smart.
“In many defeated nations we discovered new gods or novel manifestations of our known gods, and, if they appealed to us, our armies brought home copies of their statues for us to set in our own temples,” Gary Jennings writes in his 1980 novel Aztec.
“Every ritual — whether it involved flowers, animals or human hearts — was a way to keep the cosmic machinery running.
Blood was the power source of the sun. To let that flow stop would be like unplugging the universe.”
It’s a tradition that goes back to at least Ancient Rome. Why destroy another civilization’s gods when you can just add them to your own pantheon?
The Spanish, of course, were appalled (never mind how many Catholic beliefs originated in so-called pagan celebrations like Yule). They arrived preaching one true God — and promptly rolled out the Father, the Son, the Holy Ghost, the Virgin Mary, angels, apostles and a saint for every stubbed toe and lost key.
“I have heard you Christians complain of our ‘multitudes’ of gods and goddesses,” Jennings writes later, before his narrator adds, “I have counted and compared. I do not believe that we relied on so many major and minor deities as you do — the Lord God, the Son Jesus, the Holy Ghost, the Virgin Mary — plus all those other Higher Beings you call Angels and Apostles and Saints, each of them the governing patron of some single facet of your world, your lives, your tónaltin [fate], even every single day in the calendar. In truth, I believe we recognized fewer deities, but we charged each of ours with more diverse functions.”
What a dig! While Europeans obsessed over keeping heaven in order, the Mexica embraced divine chaos — a spiritual ecosystem where gods could merge, borrow faces and change form as easily as the world itself.
The Aztec Gods, A to Z
(Well, Actually C to X)
Aztec mythology wasn’t built on tidy hierarchies. It instead embraced glorious contradiction — gods who could be both creators and destroyers, lovers and warriors, rainmakers and flood-bringers. To keep things simple (or at least alphabetized), here’s a guide to the divine cast that kept the sun burning, the corn growing, and the sacrifices right on schedule.
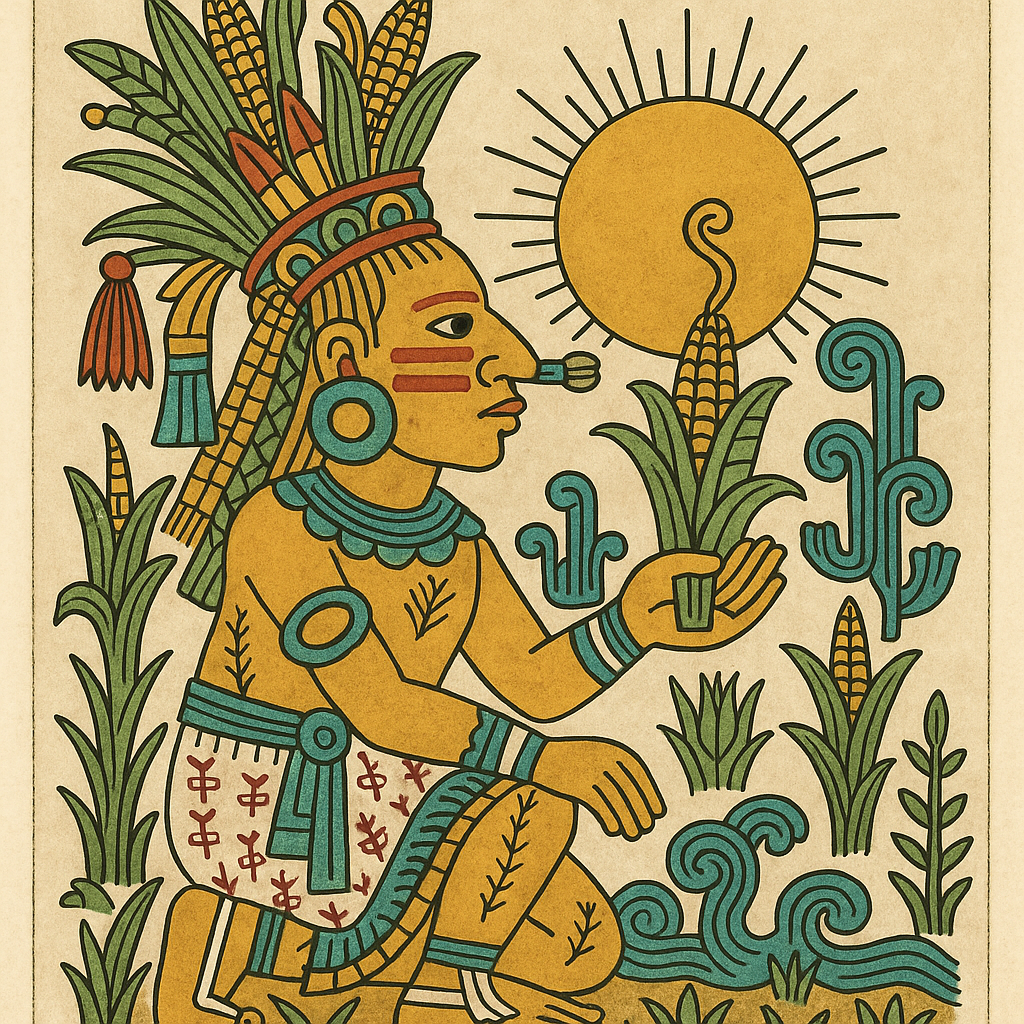
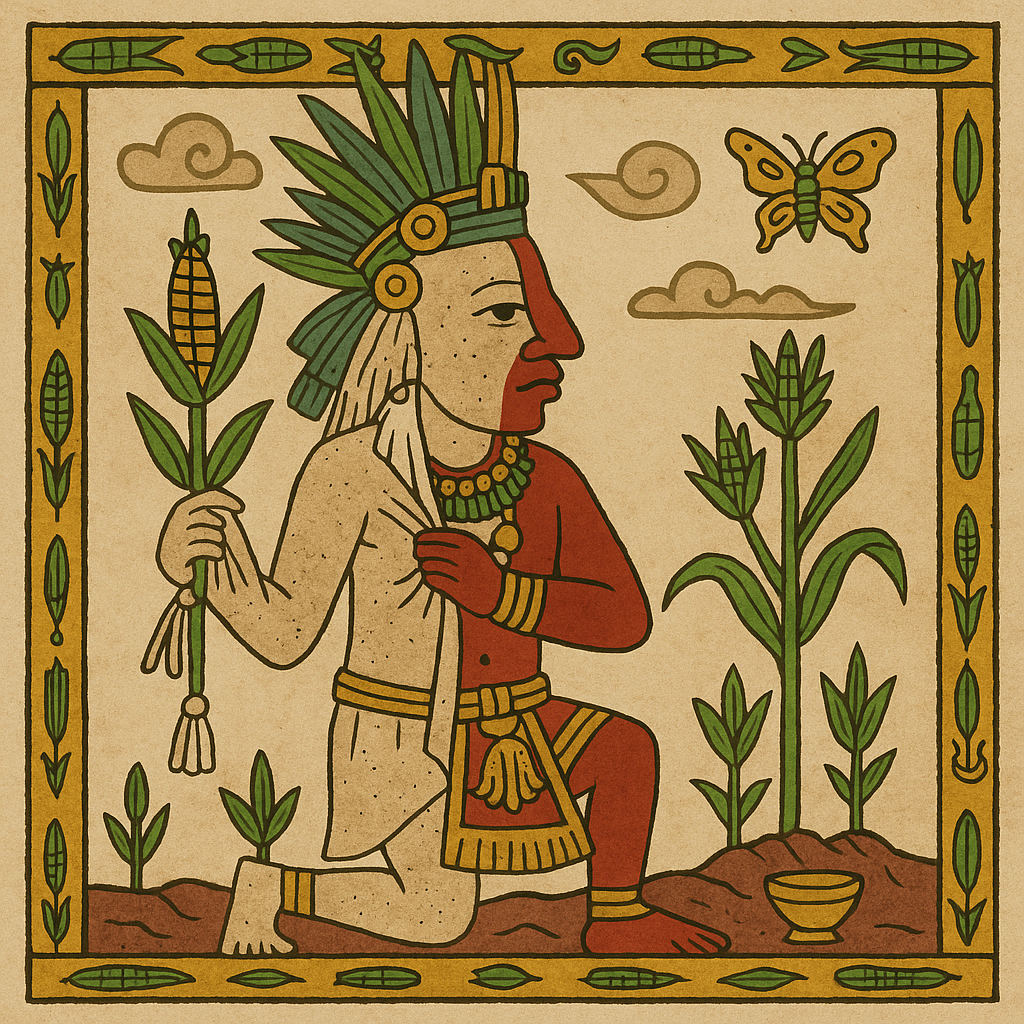
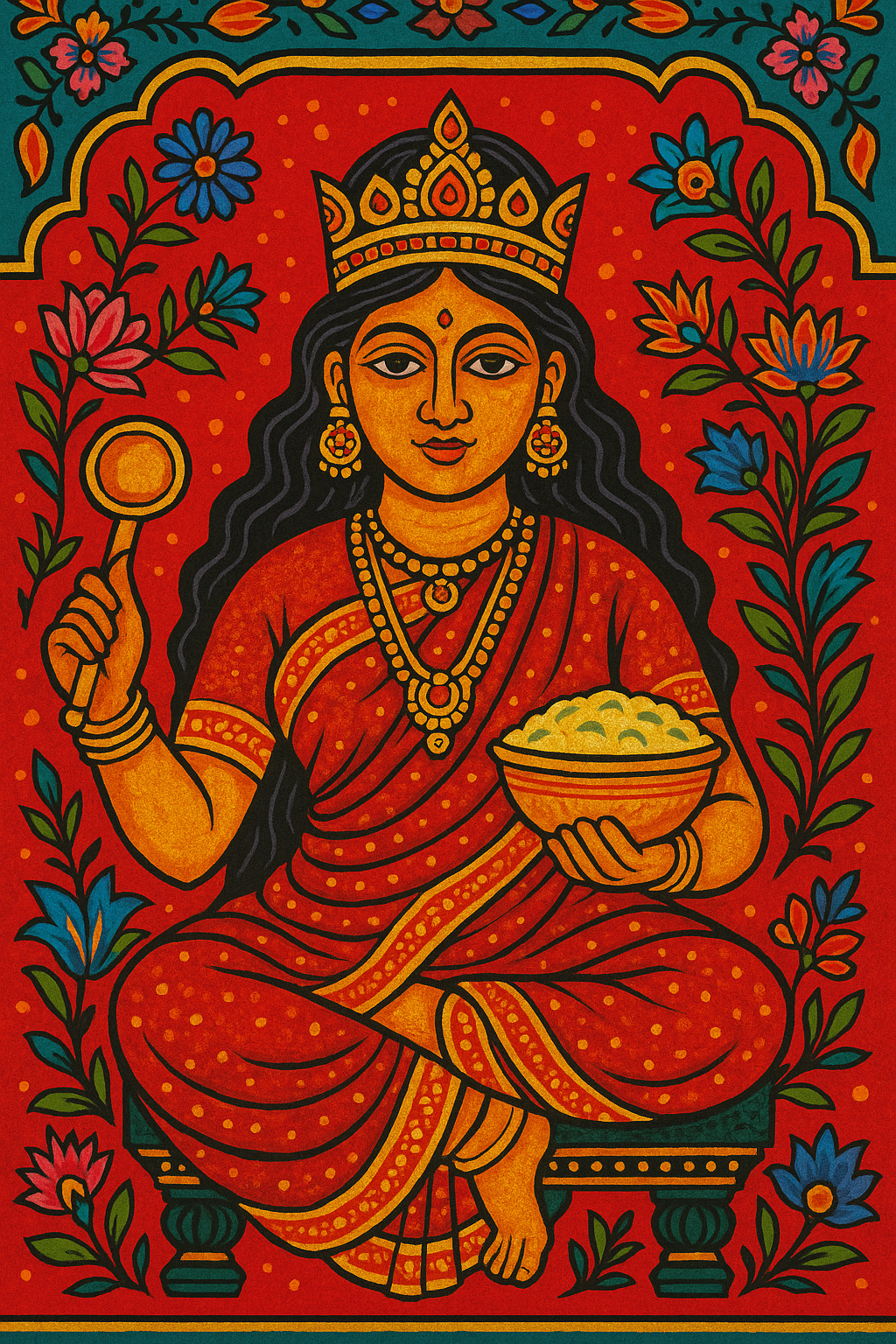
Centeotl
“God of Maize”
Pronunciation: Sen-teh-o-tull
Domain: Corn, sustenance, harvest
Vibe: The dependable one — always shows up for dinner
Story: Centeotl was the golden core of Aztec life, the maize god whose body quite literally fed the people. According to the Florentine Codex, Quetzalcoatl tore open the earth to bring corn to humankind, and from that soil Centeotl sprouted — divine, delicious and essential.
Chalchiuhtlicue
“She of the Jade Skirt”
Pronunciation: Chal-chee-oot-lee-kweh
Domain: Rivers, lakes, seas, childbirth
Vibe: The goddess of good water and bad wmoods
Story: Chalchiuhtlicue ruled over every flowing thing — from gentle rivers to catastrophic floods. One myth says she once loved humanity so much she wept for them, and her tears flooded the world. The survivors, naturally, turned into fish.
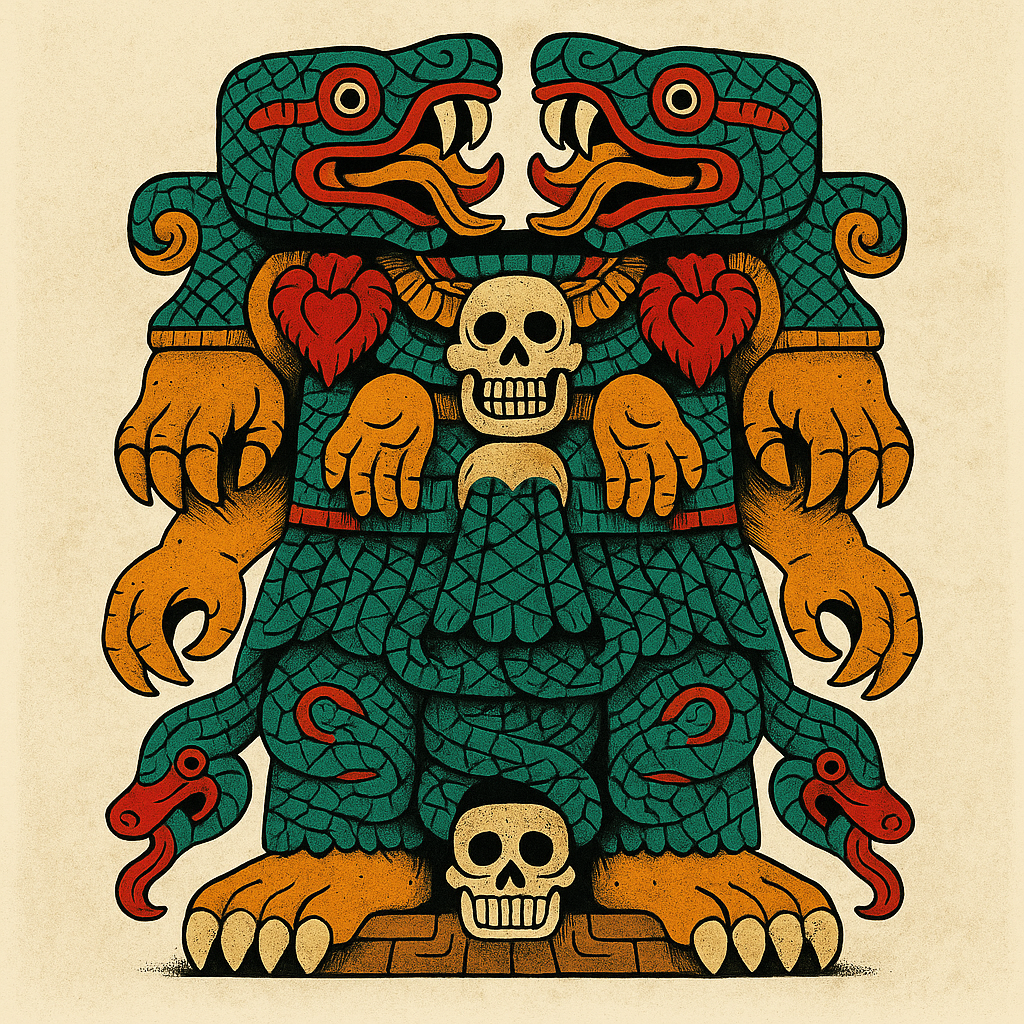
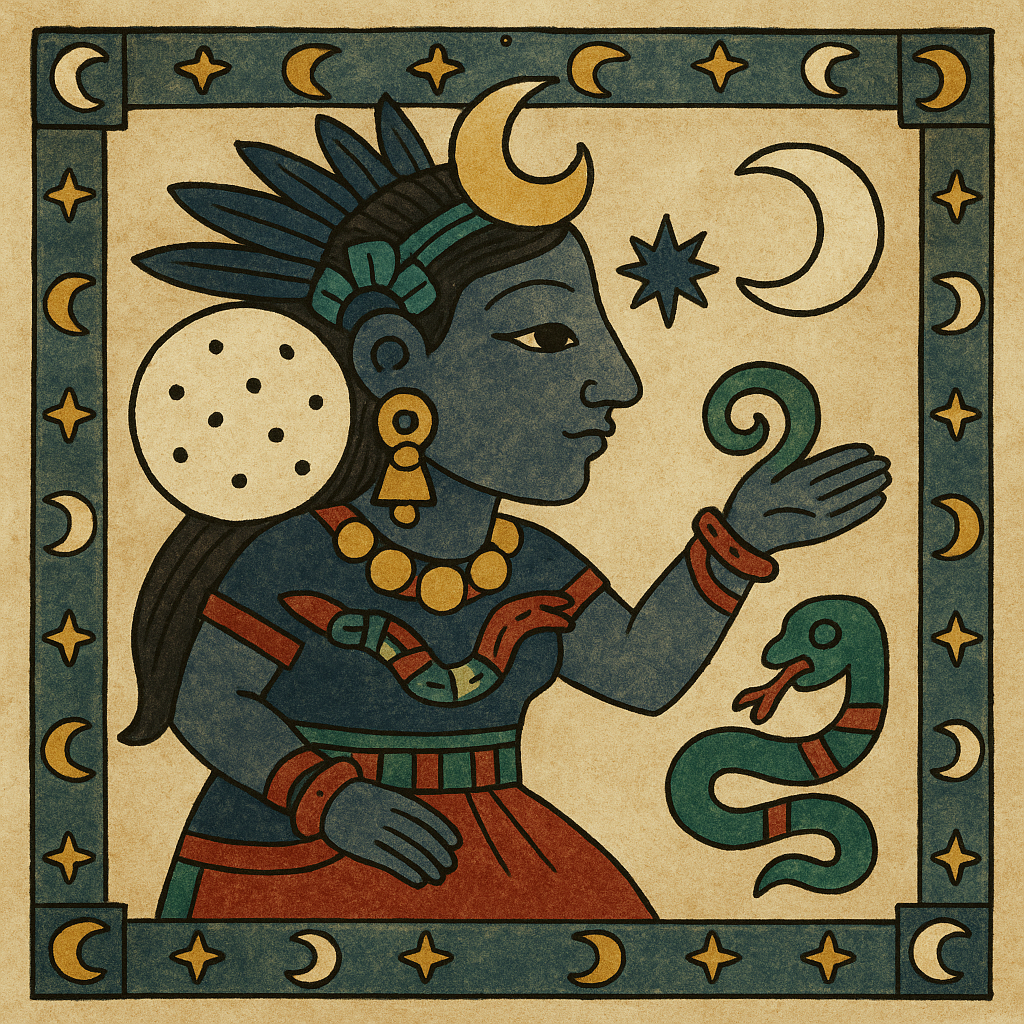
Coatlicue
“She of the Serpent Skirt”
Pronunciation: Ko-aht-lee-kweh
Domain: Earth, life and death, motherhood
Vibe: The cosmic mom you do not want to disappoint
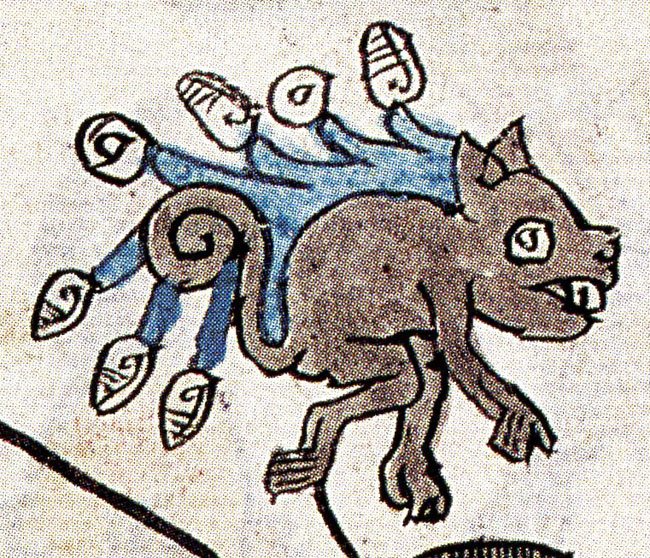
Story: Coatlicue was the ultimate Earth mother — nurturing yet terrifying. She wore a skirt of snakes and a necklace of severed hands and hearts (sharing a fashion sense with the Hindu goddess Kali). When her daughter Coyolxauhqui and 400 sons plotted to kill her, they struck off her head — but from the gushing wound sprang two serpents whose fanged mouths met to form her new face. And Coatlicue’s unborn child Huitzilopochtli burst forth from her womb, fully armed, and ended that rebellion fast.
Coyolxauhqui
“Bells on Her Cheeks”
Pronunciation: Koy-ol-shau-kee
Domain: The moon
Vibe: The rebel who lost, but still owns the night
Story: Coyolxauhqui led her siblings in a failed coup against their mother, Coatlicue, only to be dismembered by her newborn brother, Huitzilopochtli — a mythic explanation for the moon’s fragmented phases.
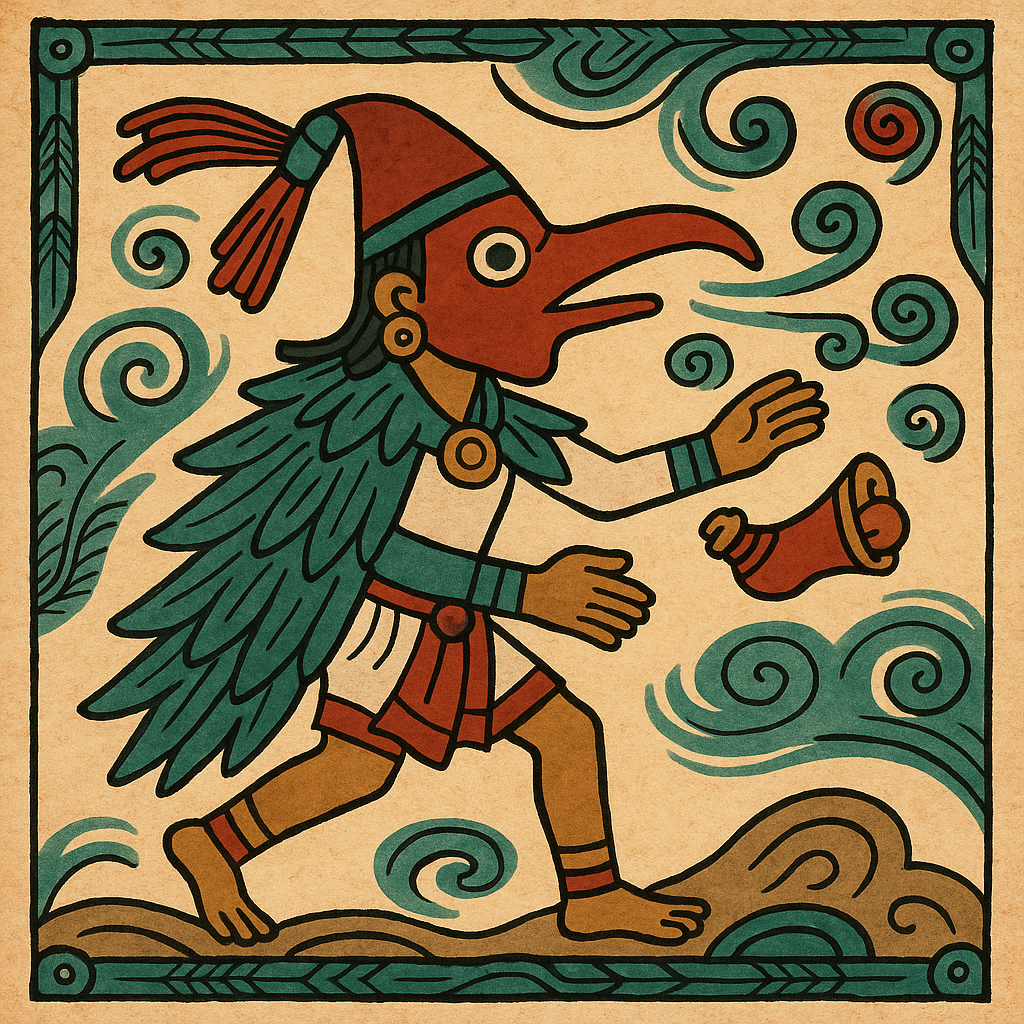
Ehécatl
“He Who Is the Wind”
Pronunciation: Eh-heh-katull
Domain: Wind, breath, motion, life
Vibe: The chill cousin who shows up, stirs things up and vanishes again
Story: Ehécatl is the wind god — a breezy form of Quetzalcoatl himself. When the newly created sun refused to move, Ehécatl blew across the heavens to push it into motion. His temples were round so the wind could pass through, a clever architectural touch in a city built on geometry. The man was literally the breath of life — and sometimes, the breath of fresh air everyone needed.
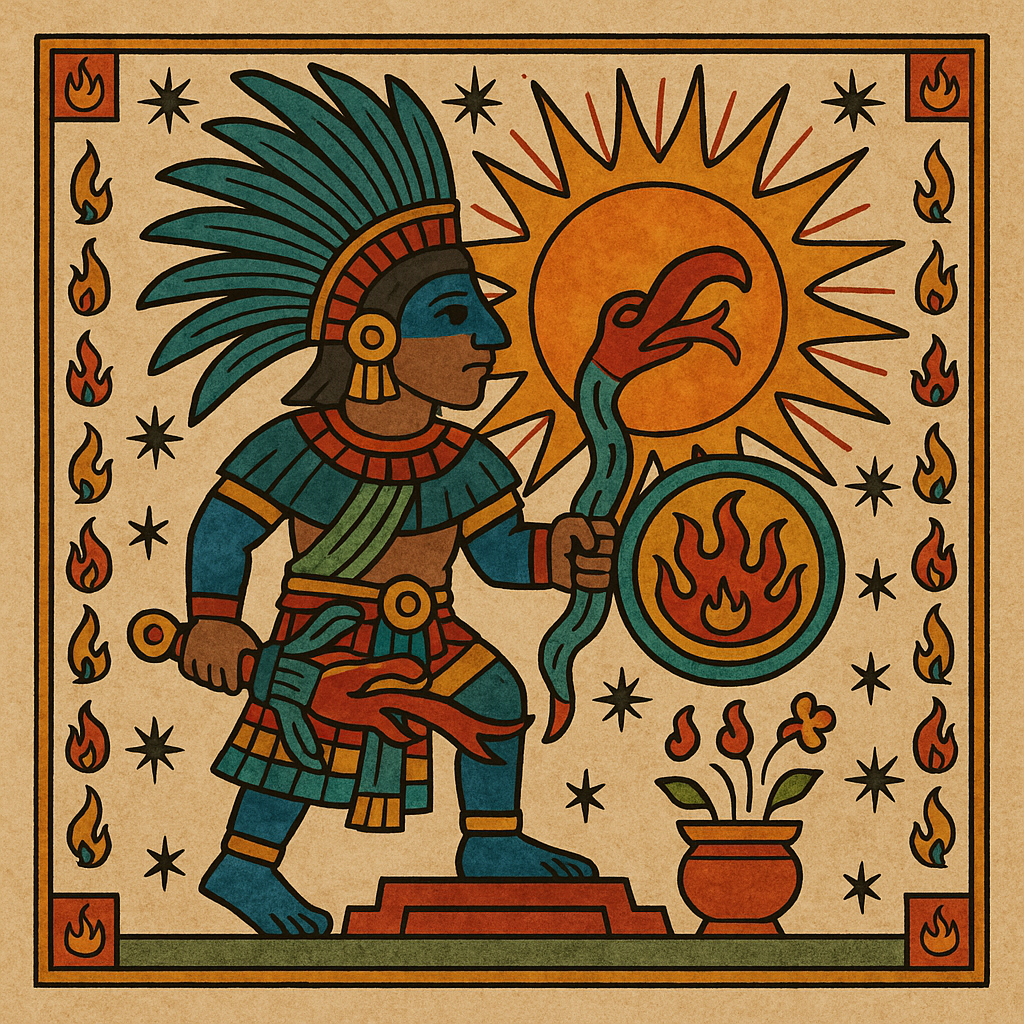
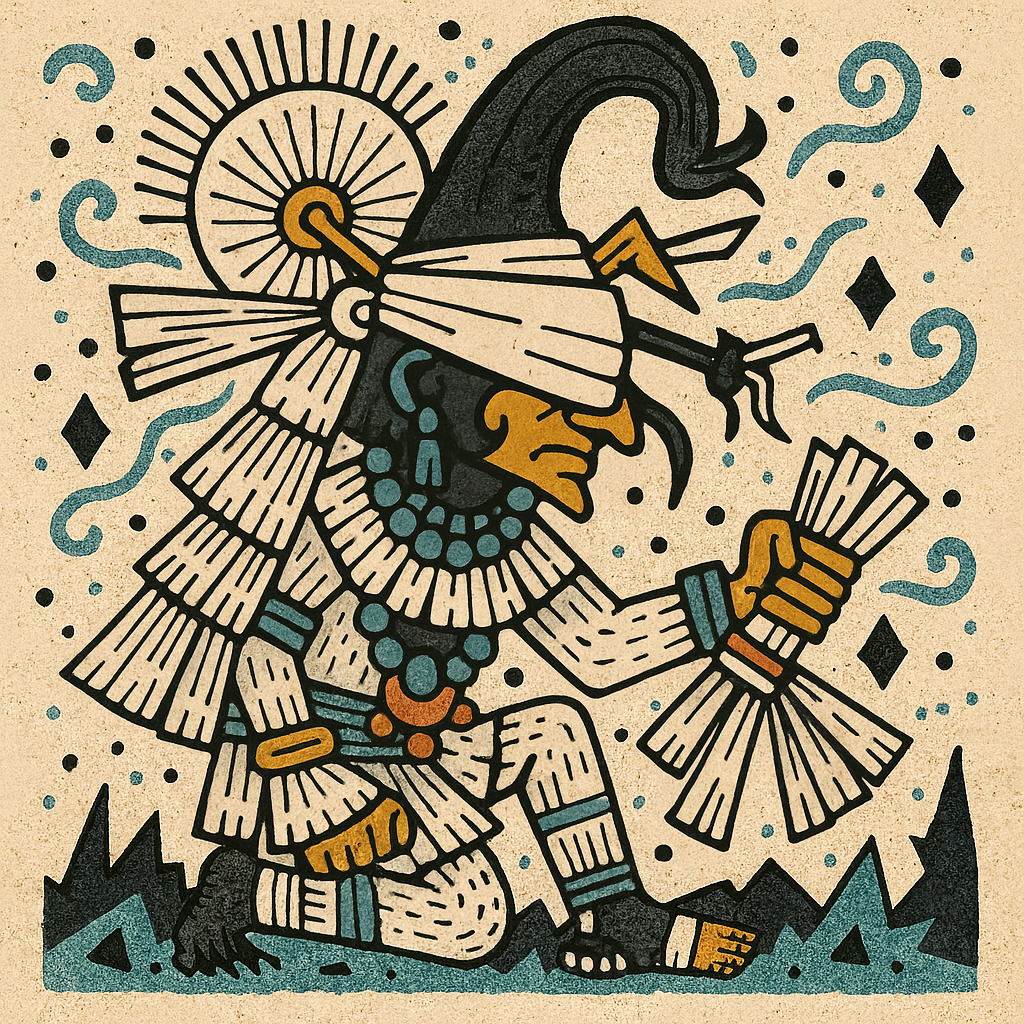
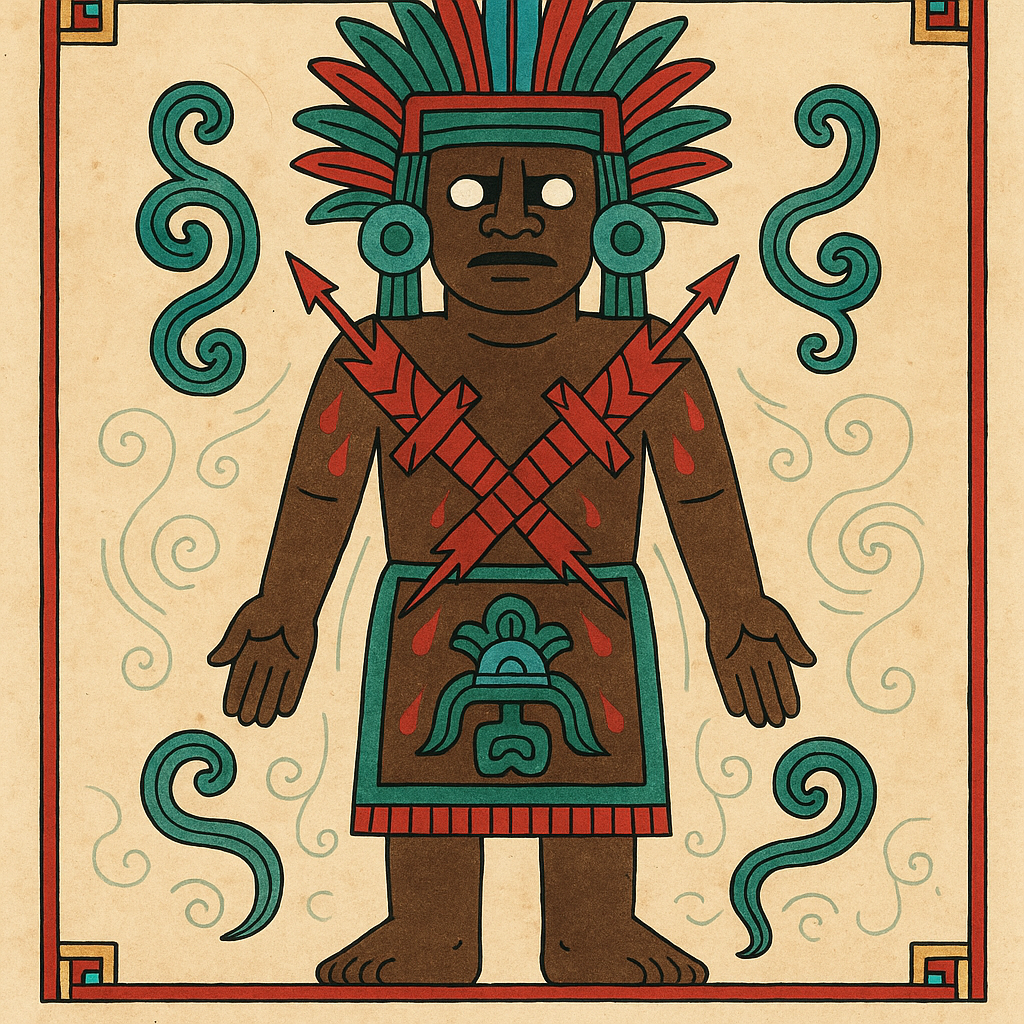
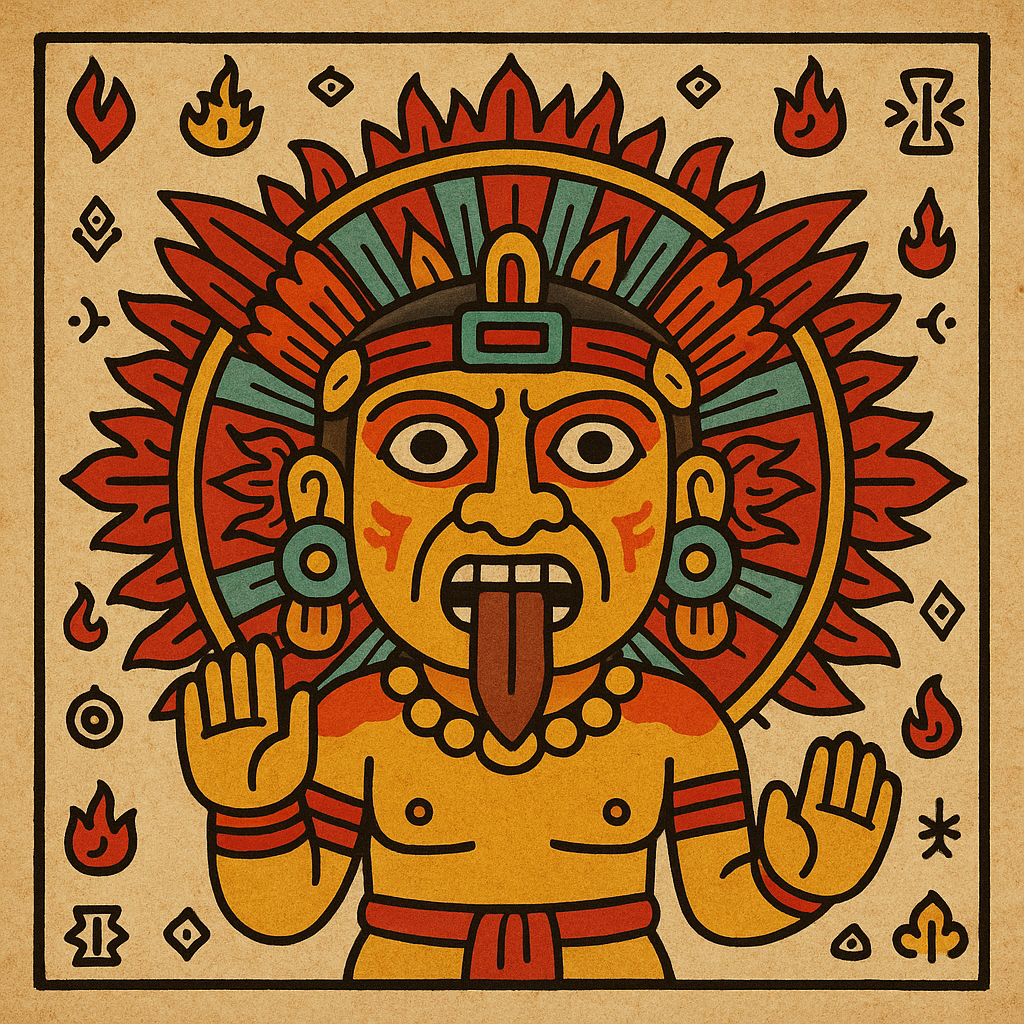
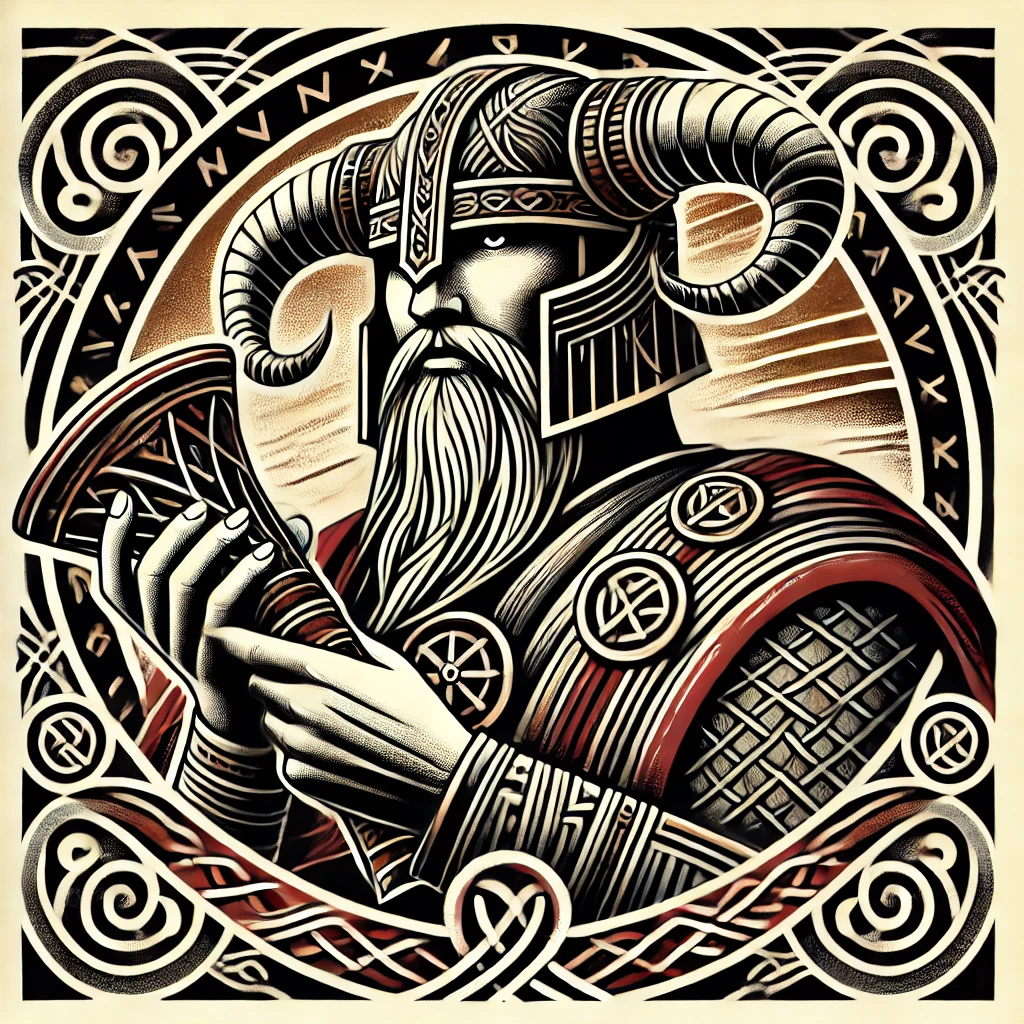
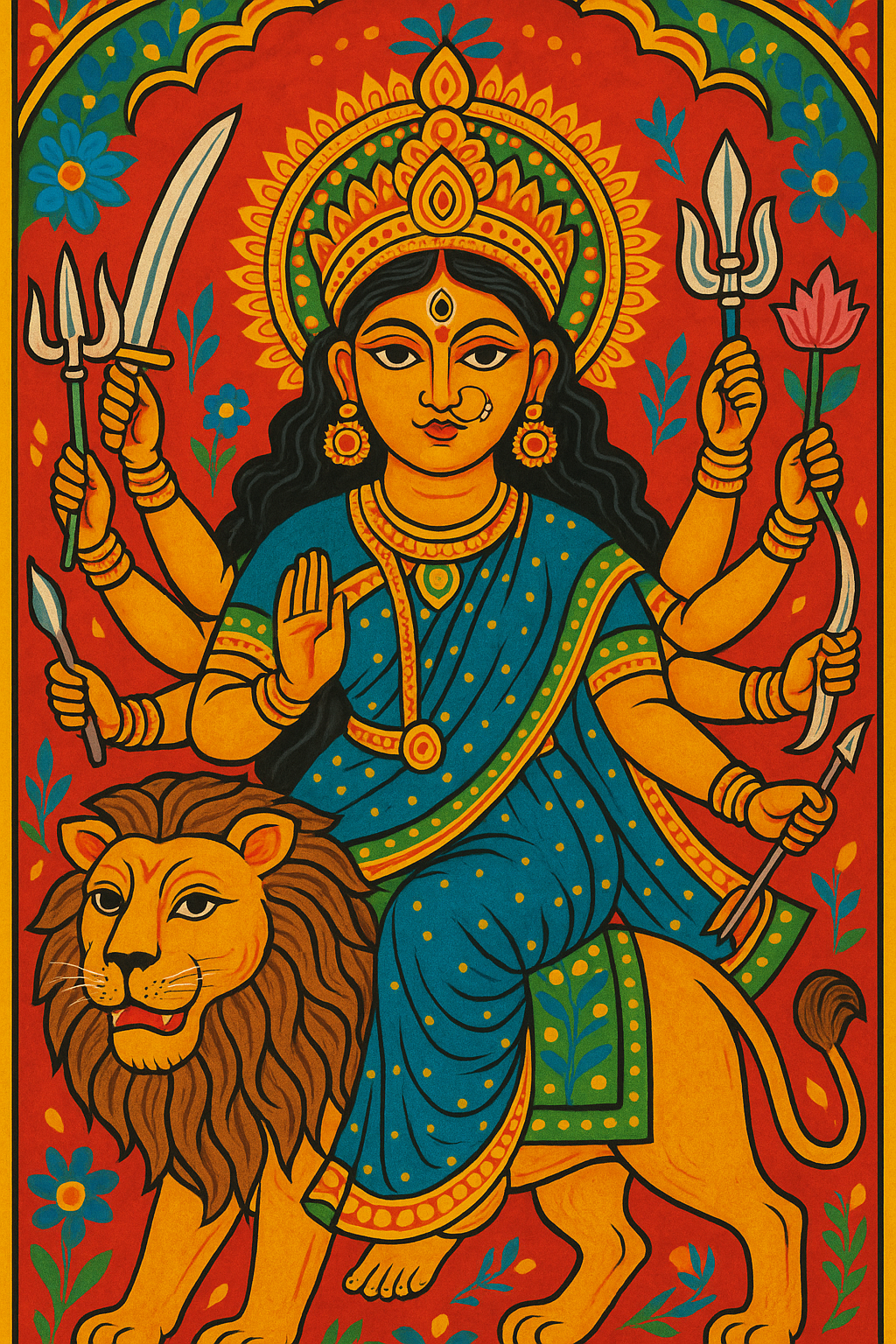
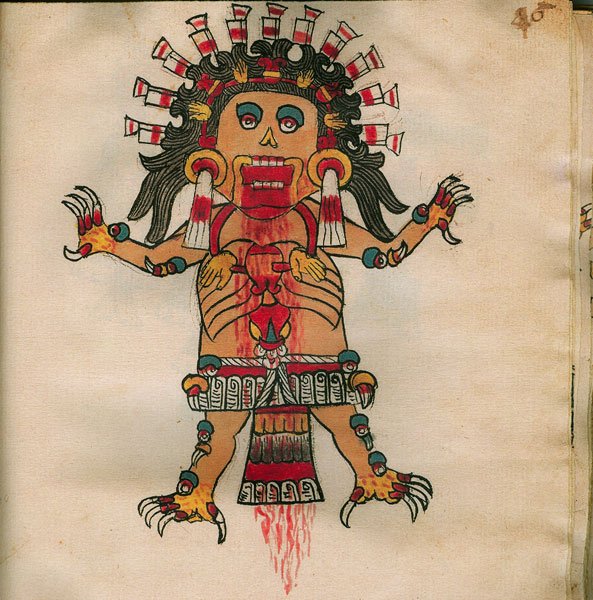
Huitzilopochtli
“Left-Handed Hummingbird” or “Hummingbird of the South”
Pronunciation: Weets-ee-loh-pohch-tuhlee
Domain: War, the sun, the destiny of the Mexica
Vibe: The overachiever with a bloody habit
Story: Huitzilopochtli was the Mexica’s personal war god and the reason they believed themselves unstoppable. Born in a blaze of feathers and fury, he beheaded his sister Coyolxauhqui moments after his birth and tossed her body down the mountainside — symbolizing the sun’s daily triumph over the moon. He needed blood to keep shining, and the Aztecs were more than happy to supply it.
Ilamatecuhtli
“The Old Lady”
Pronunciation: Ee-lah-mah-teh-koo-tlee
Domain: Age, endings, childbirth, dry corn, the turning of the year
Vibe: The venerable (and sometimes scary) grandmother
Story: Ilamatecuhtli was the Earth Mother in her oldest form — not nurturing like Teteoinnan, not frantic like Coatlicue, but ancient, heavy and utterly unavoidable. She ruled the cold, solemn month of Tititl, when people fasted, moved quietly, and lived in fear, as though Death herself was walking past their doors.
Women who died in childbirth were honored as fierce, restless spirits called the cihuateteo during this season, their cries believed to haunt crossroads at night. They belonged to Ilamatecuhtli, who understood both the agony of labor and the final stillness of death. She was the end of the cycle, the crack in the seed before it sprouts again, the winter before the earth remembers how to bloom.
Itztlacoliuhqui
“Curved Obsidian Blade”
Pronunciation: Eets-koh-lee-oo-kee
Domain: Cold, punishment, winter, misfortune
Vibe: The burnt-out star who pissed off the wrong person
Story: Itztlacoliuhqui is literally the embodiment of bad vibes. But he wasn’t always this way. He used to be a radiant god of light, the Lord of the Dawn, Venus as Morning Star, until he either insulted the sun, Tonatiuh, or accidentally loosed an arrow at him. The sun’s response was instant: a burst of searing fire. The blow broke his nose, warped his face into a permanent curve, and transformed him into the frigid, shadowy deity of winter. He’s often shown blindfolded or bent, carrying a staff like a frozen wanderer. He represents the moment when light collapses into darkness — and the consequences of making mortal enemies.
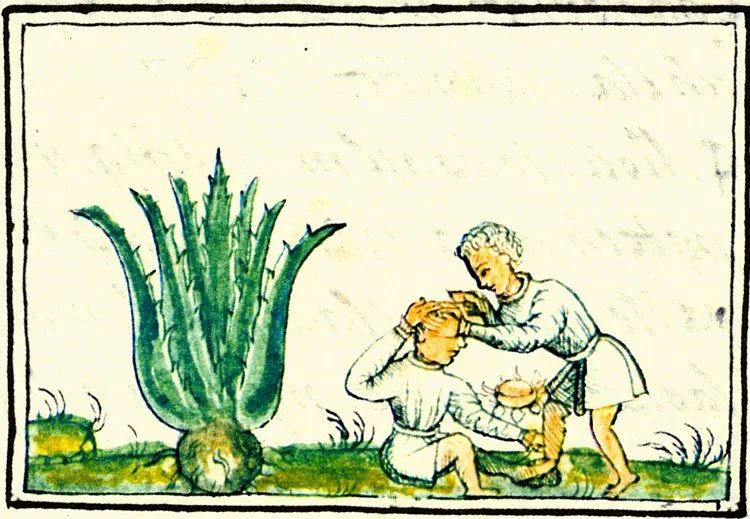
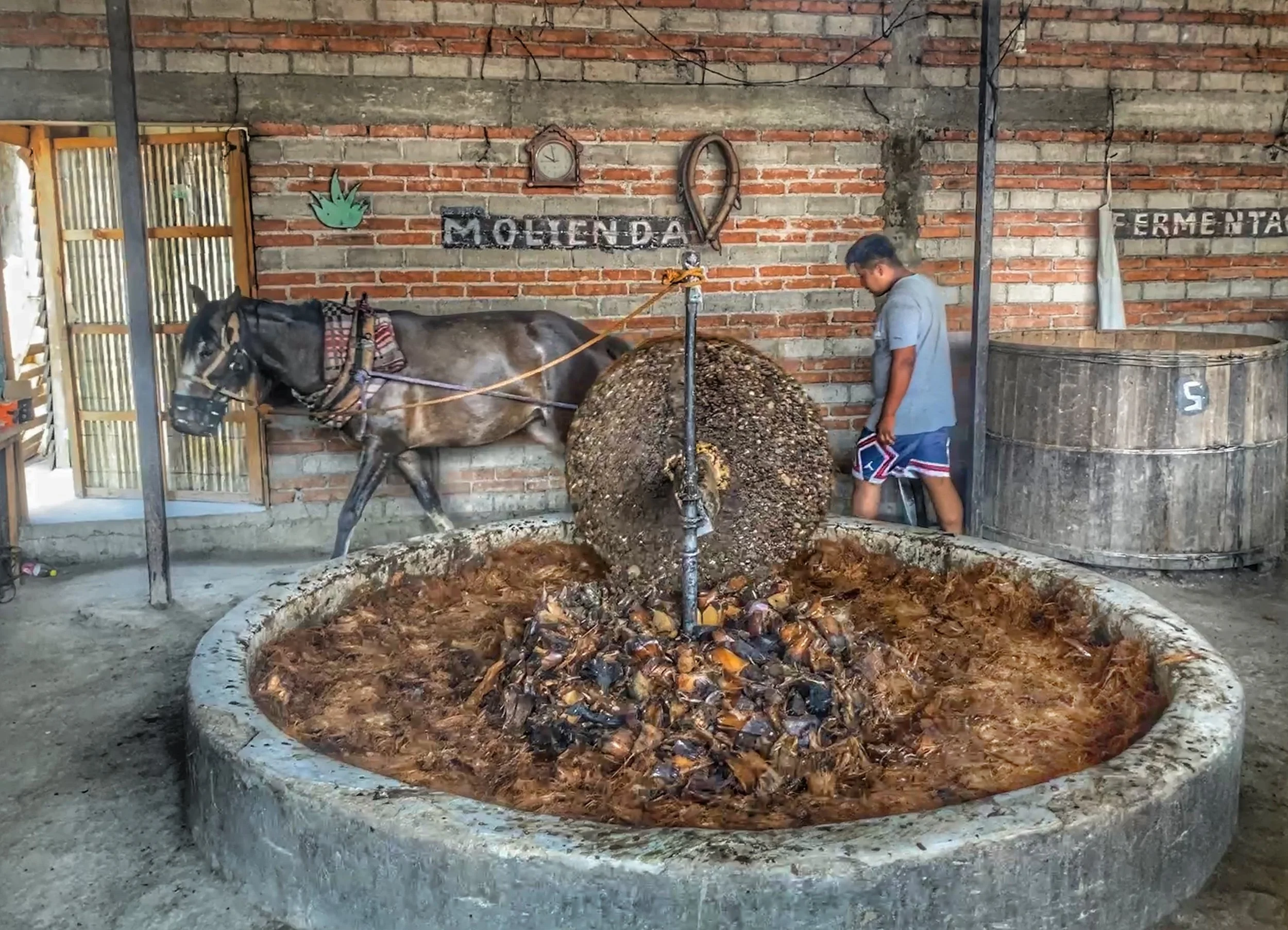
Mayahuel
“Goddess of the Agave”
Pronunciation: My-yah-well
Domain: Agave, pulque, nourishment, fertility
Vibe: The star-crossed lover
Story: Mayahuel is the spirit of the agave plant — the source of food, fiber, healing sap and the sacred drink pulque. Her family practices an extreme form of helicopter parenting: They’re star demons who’ve forbidden Mayahuel to leave the heavens. But Quetzalcoatl falls for her and the two hide by merging into a forked tree. When the goddess’ family finds them, they tear Mayahuel apart, scattering her pieces across the soil. Where they land, the maguey grows — resilient, sharp-edged and impossible to uproot.
Because the plant came from her body, every harvest was an act of reverence. The sap that fermented into pulque belonged to her. Agave and pulque folklore shows how deeply the plant shaped everything from spirituality to social rituals in Mesoamerica.
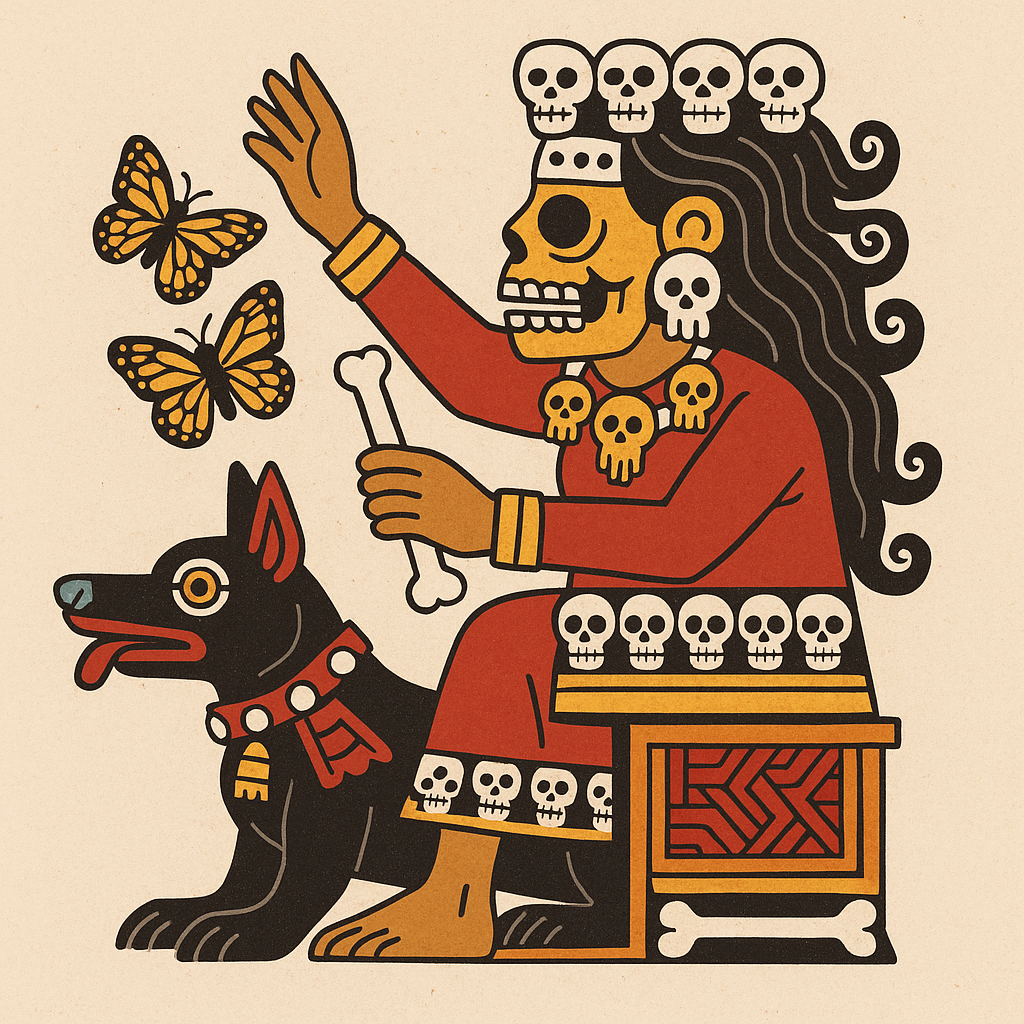
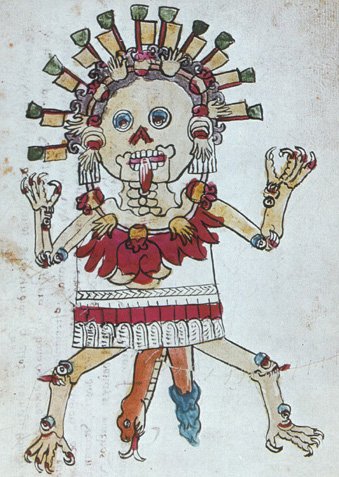
Mictecacihuatl
“Lady of the Dead”
Pronunciation: Meek-teh-kah-see-wah-tull
Domain: Death, the underworld, ancestors, bones
Vibe: The goth aunt who keeps every receipt — and by receipts, we mean bones
Story: She rules the underworld with quiet authority — no drama, no shouting, just a stare that sees straight through flesh to your skeleton. She and her husband, Mictlantecuhtli, oversee Mictlan, the final destination for most souls. Festivals in her honor later blended with Catholic All Souls’ celebrations and evolved into Día de los Muertos — meaning she’s the spiritual grandmother of the holiday that remembers the dead with candles, food and marigolds.
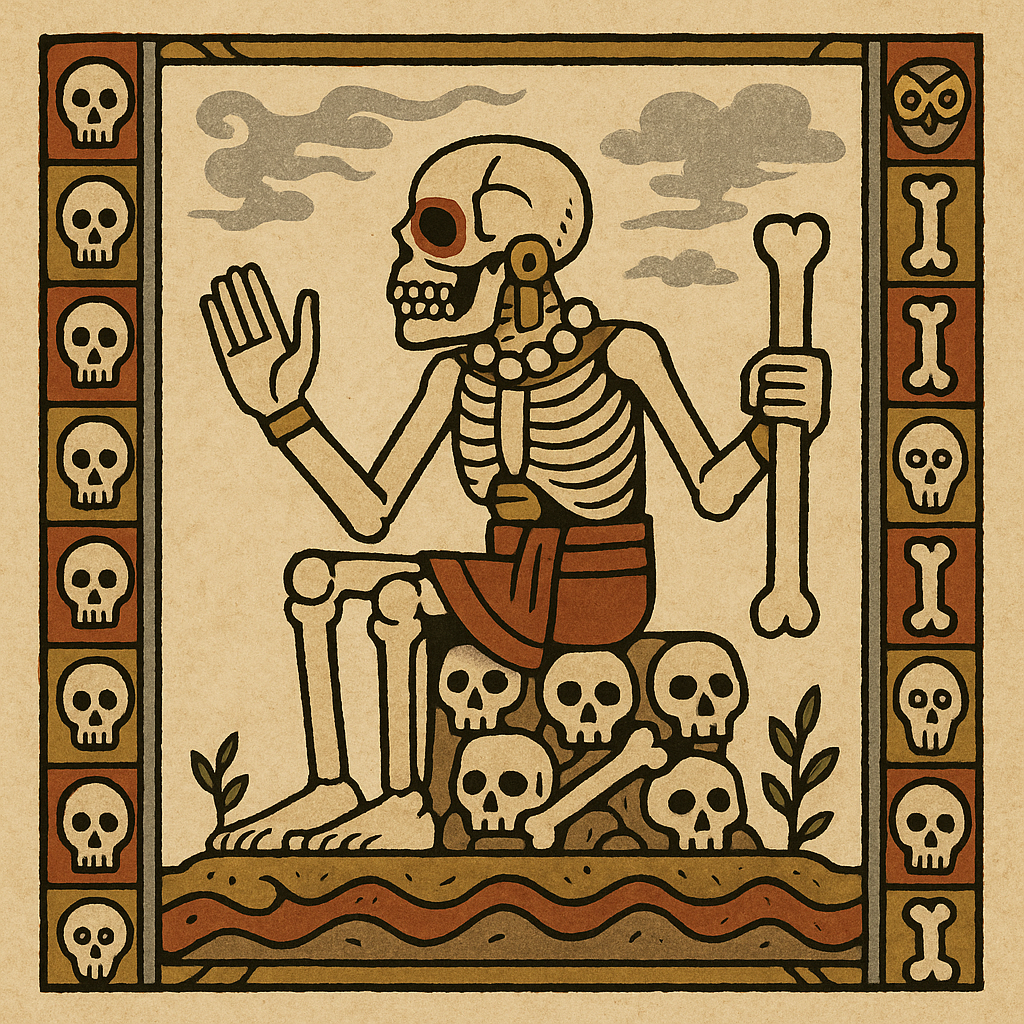
Mictlantecuhtli
“Lord of the Underworld”
Pronunciation: Meek-tuhlahn-teh-koot-lee
Domain: Death, the afterlife
Vibe: Surprisingly chill about mortality
Story: Mictlantecuhtli ruled Mictlan, the nine-layered underworld where most souls went after death — more for bureaucracy vs. punishment. The journey took four years, with challenges like mountains that crashed together and rivers of blood. When Quetzalcoatl came to borrow bones to make humanity, Mictlantecuhtli agreed — and then tried to trip him on the way out.
Ometecuhtli and Omecihuatl
“Our Lord and Lady of Duality”
Pronunciation: Oh-meh-teh-koot-lee / Oh-meh-see-wah-tuhl
Domain: Creation, balance, masculine and feminine forces
Vibe: The original power couple. Divine yin and yang — a sort of Adam and Eve for the Mexica.
Story: Before there was sun, moon or time itself, there was Ometecuhtli and Omecihuatl. Living in the highest heaven, they embodied the balance of existence. Together, they created the four great gods (Quetzalcoatl, Tezcatlipoca, Tlaloc and Xipe Totec), setting the cosmic wheels in motion. Creation wasn’t a solo act; it was a duet.
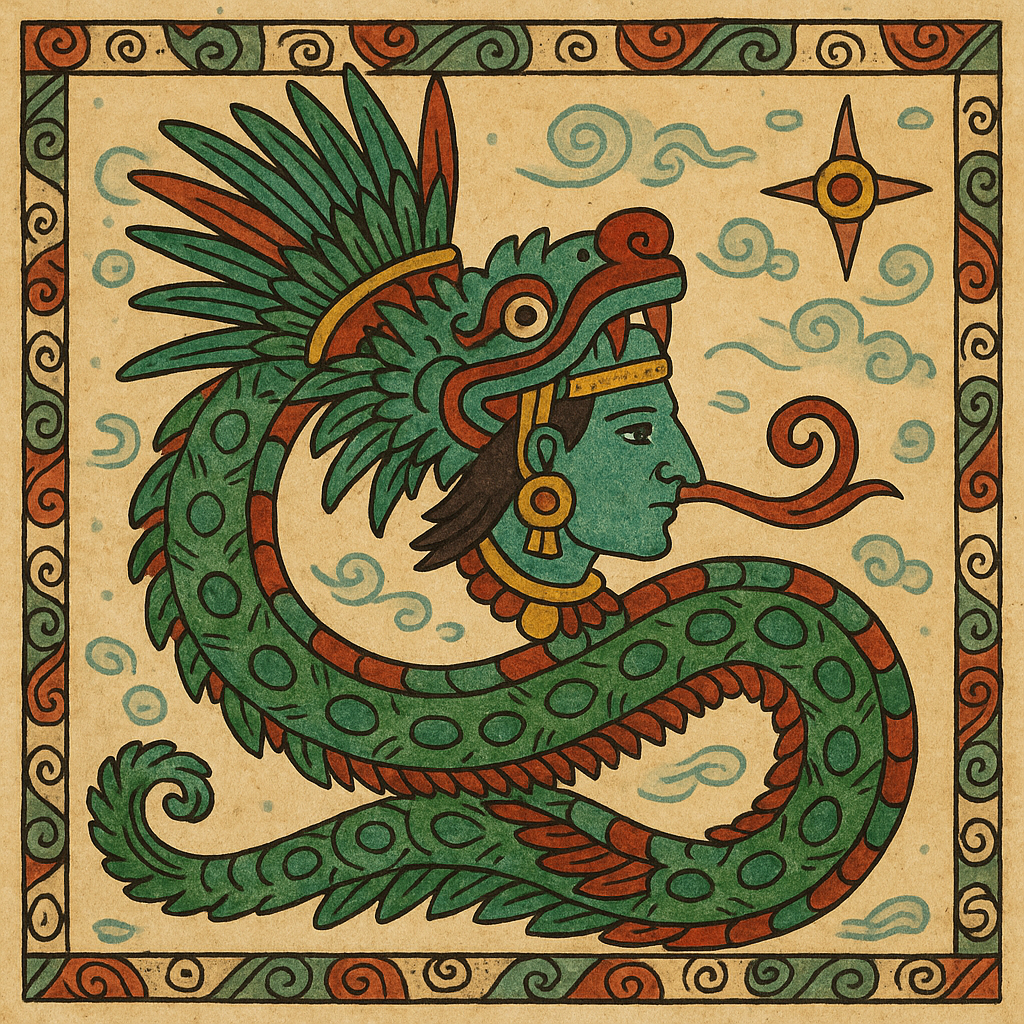
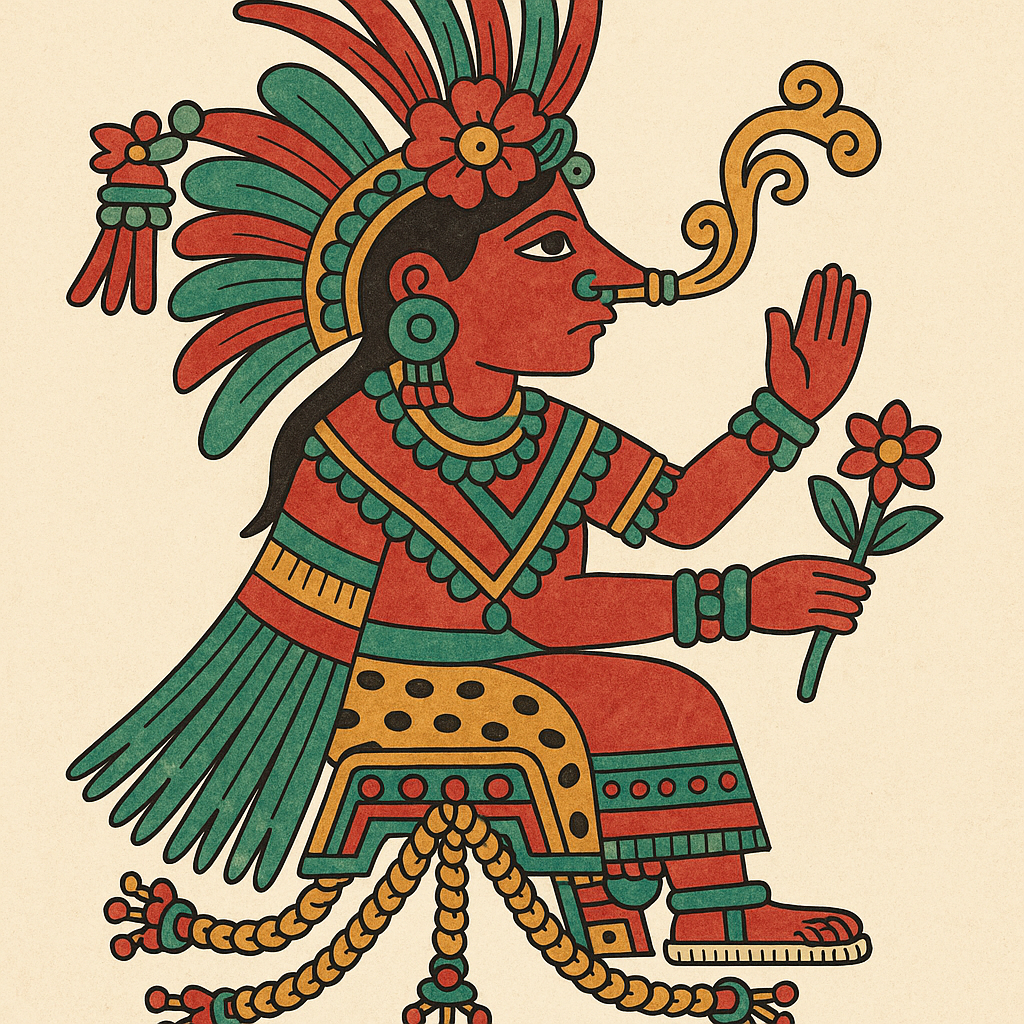
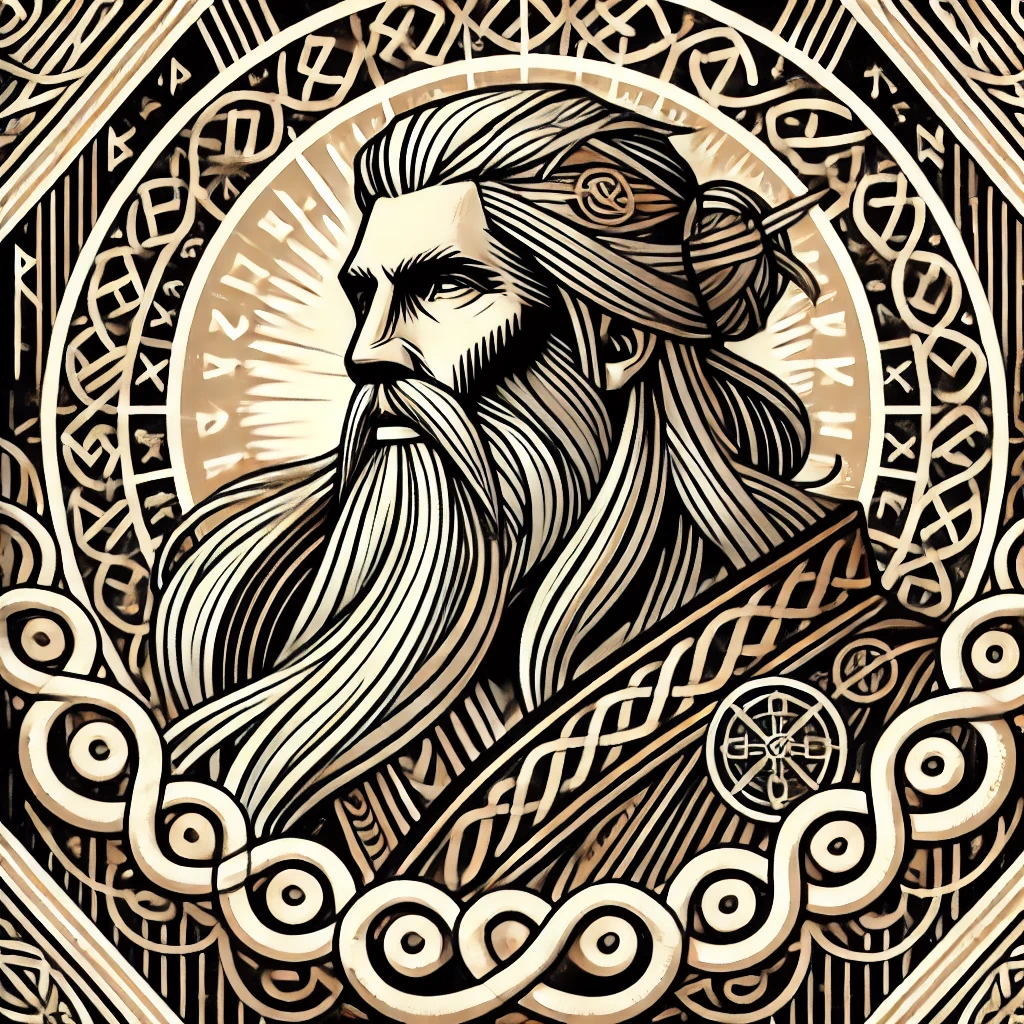
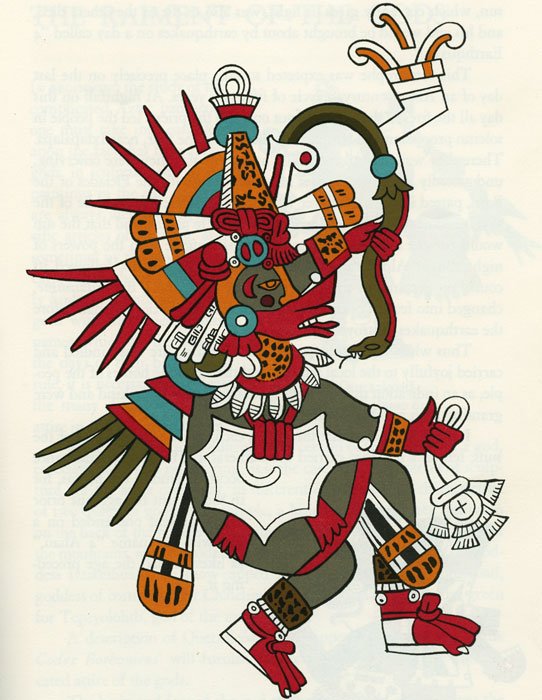
Quetzalcoatl
“Feathered Serpent”
Pronunciation: Ket-sahl-koh-ah-tuhl
Domain: Wind, knowledge, art, life, creation
Vibe: The philosopher who tried to make everyone chill
Story: Quetzalcoatl was the thoughtful one — a feathered serpent who preferred wisdom to warfare. He gave humans knowledge, maize and calendars, which is more than most gods manage before breakfast. Trickster rival Tezcatlipoca once got him drunk and shamed him into exile; some legends say he sailed east, promising to return. When the Spanish landed, later chroniclers swore the Mexica mistook Cortés for him.
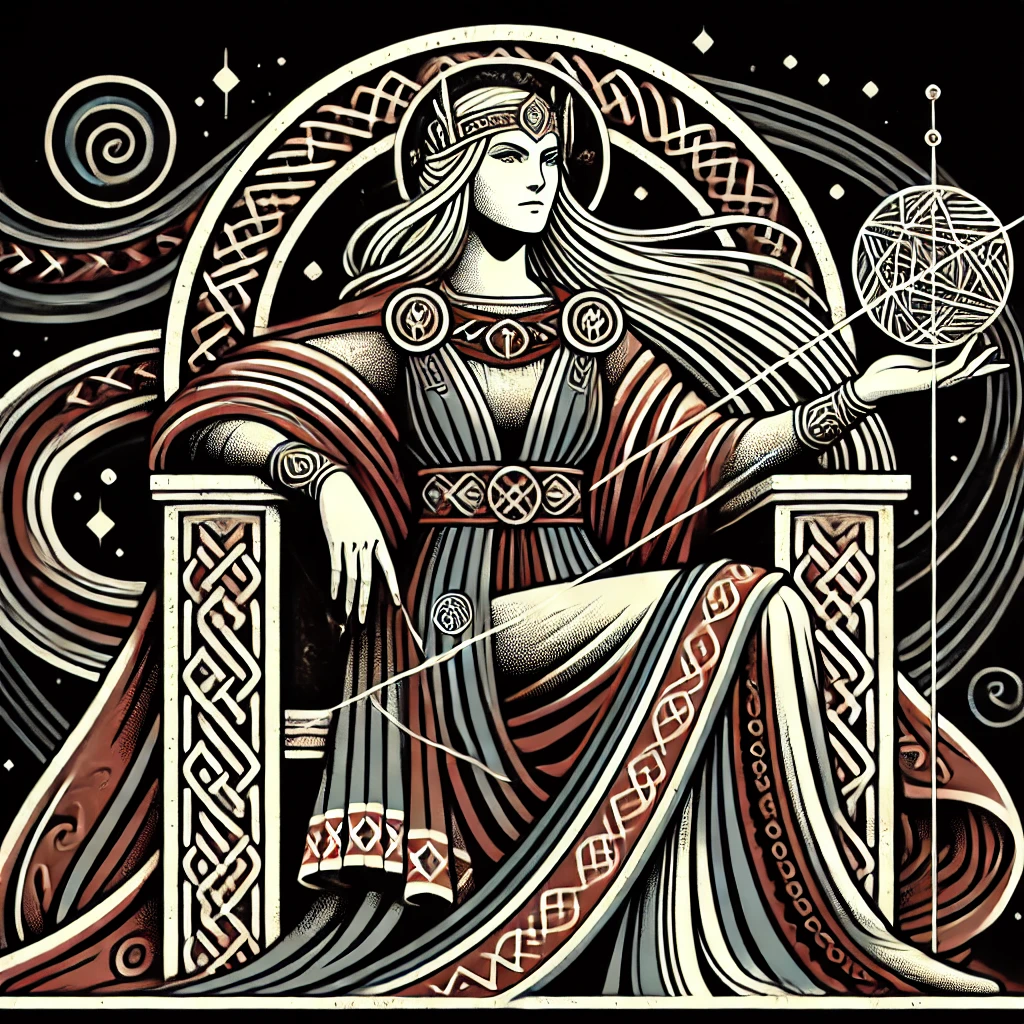
Teteoinnan
“Mother of the Gods”
Pronunciation: Teh-teh-oh-ee-nahn
Domain: Fertility, death, renewal
Vibe: Brutal, maternal, unstoppable
Story: Teteoinnan was the primordial Earth Mother — the one who birthed the gods and demanded blood to keep creation fertile. During the festival of Ochpaniztli, “the Sweeping,” a woman chosen to represent her was pampered for days, then shot to death by arrows. Her skin was flayed and worn by a priest, symbolizing the earth shedding its old season so a new one could grow. Teteoinnan was life itself: the womb and the tomb, the soil that feeds and devours.
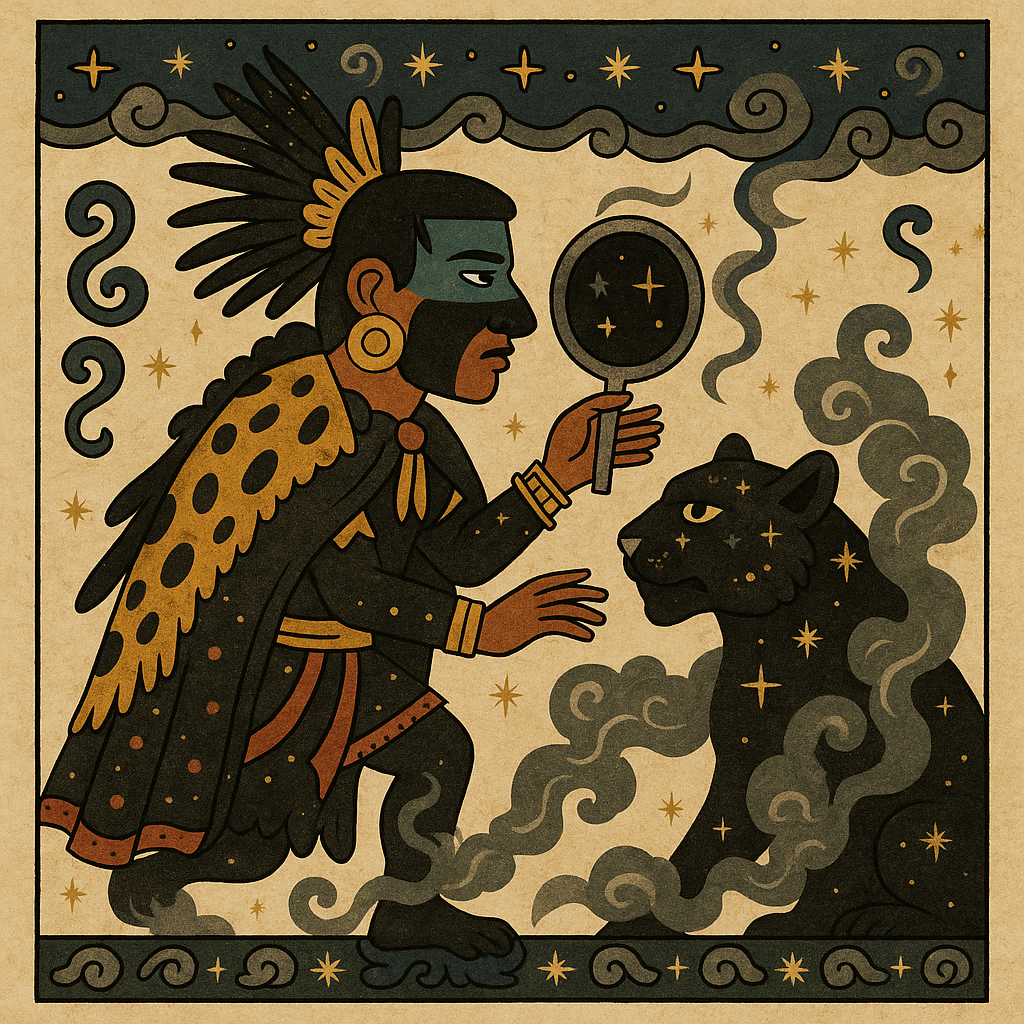
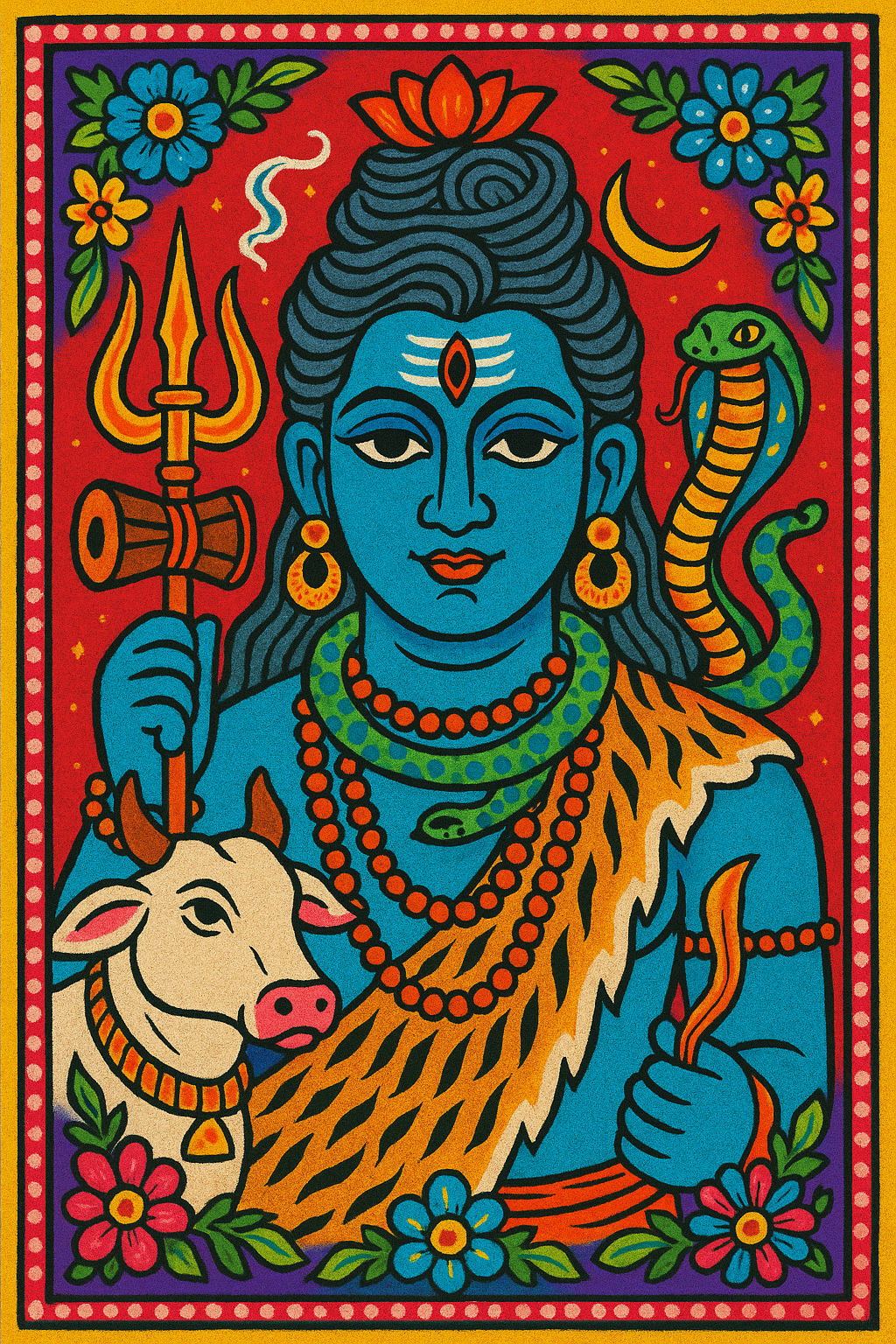
Tezcatlipoca
“Smoking Mirror”
Pronunciation: Tes-kaht-lee-poh-kah
Domain: Night, chaos, destiny, trickery
Vibe: The original frenemy — chaos with cheekbones
Story: Tezcatlipoca was Quetzalcoatl’s equal and opposite — the shadow to his light. With his obsidian mirror, he could see into hearts and futures, which made him the ultimate gossip. One myth has him turning into a jaguar to destroy the world, just to prove a point. The Aztecs loved him for it; he reminded them that fate has teeth.
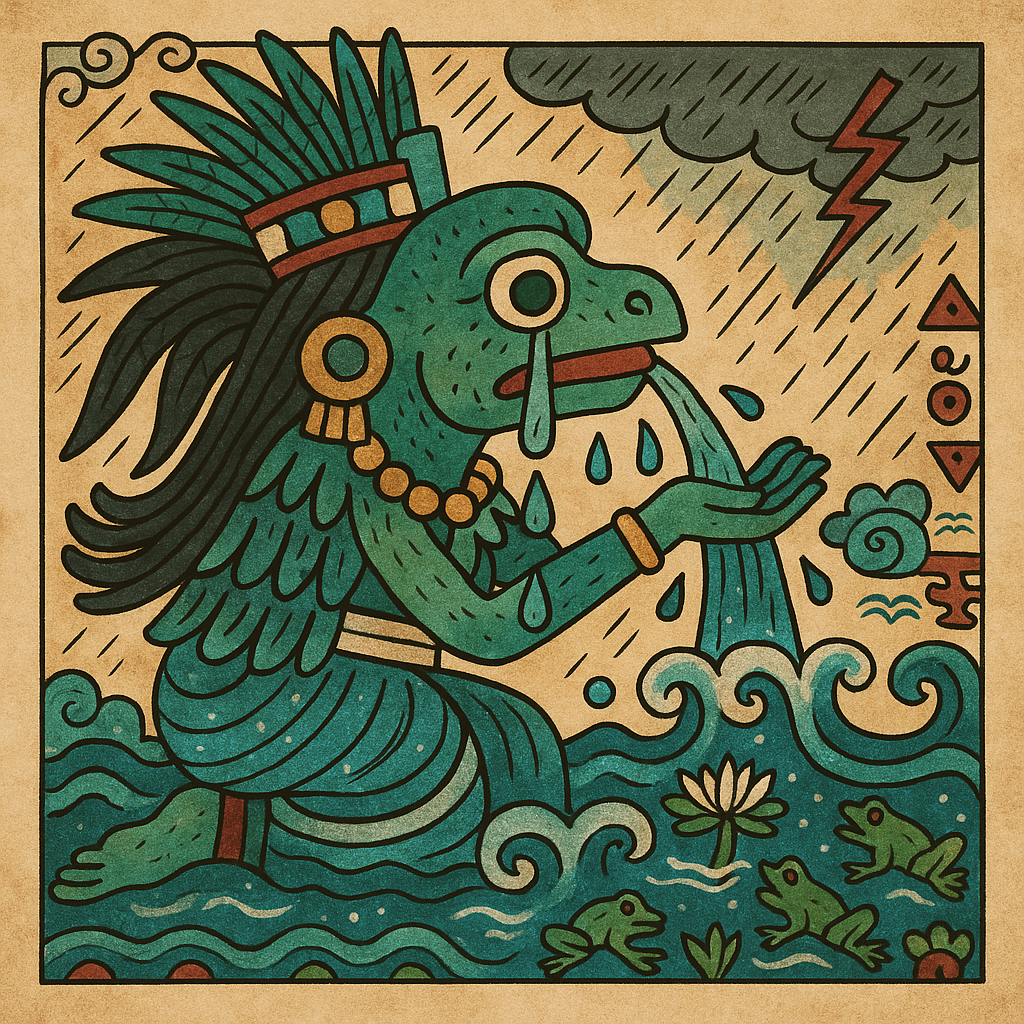
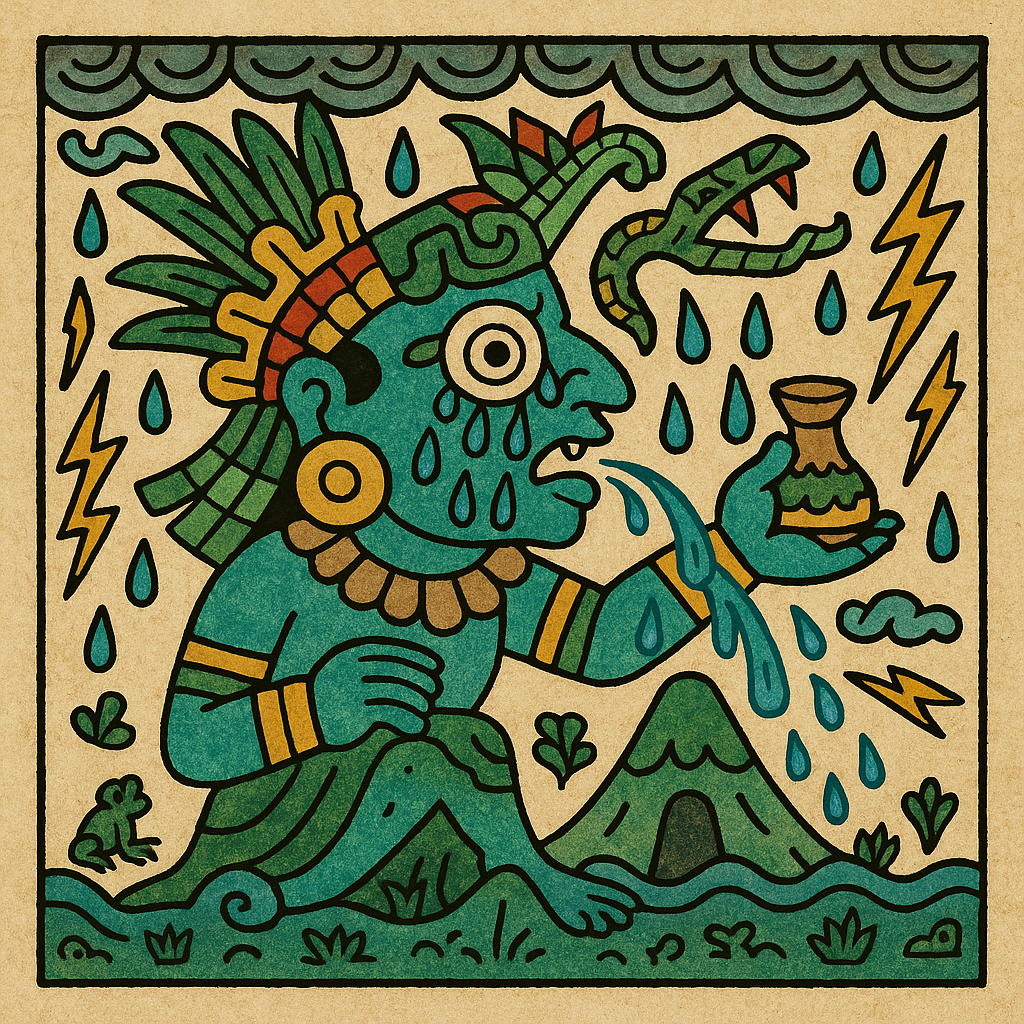
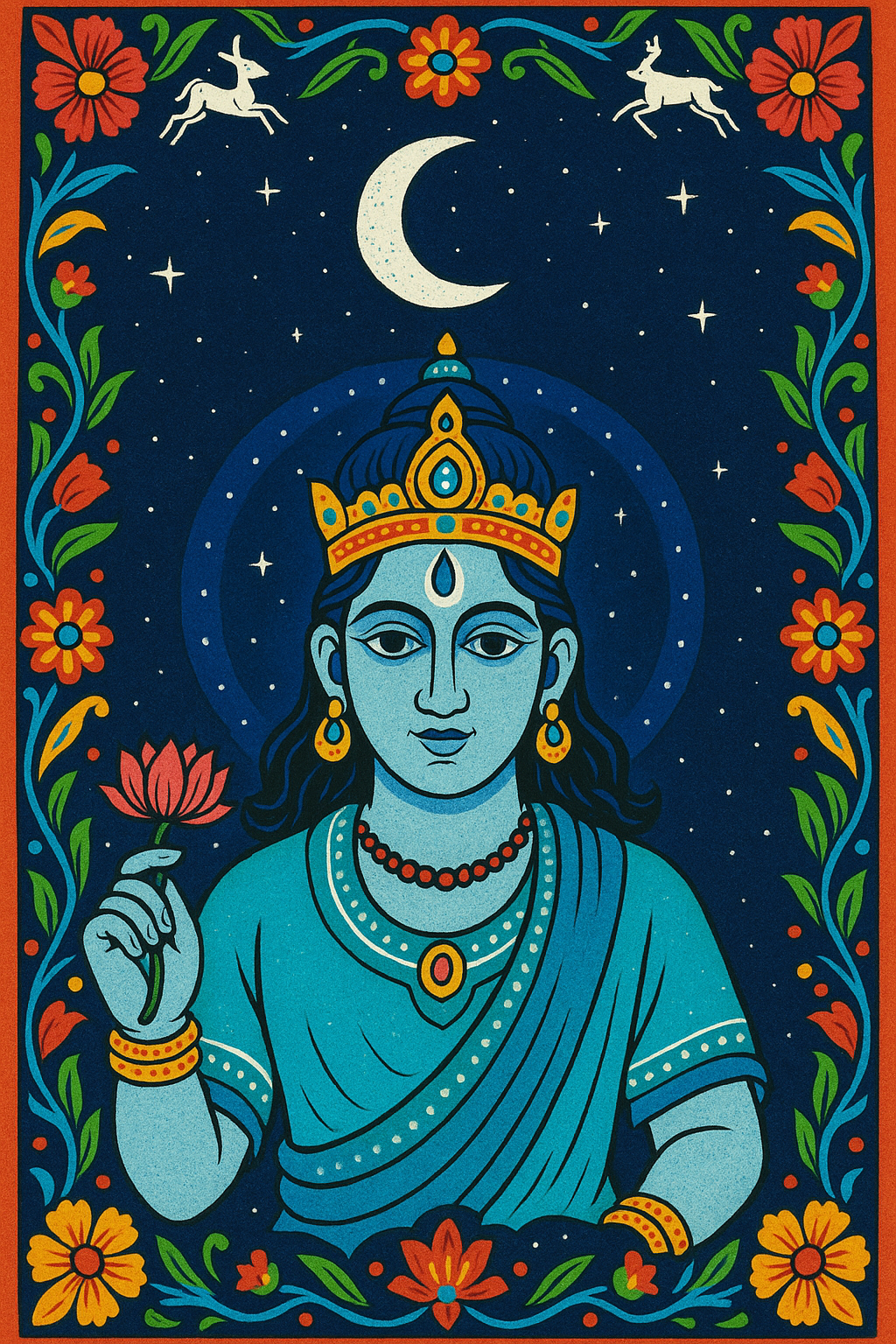
Tlaloc
“He Who Makes Things Sprout” (possibly)
Pronunciation: Tuhlah-lok
Domain: Rain, storms, fertility
Vibe: The moody meteorologist
Story: Tlaloc could bless or drown with equal enthusiasm. Farmers adored him; everyone else kept a respectful distance. Children were sometimes sacrificed in his honor, their tears believed to bring rain. Archaeologists have found offerings of tiny skeletons near his temple, a haunting reminder that the weather is often a matter of life and death.
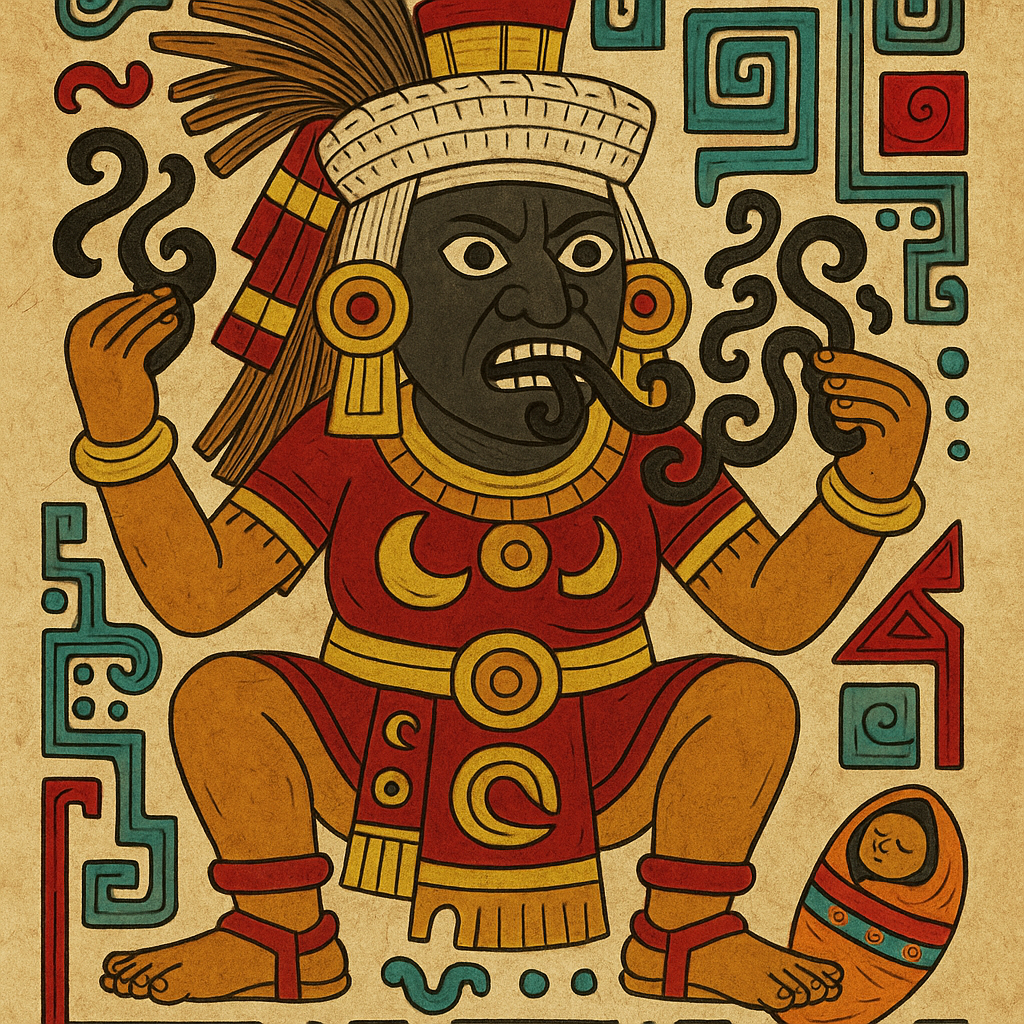
Tlazolteotl
“Goddess of Filth”
Pronunciation: Tuhlah-zohl-teh-o-tuhl
Domain: Sin, purification, lust, confession
Vibe: The confessor — sharp-tongued, forgiving and uncomfortably honest
Story: Tlazolteotl was the goddess of both sin and cleansing. People confessed their moral missteps to her once in their lifetime, and she “ate” their spiritual filth, leaving them pure again. Basically the Aztec equivalent of Jesus Christ taking away the sins of the world — only with black face paint, dirty rags and rotten food.
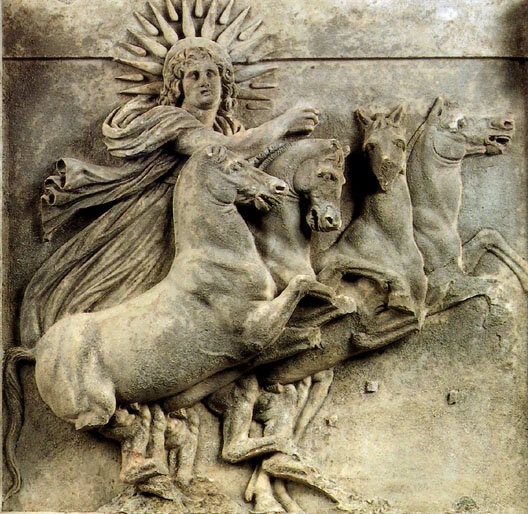
Tonatiuh
“The Radiant One”
Pronunciation: Toh-nah-tee-uh
Domain: The sun (the current one — there were four before him)
Vibe: The jock who knows the world literally revolves around him
Story: Tonatiuh is the fifth sun — the version we live under now. The Aztecs believed the universe had been destroyed and reborn four times already, and keeping Tonatiuh burning required constant human sacrifice. If the flow of hearts stopped, so would the sun. No pressure, humanity.
Xipe Totec
“Our Lord, the Flayed One”
Pronunciation: Shee-peh Toh-tek
Domain: Renewal, spring, agriculture, goldsmiths
Vibe: Horrifying but optimistic
Story: Xipe Totec wore human skin to symbolize the shedding of the old and the rebirth of the new. Each spring, priests honored him by donning the flayed skin of sacrificial victims until it decayed — a vivid, if disturbing, metaphor for renewal. He was terrifying, but also proof that life always grows back.
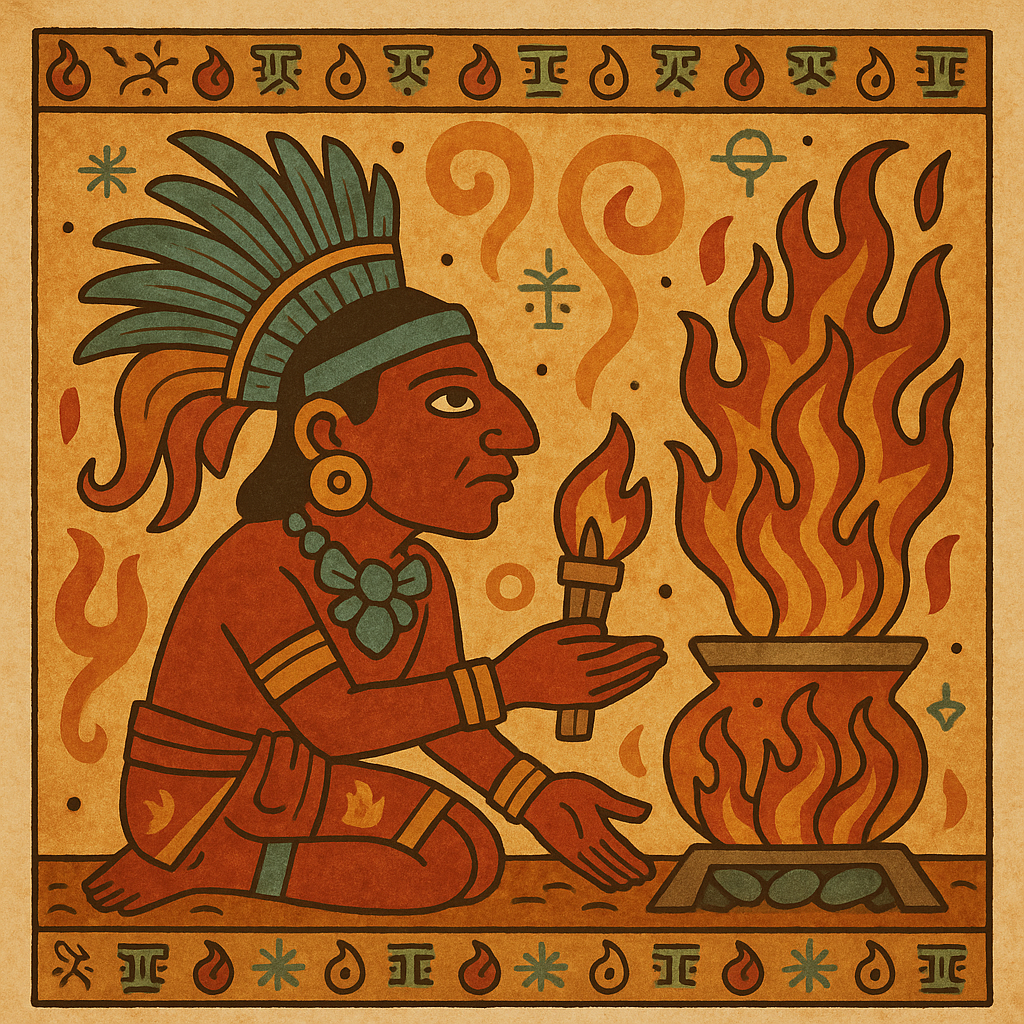
Xiuhtecuhtli
“Turquoise Lord”
Pronunciation: Shee-ooh-teh-koot-lee
Domain: Fire, time, renewal
Vibe: The spark that keeps the universe’s pilot light on
Story: Xiuhtecuhtli rules over fire and time — the heart of every hearth and the flame that ties life together. Every 52 years, the Aztecs extinguished all the blazes in the empire for the New Fire Ceremony, then rekindled it atop a sacrificial victim’s chest to reboot the cosmic clock. A bit extreme, but supposedly effective.
Xochipilli
“Flower Prince”
Pronunciation: Soh-chee-pee-lee
Domain: Pleasure, art, dance, song and sacred intoxication
Vibe: The good time guy — who’s always got the good stuff
Story: Xochipilli ruled over music, poetry and hallucinogenic ecstasy. His statues show him in blissful trance, covered in carvings of psychoactive plants like morning glory and mushrooms. Scholars debate whether he’s communing with fellow gods or just having an incredible trip. Either way, he’s the patron of joy.
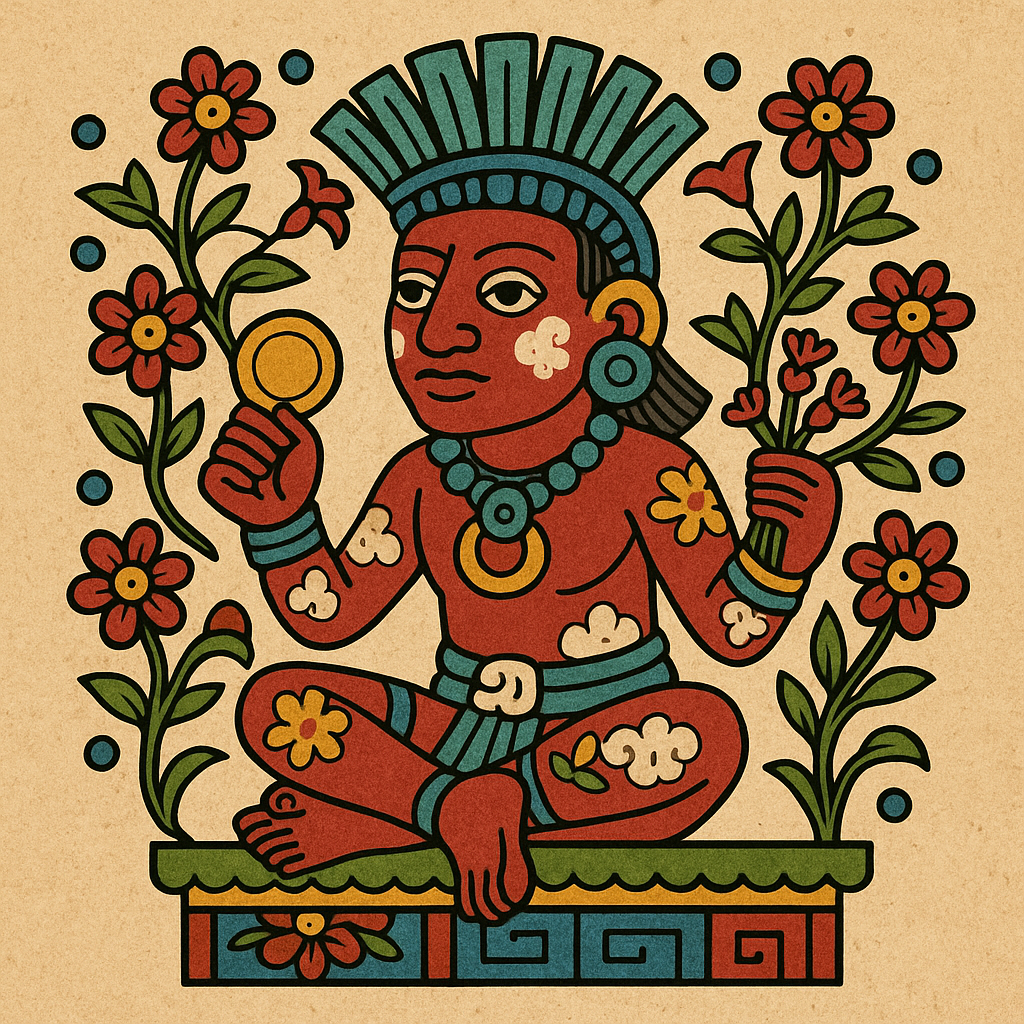
Xochiquetzal
“Precious Flower”
Pronunciation: Soh-chee-ket-sahl
Domain: Love, beauty, fertility, female sexuality, arts
Vibe: The divine muse with petals and power
Story: Xochiquetzal ruled over everything pleasurable: love, sex, beauty, art and weaving (opinions differ on how fun that last one is). She was beauty incarnate, the kind people write terrible poetry about. Naturally, this led to drama: At one point Tezcatlipoca abducted her, proving that even gods make bad romantic decisions. Worshiped by artists and universally adored, she was the eternal muse — always in bloom.
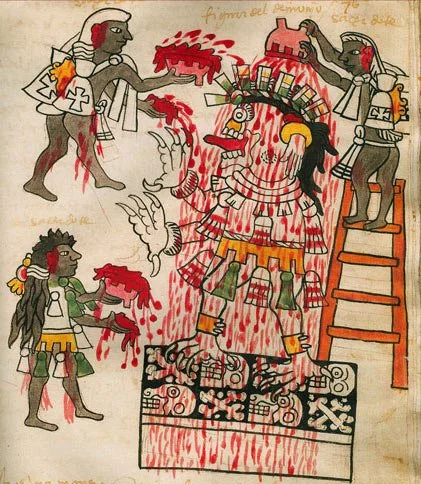
Aztec Offerings: Blood and Blossoms
For the Mexica, the gods needed constant nourishment to keep creation from falling apart. In a universe born from divine sacrifice, the only fitting offering was more of the same.
The Florentine Codex, compiled by Franciscan friar Bernardino de Sahagún and his Nahua collaborators between 1540 and 1577, is a 12-book encyclopedic record of Aztec culture, language and religion created to document and ultimately aid in converting indigenous peoples after the Spanish conquest.
According to the codex, every ritual — whether it involved flowers, animals or human hearts — was a repayment, a way to keep the cosmic machinery running. Blood was the power source of the sun. The gods had given their own essence to ignite the world. To let that flow stop would be like unplugging the universe.
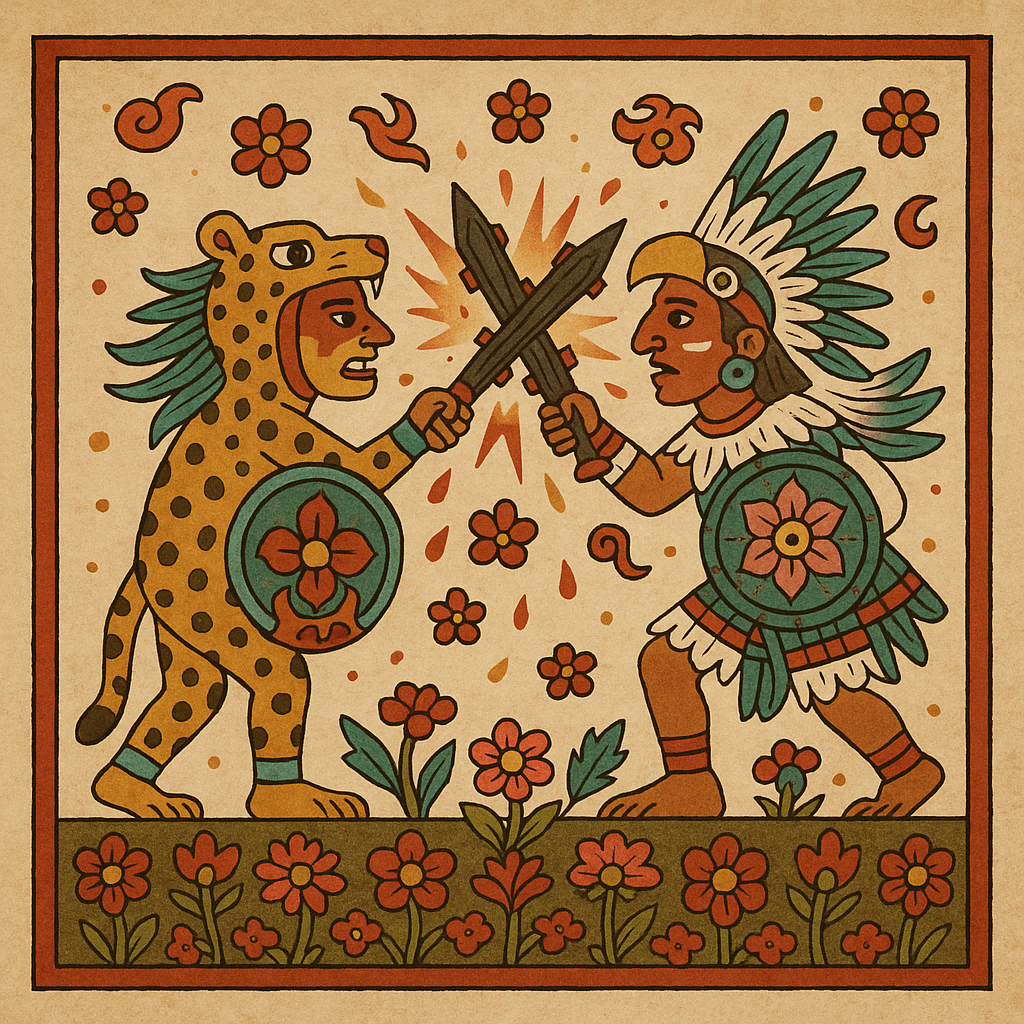
The Flower Wars (Xochiyaoyotl)
The Aztecs even had a word for the ultimate warrior’s death: xōchimiquiztli, the “flowery death.” Dying in battle or on the sacrificial stone wasn’t seen as tragedy but transcendence. To fall for Huitzilopochtli or Tonatiuh was to bloom forever in the sky, your soul reborn as a hummingbird or butterfly chasing the rising sun.
And the gods demanded a lot of blood. So the indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica came up with an interesting proposal: battles not for conquest but purely to feed the gods. These ritualized clashes between city-states — most famously Tenochtitlan and Tlaxcala — were called the Flower Wars. The goal wasn’t land or wealth; it was captives.
The Mexica believed these chosen warriors made the best offerings: brave, beautiful and unafraid. To die in one of these sacred battles was an honor. As The Florentine Codex notes, they were “debt payments” to the gods — each body a line item in the cosmic ledger.
It sounds kind of poetic — if you ignore the gruesome obsidian knives carving out all those still-beating hearts.
Yet within that brutality lived a strange kind of grace. The Aztecs saw the world as a vast cycle of giving and renewal. Flowers wilted, rain fell, the sun rose again — and so did life. In their eyes, blood was just another bloom, proof that everything beautiful demands something in return.
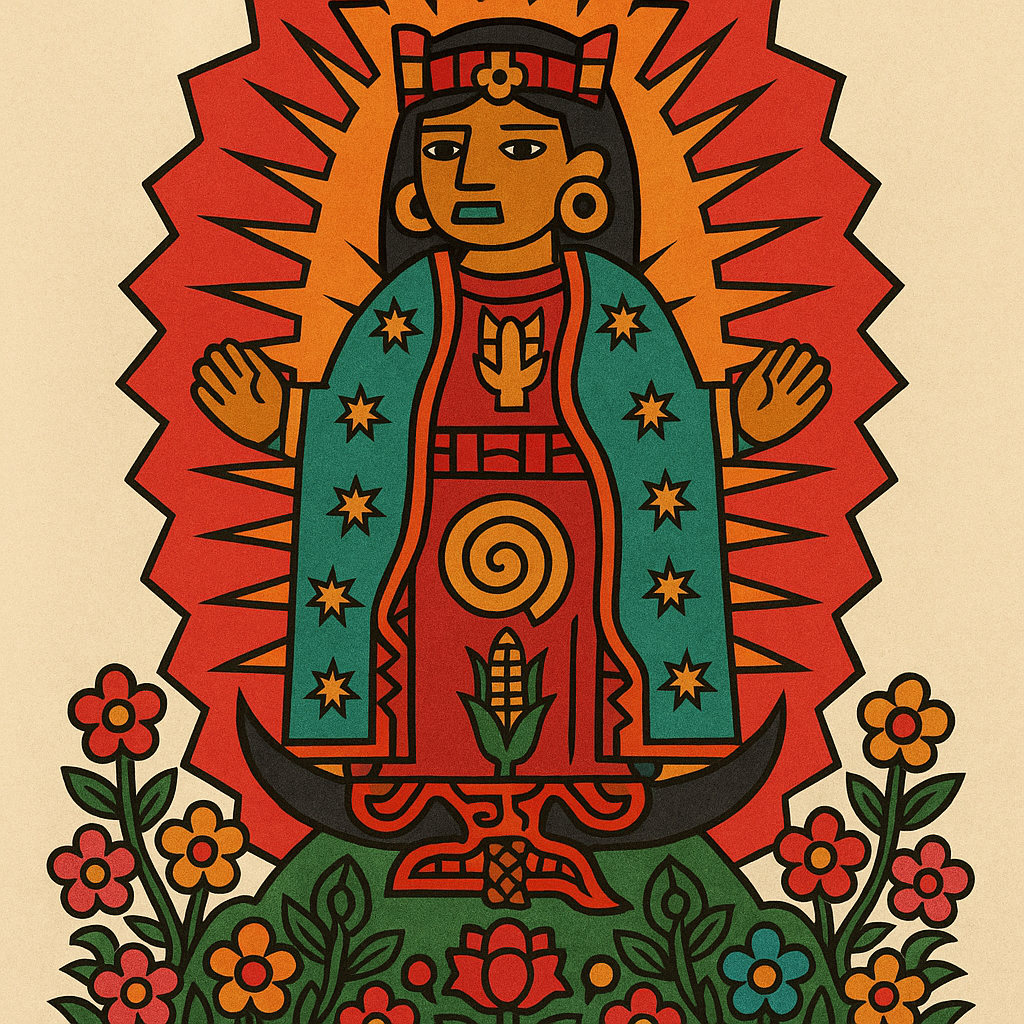
Tonantzin: The Reverend Mother Who Became the Virgin Mary
If you climb Tepeyac Hill, on the north side of Mexico City, at sunrise, people say you can still feel her presence.
Before the Spanish ever arrived, the Mexica made pilgrimages up that hill to honor Tonantzin (Toh-nahn-tseen), “Our Revered Mother.”
But the name wasn’t tied to one figure. It was a title, a crown shared by the great mother goddesses:
Coatlicue when she was fierce
Teteoinnan when she was the ultimate authority
Chalchiuhtlicue when she flowed with kindness
Then the conquest happened. The Spanish tore down her temple and built a church on the exact same hill dedicated to the Virgin Mary.
They expected the indigenous people to move on. They didn’t. The locals kept making pilgrimages, lighting candles and praying — but they kept calling the Virgin Mary Tonantzin.
Fray Bernardino de Sahagún, a Franciscan friar, lost his mind over it, writing “This appears to be a Satanic device to mask idolatry,” in his Historia General de las Cosas de Nueva España.
Tonantzin is the Aztec mother goddess who survived colonization by putting on a new outfit. –Wally