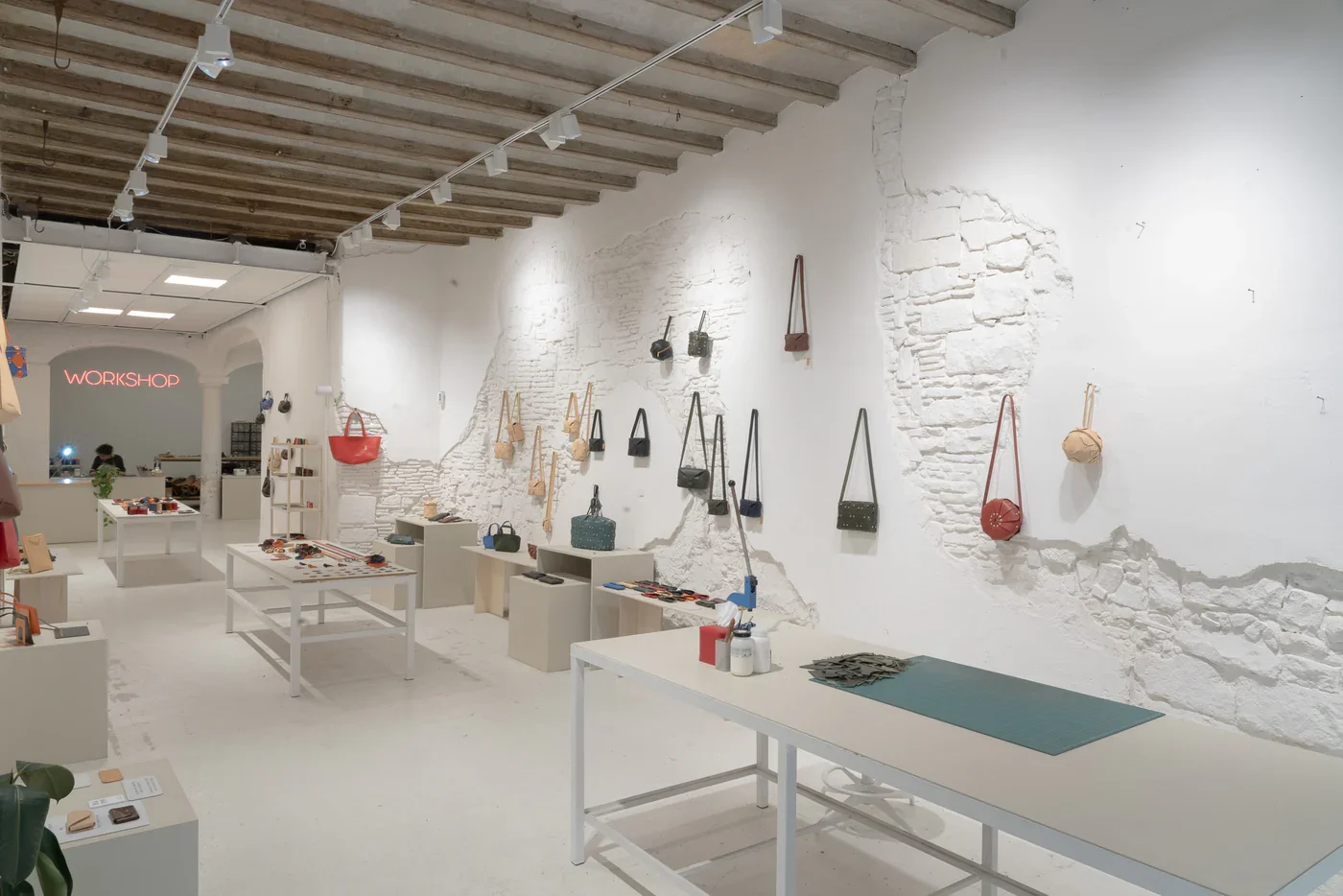
Full-grain, vegetable-tanned leather from local tanneries, zero-waste habits, and a design philosophy that owes more to architecture than fashion all come together here, one piece at a time.
Before Atelier Madre became one of the most quietly beautiful leather studios in Barcelona, Spain, it was just Manuel Dreesmann, a few hides and a belief that good design should feel as honest as it looks.
He started the project back in 2018, tinkering with leather for friends and curious strangers online, and by 2021 he had opened a combined workshop and store on Carrer del Rec in the El Born neighborhood — the kind of space you wander into thinking you’ll browse for five minutes and end up staying far longer just watching the craft happen.
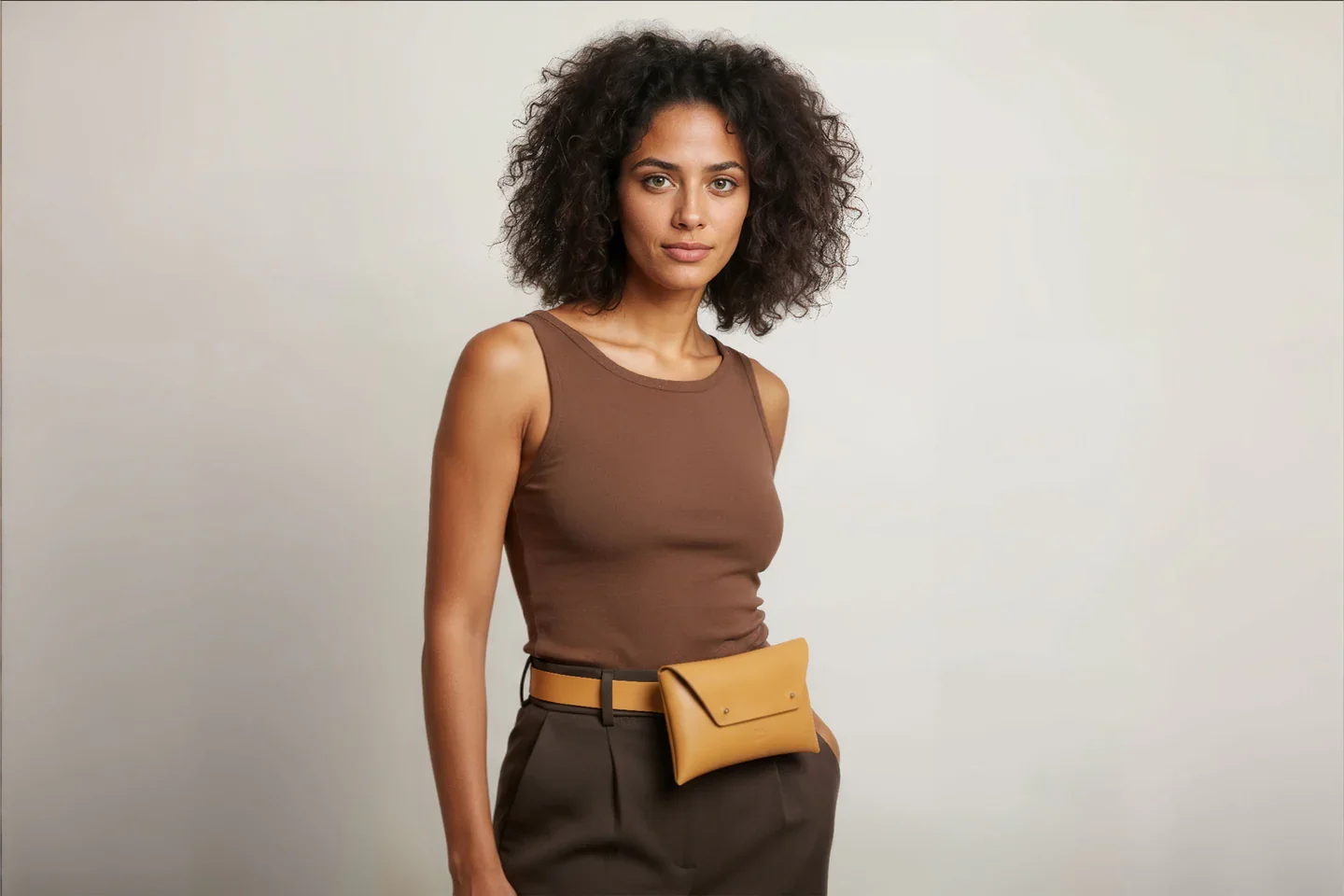
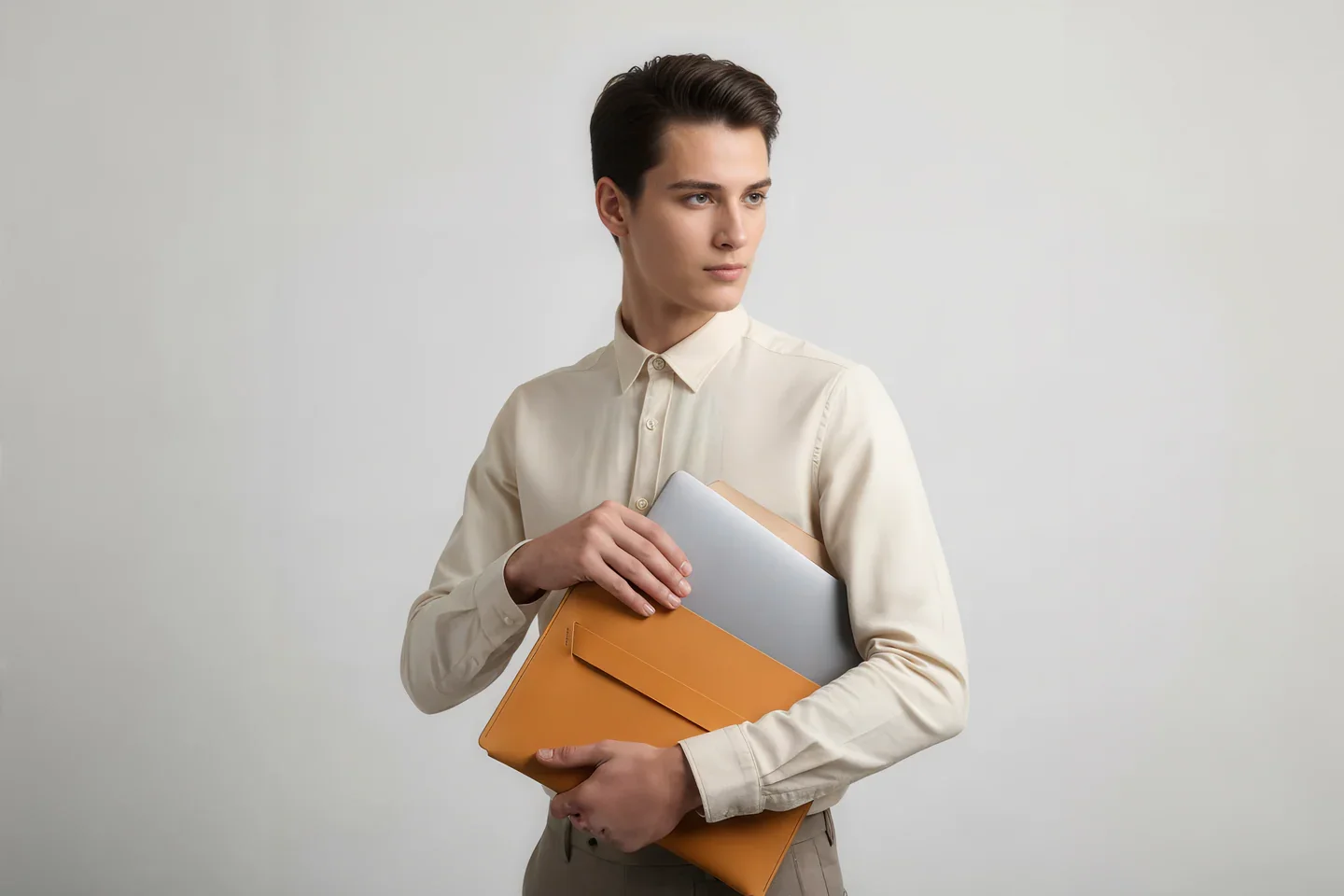
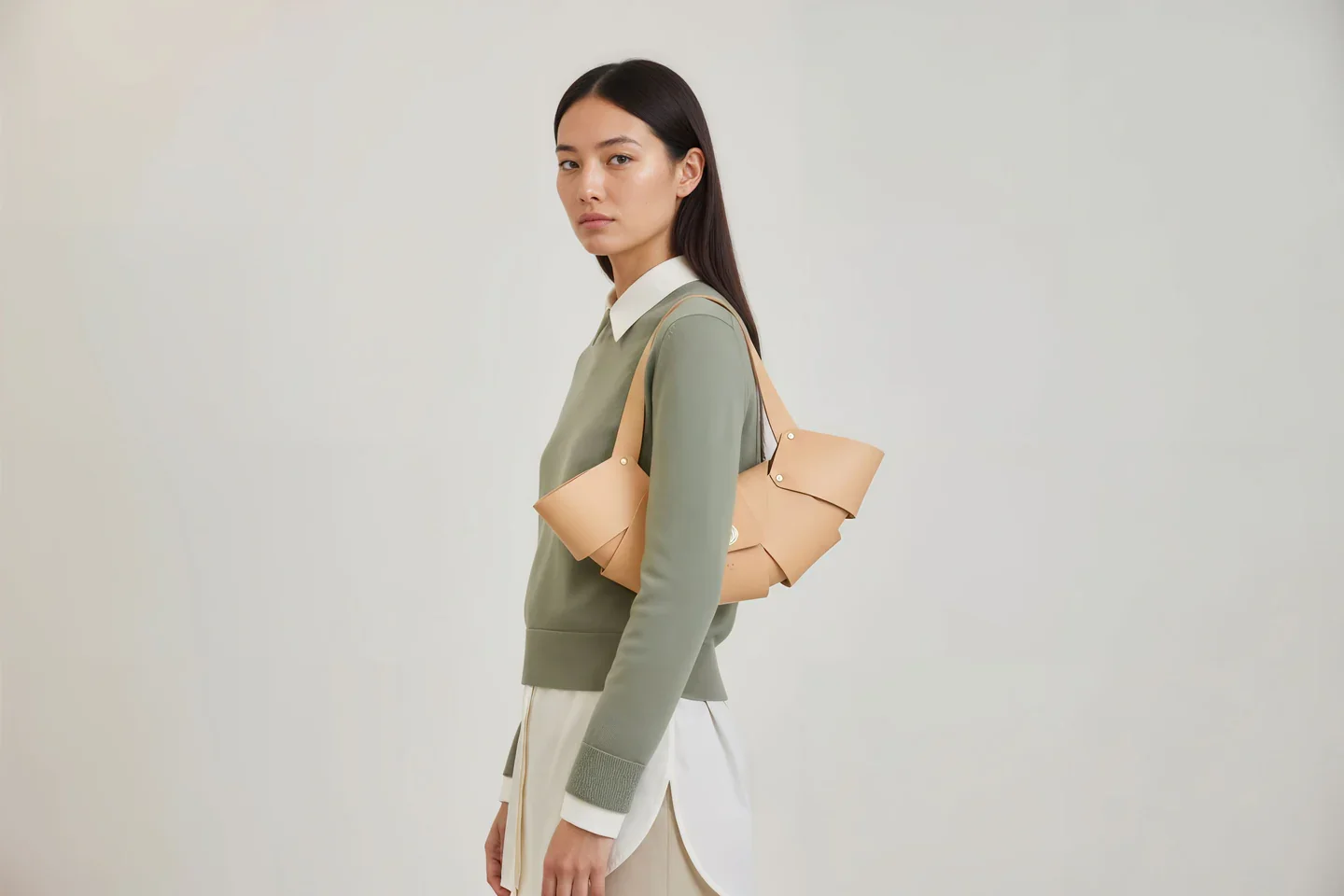
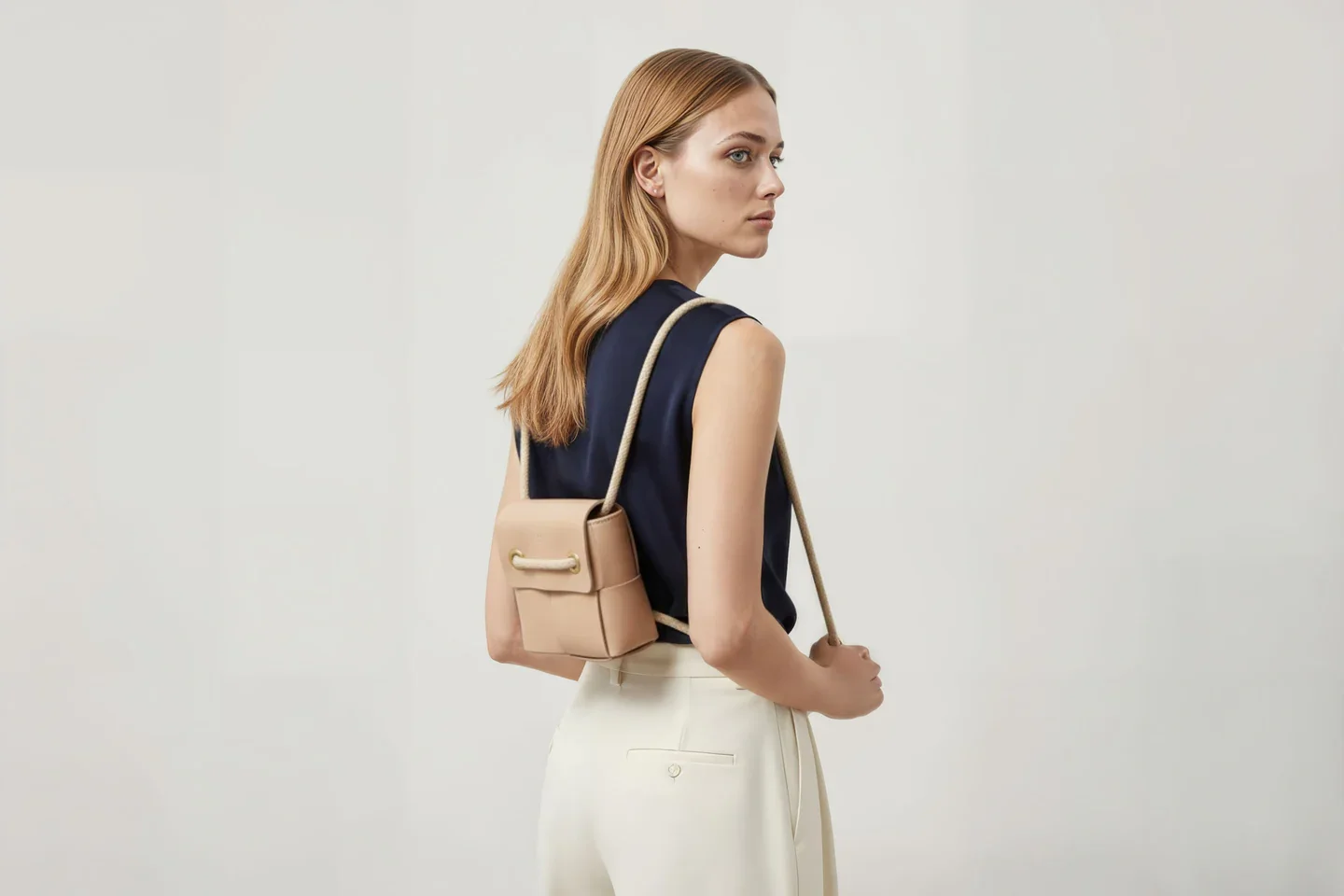
Today the shelves hold a small but striking family of pieces: structured bags, minimalist wallets, sleeves for laptops and tablets, desk mats, key holders, even tiny accessories cut from the very last offcuts.
Founder Manuel Dreemann answered our questions about how it all began, what “handmade” really means to him, and why Barcelona remains the perfect home for his quietly obsessive little atelier — even its name, cleverly formed by taking the beginning of his first and last name to create the Spanish word for “mother.” –Wally
How did Atelier Madre get started? What was the defining moment that set the brand’s direction?
I’d been doing leather projects as a hobby for a while. When Covid ended, I started looking at spaces to rent and, by accident, found the atelier we’re in now. I’d renovated spaces before, so I knew that with some work I could turn it into something of my own.
At first I didn’t even plan to run it as a shop. I saw it more as a place to design and make things, mainly because my home workspace had become too small. But the atelier had a front door to the street, so I opened it and let people walk in.
In the beginning it was quiet. Mostly just me. I listened to the few people who came, got to know them, adjusted products, added new ones. Slowly the room filled up: with visitors, pieces on the shelves, and eventually people helping.
I didn’t have a big master plan for where it should go, and I still don’t. I treat it as a daily practice: See what happens, learn from it and steer accordingly.
Could you walk us through a typical piece’s journey from hide to finished product?
I don’t come from the leather or fashion world. I taught myself by doing: reading, watching, testing, ruining pieces and starting again.
With a very small budget, I took the train to a town near Barcelona where they still make good vegetable-tanned leather. I bought a few hides, went back to the atelier, and started cutting and selling.
Today the process is basically the same, just more structured:
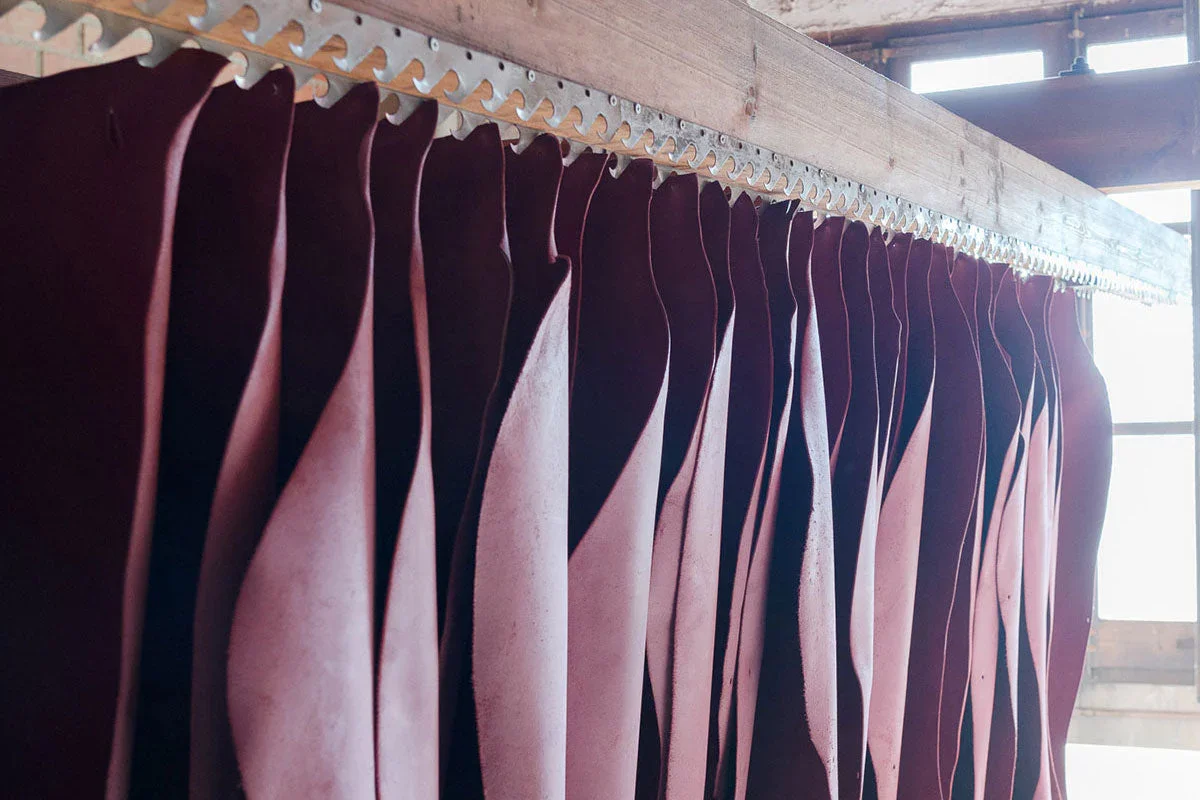
We buy full-grain, vegetable-tanned hides from those tanneries around Barcelona and keep a small stock of standard colors in the atelier.
Sometimes other brands overproduce, so we take their leftover hides. Many of our “standard” colors started life as someone else’s surplus.
Every product starts with selecting the right part of the hide: avoiding scars where needed, using natural marks where they add character.
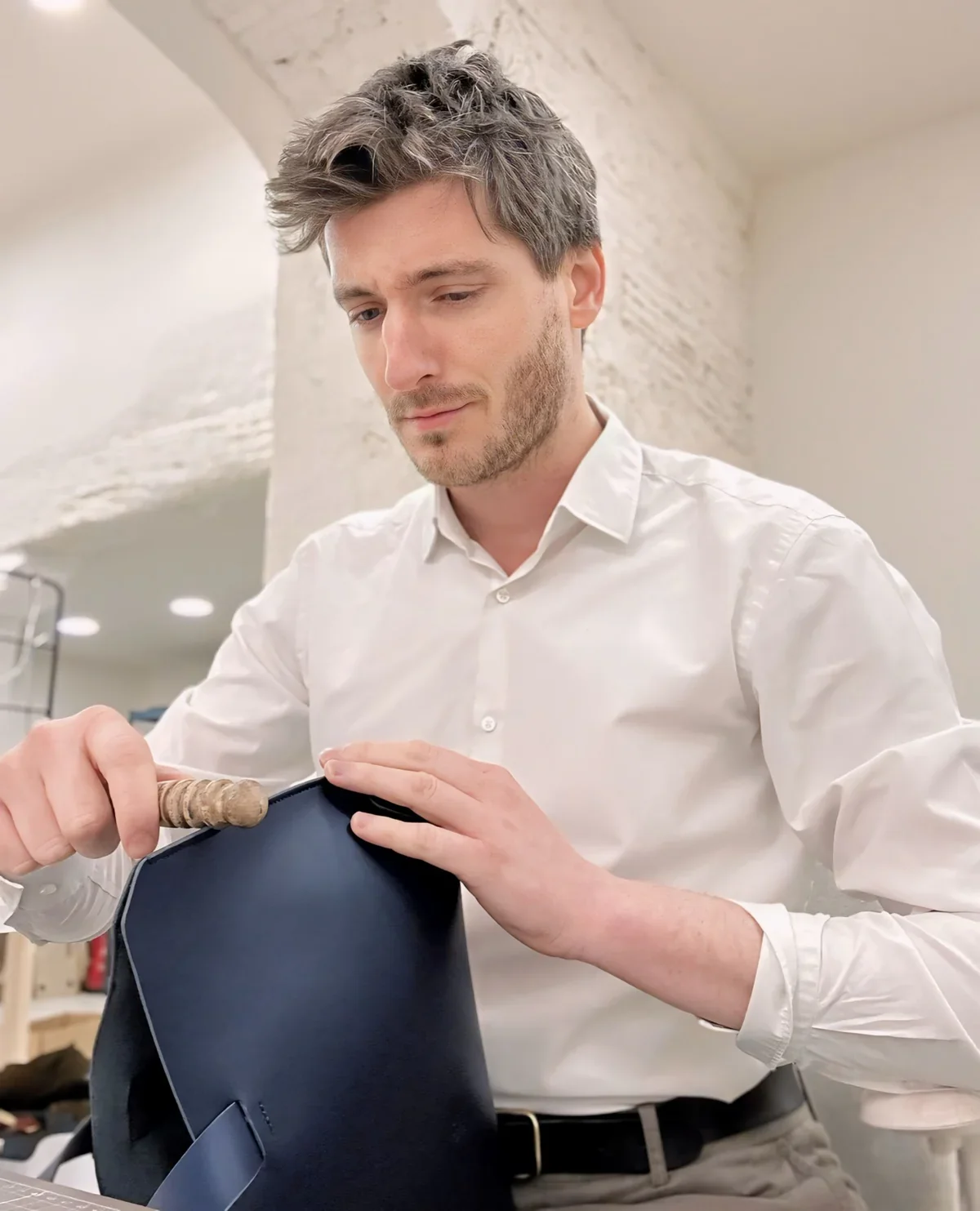
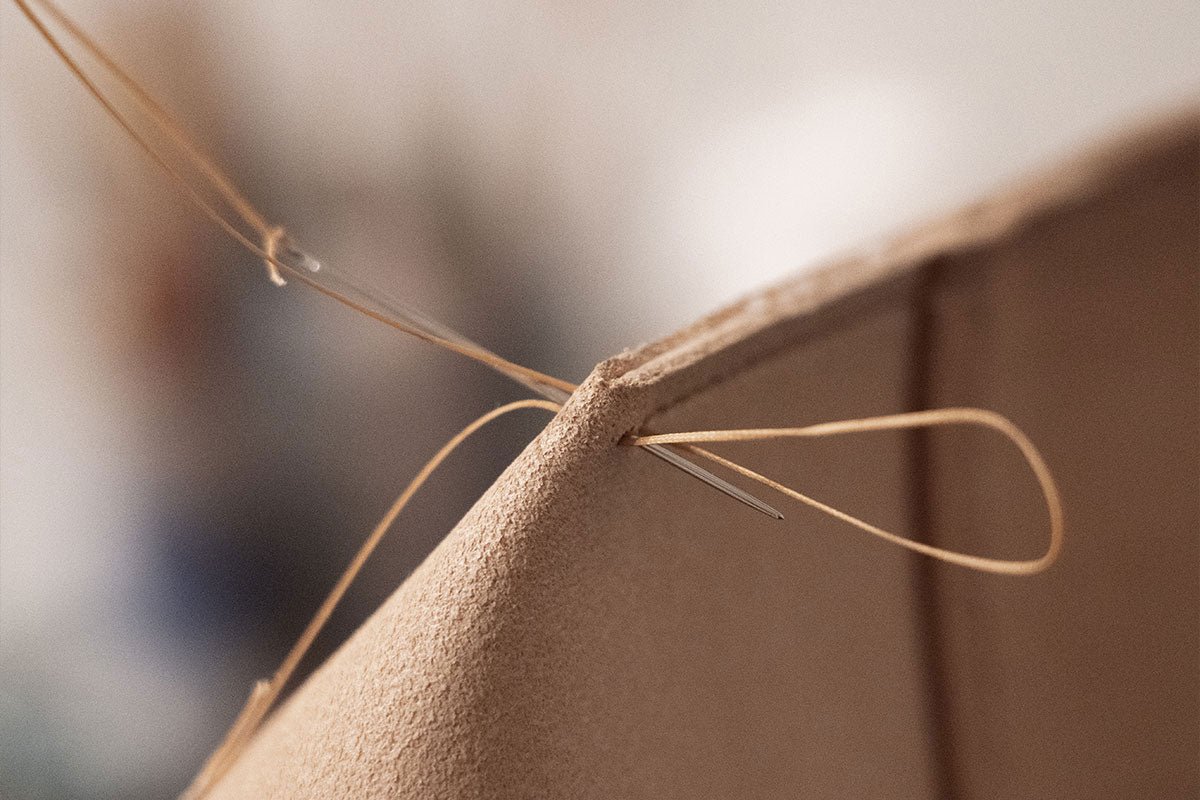
From there we cut the patterns, prepare the edges, glue and stitch the layers, then finish the edges and attach hardware.
Each piece gets a final check, a quick cleanup, and goes onto the shelf or into a box.
All of this happens in the same space people walk into from the street. Some come to buy, some just to watch us work, and some are happy just looking through the window.
What design philosophy guides you when creating a new bag or accessory?
Before I start designing, there are already constraints. Everything has to be possible in our own atelier, with our team, our machines and our materials.
That is very different to brands where design is completely free and production happens somewhere else. My job is to create pieces that people actually want to use, within the limits of what we can honestly make ourselves.
I can’t deny my German roots; there is a strong pull towards structure and coherence. Nothing is decorative for its own sake. The shapes are closer to architecture than to fashion. The products should age with pride, and ideally, when you look at them in 50 years, they still feel contemporary.
How does Atelier Madre approach responsible sourcing, production and longevity of its pieces?
I started alone, so I built the workspace in a way I would actually want to work in myself.
Apparently it’s not the worst place to be, because every time we hire, we receive hundreds of applications from all over the world and can choose the right fit. For me, that is the first filter for ethics: people genuinely want to work here.
Everything happens in one open space. Customers see the machines, the hides, the people, the mess. There’s not much room for pretending.
For sourcing, we work with tanneries in Igualada. We know them, we visit them, and they work under European regulations for labor and chemical standards. We prefer full-grain, vegetable-tanned hides and we keep the supply chain as short as possible.
We also try not to waste material. We use every piece of leather we bring in. Larger parts become bags, sleeves and mats; smaller ones become wallets and accessories; and the very last offcuts end up as earrings.
Longevity is probably the most important part. In four years, only a handful of customers have come back with issues. When something does fail, we repair or help them fix it. If a product can be worn, used and repaired for many years, it’s more honest than talking about sustainability in abstract terms.
What does being based in Barcelona contribute to your brand identity, craft and community?
Most of us made a very deliberate choice to come to Barcelona. Our team is from different parts of the world, and so are many of our visitors. That constant movement brings a natural exchange of cultures into the atelier every day.
Like many harbor cities, Barcelona has always been a place of trade, crossing paths and relatively open minds. You feel it in the streets: People come and go, test ideas, start projects.
It’s a good environment for a small, slightly obsessive workshop.
In terms of “influence,” we are quite inward-looking. We focus more on improving what we do inside the atelier than on following what happens outside. There’s a long list of things to refine here: processes, products, how we work together. Barcelona gives us the context and the people, but most of the work is quietly done at the workbench.
What are the biggest challenges you face in small-batch, handcrafted leather goods today?
The way we work is, by design, not very efficient. There’s no production line. Each piece is made by exactly one person, start to finish. Combined with the fact that we produce in Barcelona, it creates a very different business model to most of the fashion industry. The challenge is to make this viable and still keep the quality where we want it.
Sourcing is the other big topic. As a small brand, it’s difficult to access the level of hardware and components we’re looking for. Finding the right buckles, zippers or metal parts can take months.
In the beginning we also had to convince suppliers to even work with us and to believe that we weren’t just a short-lived project. That part doesn’t show in the final product, but it’s a big part of making it possible.
Could you tell us about one of your favorite artisan or workshop moments that exemplifies your work?
There was a family visiting our workshop once. They had come from far away, I think from Kuwait, because friends had told them to visit us while they were in Barcelona.
They chose a few pieces and we started finishing them at the workbench. A bit later, the children came back inside and stood very close to the table, watching every step in silence.
We started talking and they told us their story: Their father had recently passed away, and this was their first trip together as a family since then.
It felt very special that they chose to spend that moment in our atelier. When I think about what our work can mean, I often picture those children at the workbench and imagine the family using those bags somewhere in the world.
What stories or feedback from customers resonate most with you?
Because the store and the studio are the same space, a lot of the connection just happens on its own. People walk in, see us working, ask questions, watch for a while. Some get something personalized, some just talk. A lot of locals come back regularly, even if they don’t need anything, just to say hi.
Many of our customers find us through friends, or because someone told them, “You should go there while you’re in Barcelona.” Those are the stories I like most: people coming straight from the airport with their luggage because a friend insisted they visit.
With international customers, we mostly stay in touch through email and social media. They send photos of their bags or sleeves after a few years, with scratches, marks and the shape of their daily life. Those messages are the ones that stay with me. It’s less about perfect feedback and more about seeing that the piece is actually being used and has become part of their routine.
Looking ahead, what are the next steps or aspirations for Atelier Madre?
We have a very long list of products we would like to design and make. The idea is not to rush through it, but to build a collection slowly, with pieces that can stay for many years.
At the same time, we are trying to translate the feeling people get in the atelier to our online presence. How the space looks, how we work, how materials behave over time. The website and our photography are still work in progress.
On social media, we are still testing what feels right: formats, frequency, how much of ourselves we show. One of our main goals is to use these channels to connect people through craft, not just to post product photos.
Sharing our story on a platform like this can help by giving more people a clear view into this world: showing the making, the people, and the way the products are actually used. If that comes across, it supports very well where we want to go.
What’s something about Barcelona you’d advise travelers? Any hidden gem spots near the atelier?
If you’re visiting Barcelona, take time to explore the independent ateliers, especially around El Born and Gràcia. These neighborhoods are full of small workshops and studios where the person serving you is often the one who designed and made the piece.
Around our atelier, it’s worth simply walking the side streets and stepping into any place that looks like real work happens there: leather, ceramics, jewelry, print. What you take home becomes less of a generic souvenir and more a reminder of a conversation, a workshop, a person. That usually stays with you longer than anything else.
Atelier Madre
Carrer del Rec 20
08003 Barcelona
Spain