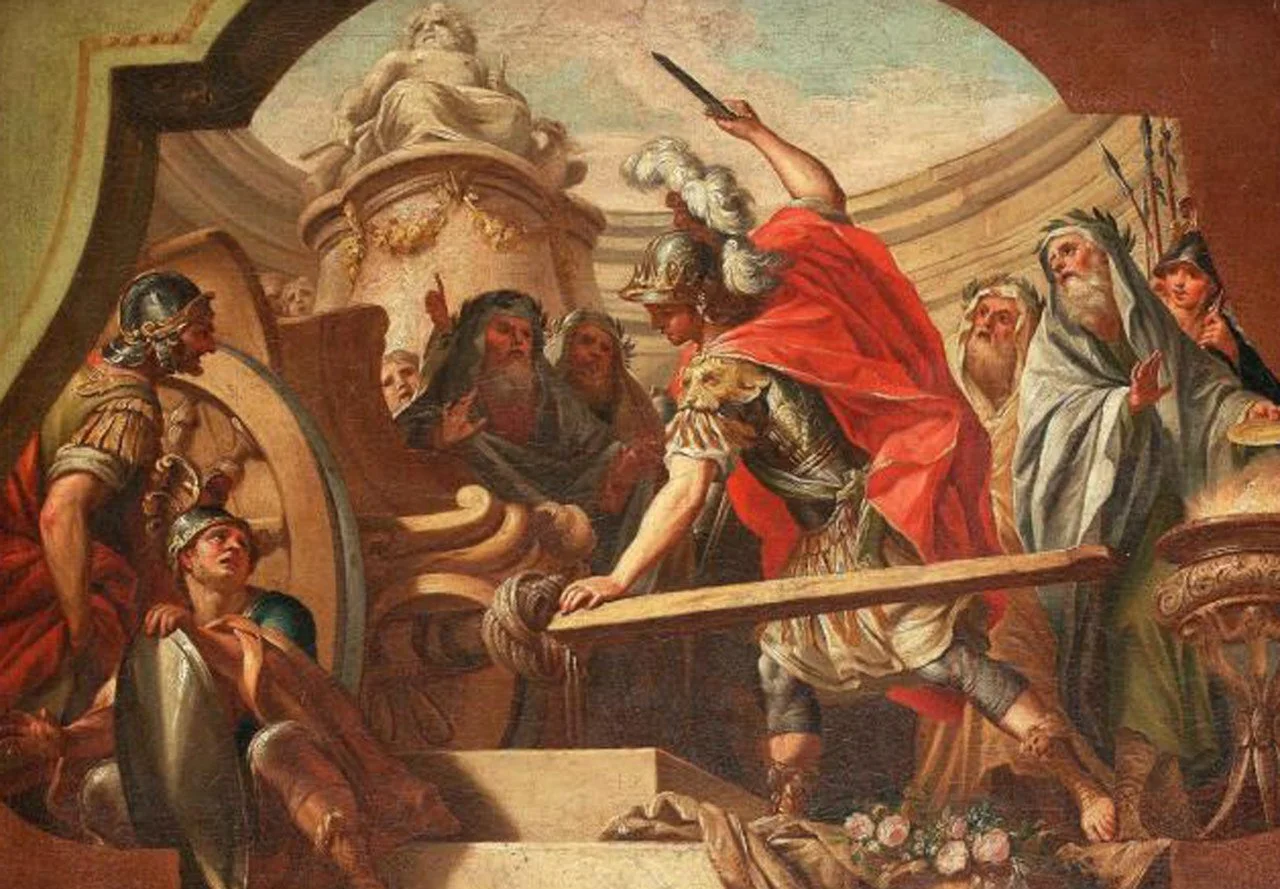
The famed king of Macedon and military leader could be ruthless and cruel, especially when he dealt with Tyre, Gaza and Persepolis.
Alexander might have had a great body, but his actions weren’t always so great — especially when it came to conquering three major cities of antiquity
It’s all a matter of perspective. You can read through these stories about the man history has dubbed Alexander the Great and think, “What a dick.”
But you shouldn’t view ancient history solely through a modern lens. Even Dante was guilty of reducing the legendary conqueror to barbarian status: He placed Alexander in the seventh circle of Hell, boiling for eternity in the blood he shed.
As far as ancient history goes, though, Alexander’s brutality was typical: “He was a man of his own violent times, no better or worse in his actions than Caesar or Hannibal,” writes Philip Freeman in Alexander the Great. “He killed tens of thousands of civilians in his campaigns and spread terror in his wake, but so did every other general in the ancient world.”
“Armies in the ancient world firmly believed it was their natural right to pillage any city they encountered.
As for captive women, in the minds of the soldiers they were nothing more than the spoils of war and were to be treated as such.”
Here are a few instances when the legendary conqueror was far from “Great” and acted with particular cruelty in amassing his empire.
The Phoenician city of Tyre was prosperous and well-protected
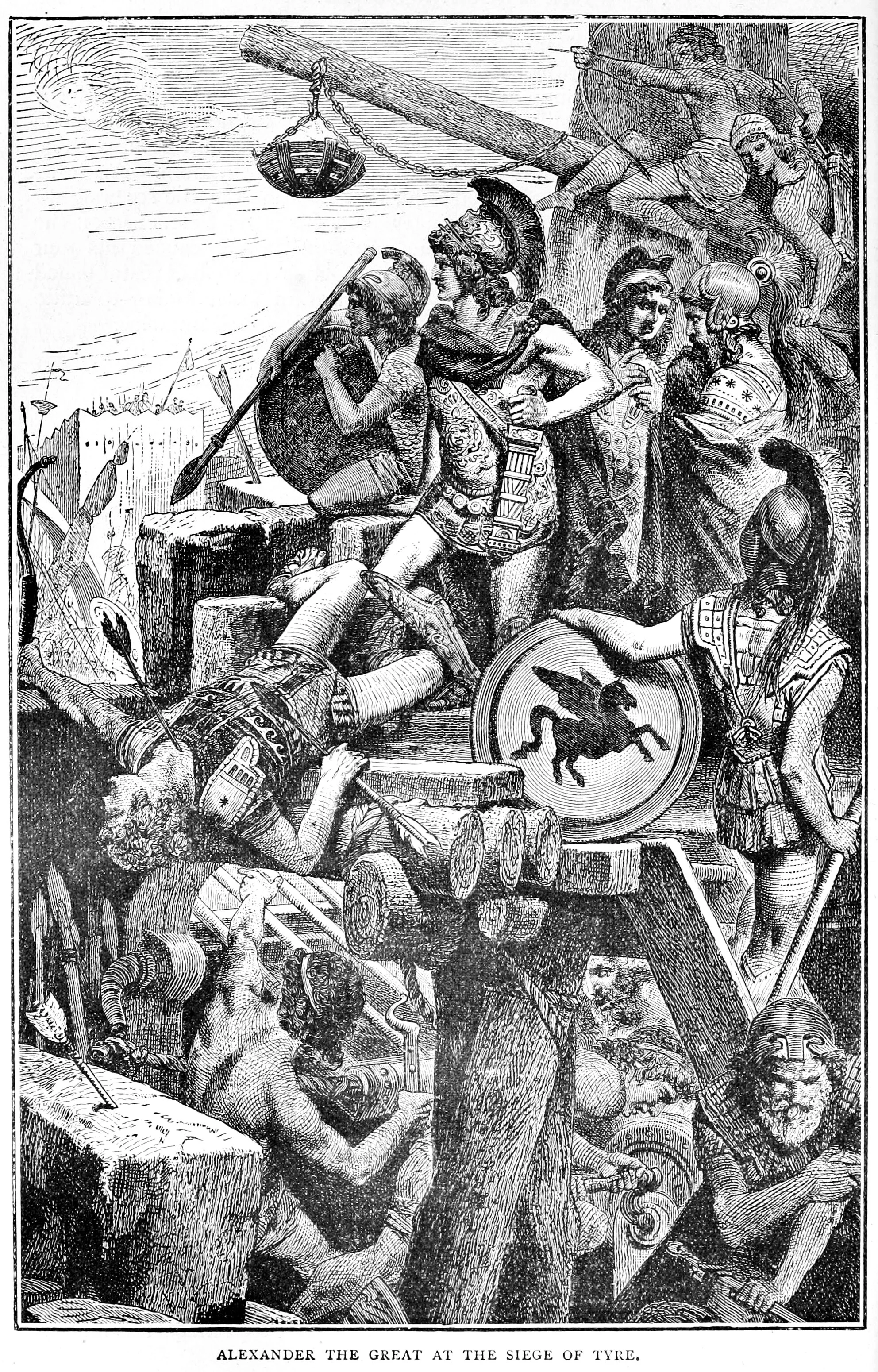
1. The Siege and Massacre of Tyre
As part of his world conquest, in 332 BCE, Alexander set his sights on Tyre, located on an island off the Lebanese coast. This was the most powerful of all the Phoenician cities and one of the richest trading centers in the Mediterranean.
Attacking the city of Tyre was no easy feat, as it was situated half a mile off the coast and protected by strong currents and winds. Alexander decided to build a causeway, chopping down some of the famed cedars of the area and destroying the older parts of the city on the mainland to use as construction material.
The long, arduous task took over half a year, interrupted by violent storms, a fire the Tyrians started by sending a flaming ship crashing into the causeway, and even a “sea monster” getting trapped upon it (most likely a whale).
An aerial photo of Tyre taken by the French military in 1934 shows the land bridge that resulted from Alexander the Great’s causeway
At last, Alexander’s men completed the causeway. While a battle raged on land, the king boarded his lead ship and led a naval battle that struck simultaneously at all the seaward walls around the city. The Tyrians didn’t know where to focus their defense. When a battering ram on an armored ship opened a breach, the Macedonian army flooded into Tyre. It’s said that Alexander himself was the first to reach the top of the city walls. Then the carnage began.
Alexander assaulted Tyre from all directions on both land and sea
“The ferocity of the slaughter was staggering,” Freeman writes. “The Macedonians had spent seven long months laboring to take the stubborn town. They had seen many of their friends crushed by stones hurled from the walls or burned to death by fire bombs. They were angry, exhausted, and passionately hated the people of Tyre for putting them through hell. Alexander didn’t even try to hold them back as they killed every man, woman, and child they could lay their hands on.”
Corpses of men, women and children lined the streets of Tyre after Alexander and his army breached the walls of the city
Thousands died within the first few hours, and the rest were sold into slavery — aside from the lucky few who sought sanctuary in the temple of Hercules. And then there were the 2,000 men of fighting age who were taken to a mainland beach across from Tyre and crucified.
A painting of Gaza in 1839 by David Roberts
2. The Unmentionable Death of Gaza’s Eunuch Governor
En route to Egypt, also in 332 BCE, Alexander faced an obstacle: the hilltop fortress town of Gaza, ruled at the time by the Persians. Its marketplace held the riches of the Arabian caravan trade, including frankincense, gold and myrrh.
A bas-relief from Alexander the Great’s sarcophagus depicting the battle of Gaza
Alexander was, in many ways, not only a daring army commander but also an engineering genius. When his men weren’t fighting or trekking halfway around the world, they were engaged in impressive construction projects. In Gaza, Alexander ordered them to build a ring around the city equal to its height. Using the siege towers from Tyre, the Macedonian army stormed the walls of Gaza but were driven back three times. On the fourth attempt, though, Alexander led a successful foray into the city, despite a wounded shoulder from a previous skirmish.
All the men of Gaza were killed, and the women and children sold into slavery. The local governor, a eunuch named Batis, was brought before Alexander, who insisted he bow down before him. Batis refused, looking upon his conqueror in contempt.
The hero Achilles dragged his enemy Hector from his chariot — a gruesome act that inspired Alexander the Great’s humiliation of the governor of Gaza
“Then Alexander in his anger did something so horrific that most ancient historians omit the episode altogether,” Freeman writes. Inspired by Achilles’ shocking treatment of his enemy Hector in The Iliad, Alexander tied Batis to his chariot by his ankles and dragged his mutilated body through the surrounding rocky desert around Gaza long after he was dead.
The burning of Xerxes’ palace in Persepolis. Was it an act of drunken stupidity — or premeditated revenge?
3. The Needless Sacking of Persepolis
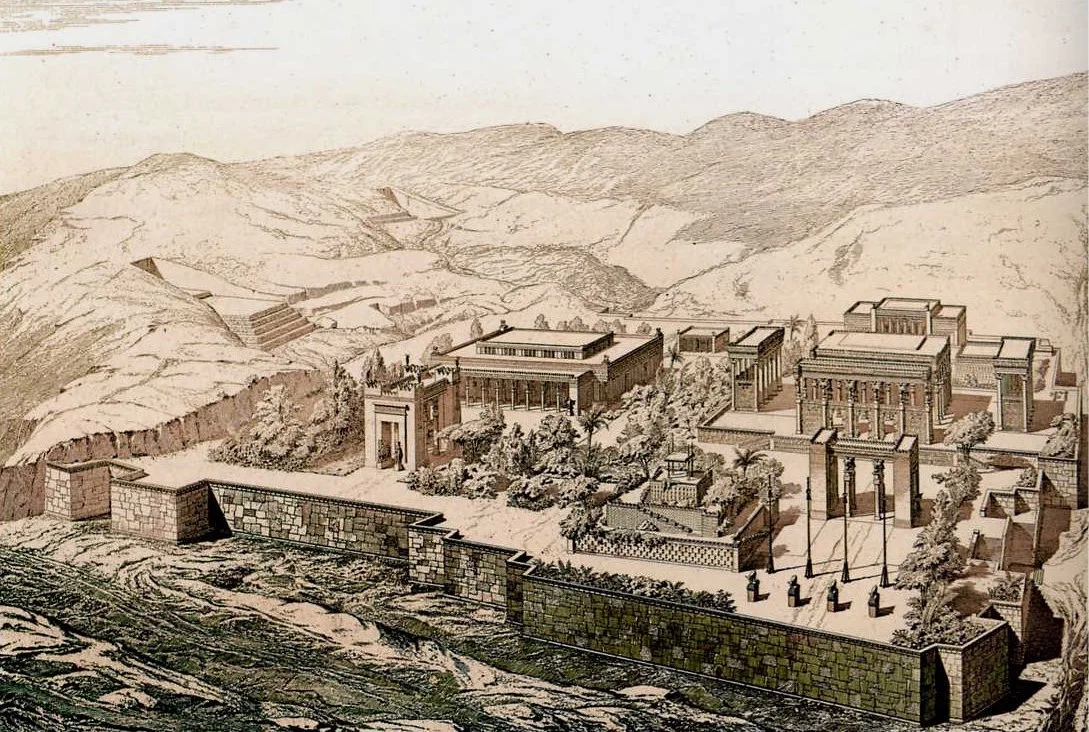
Unlike these previous battles, Alexander and his army marched right into Persepolis, the heart of the great Persian Empire, unopposed, in 330 BCE. It was a new city for the era, and a gorgeous one at that, filled with statues, impressive architecture and luxurious accommodations.
Architectural and artistic wonders filled the city of Persepolis, though Alexander’s army viewed them only as the spoils of war
Alexander had spent too much time calling Persepolis the most hated city in Asia and claiming that the ultimate goal of his campaign was to destroy the Persian Empire (even though he would continue on after this, much to some of his men’s dismay). Having finally reached the city that had been demonized for so long, Alexander’s soldiers didn’t give even the remotest thought to preserving this pinnacle of culture; they wanted booty in all senses of the word.
“Armies in the ancient world firmly believed it was their natural right to pillage any city they encountered,” Freeman writes. “After all, they put their lives on the line fighting for king and country. Glory was well and good for princes and nobles, but they longed for tangible treasure to spend while they were still young enough to enjoy it and gold to buy that farm they had always had their eye on back home. As for captive women, in the minds of the soldiers they were nothing more than the spoils of war and were to be treated as such.”
A drawing of Persepolis by the architect Charles Chipiez
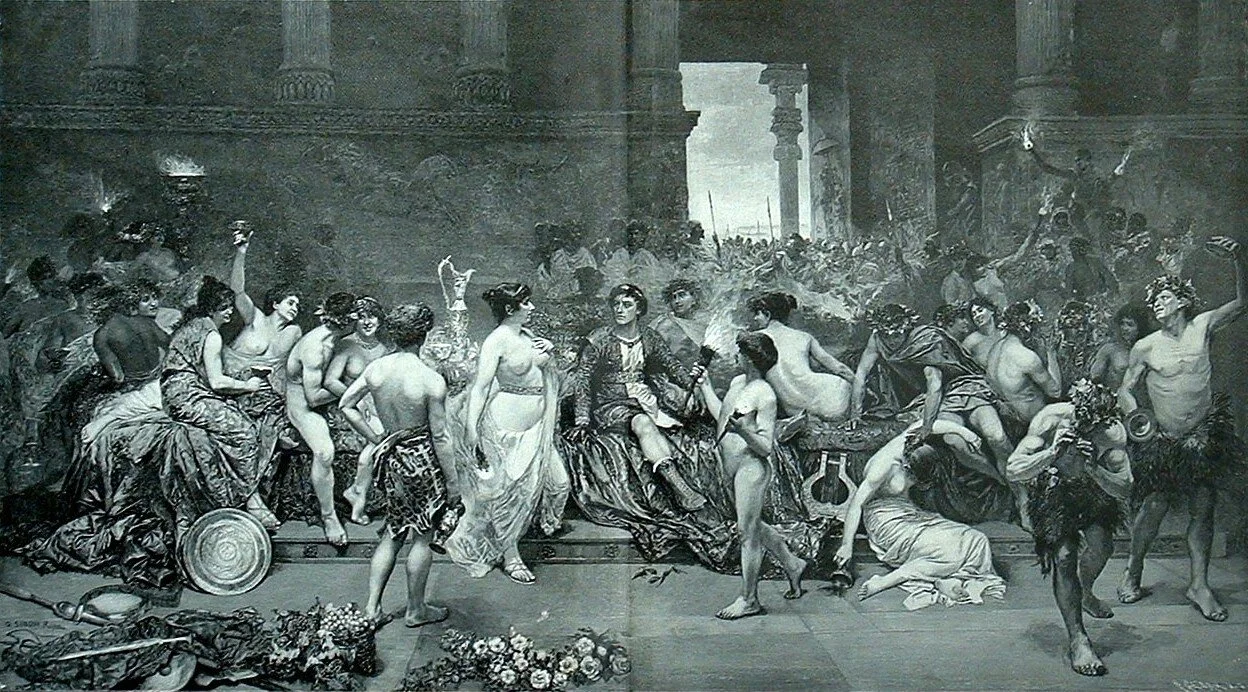
Once he was situated in the palace complex, Alexander knew he couldn’t contain his men. He gave his army free reign to sack Persepolis — the first time he had done so to a city that had willingly surrendered.
What resulted was “an orgy of ferocious greed,” as Freeman calls it. The soldiers broke into homes, killing the men and raping the women and girls. They grabbed anything of value, hacking limbs off golden statues and sometimes even killing each other in the quarrels over fine purple cloth or silver jewelry.
“The bravest among the citizens saw what was coming and set their own houses on fire with themselves and their families inside before the Macedonians could break down the door,” Freeman writes. “Others put on their finest clothing and threw their wives and children from the roofs to their deaths in the streets below, then followed themselves.
After one day, “Persepolis was a smoking ruin filled with the dead, an indescribable scene of horror as naked widows and orphans were led away in the winter cold to the slave markets,” Freeman continues.
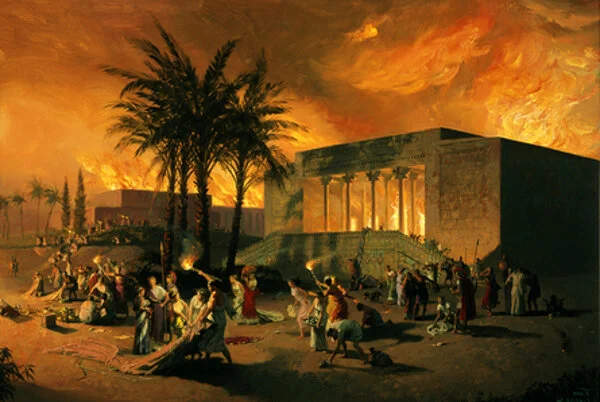
Some time later, in what the author calls “a fine Greek tradition to blame women for the foolish deeds of men,” Alexander burned down the great palace of Xerxes. A courtesan (which is just a nice way of saying “high-class whore”) named Thaïs had spoken so eloquently of destroying the palace, that a drunk Alexander grabbed the nearest torch and started the blaze himself — an act he almost immediately regretted. But it was too late. The palace was reduced to ash.
The woman is always to blame. The courtesan Thaïs is said to have convinced Alexander to burn down Xerxes’ palace — which he instantly regretted
A different version of the story comes from Arrian, often the best source for information about Alexander the Great. The historian stated that the Macedonian king had always planned to burn down the palace in revenge for all the evils the Persian Empire had perpetrated upon the Greek world. Evidence supports this claim: Archeologists have found the remains of the palace but no treasures destroyed at the time — revealing that the fire was most likely premeditated and not started until all valuable objects had been removed.
“In the end, we simply cannot know whether or not the king deliberately burned down the palace of Xerxes,” according to Freeman. “But we can be sure that most of the ancient historians who wrote of the episode were deeply uncomfortable with Alexander’s actions and preferred to blame the events of that night on too much wine and the silken tongue of a woman.” –Wally
“He killed tens of thousands of civilians in his campaigns and spread terror in his wake, but so did every other general in the ancient world.”