Long before twinkle lights and decorated trees, the Winter Solstice was a moment of cosmic suspense when the sun hovered at its weakest and people hoped for its return. Across cultures, people told strikingly similar stories about light slipping back into the world.
The longest night arrives quietly. A sky as black as ink, a stillness so deep it feels ancient, a cold that settles into the bones. For early peoples this wasn’t just winter — it was the edge of everything. If the sun kept fading, if the darkness swallowed just a little more each day, what then?
So they watched the horizon, prayed to familiar gods, whispered old tales and waited for proof that the world was not ending but turning. And when the sun finally paused, then tipped toward brighter days, it wasn’t just an astronomical event. It was a miracle unraveling in real time.
The stories born from that fear and relief — of divine children, returning heroes and unconquered light — became the backbone of Yule lore and rituals that later threaded their way into traditions we still keep without realizing it.
Yule: The Longest Night and the Eternal Return
As the year thinned toward winter, people watched the sun sink lower on the horizon and felt the days draining away. Farmers, priests and sky-watchers across the ancient world tracked its movements with care because the shrinking daylight meant colder nights, dwindling food and a long stretch of uncertainty before spring.
By the time the winter solstice arrived, the world felt paused. The sun hovered at its weakest point, rising late and setting early, and everything seemed to hold its breath with it. Homes glowed with firelight, animals stayed close and communities waited for proof that the darkness had reached its limit.
Then came the turning. The sun lingered at the edge of the sky, steadied and began — almost shyly — to climb again. That small increase in light was a promise that life would return. Relief blossomed into celebration, and storytelling followed: tales of gods reborn, heroes returning and divine children whose arrival signaled that the world still had a future.
The Child of Light: Shared Myths Across Civilizations
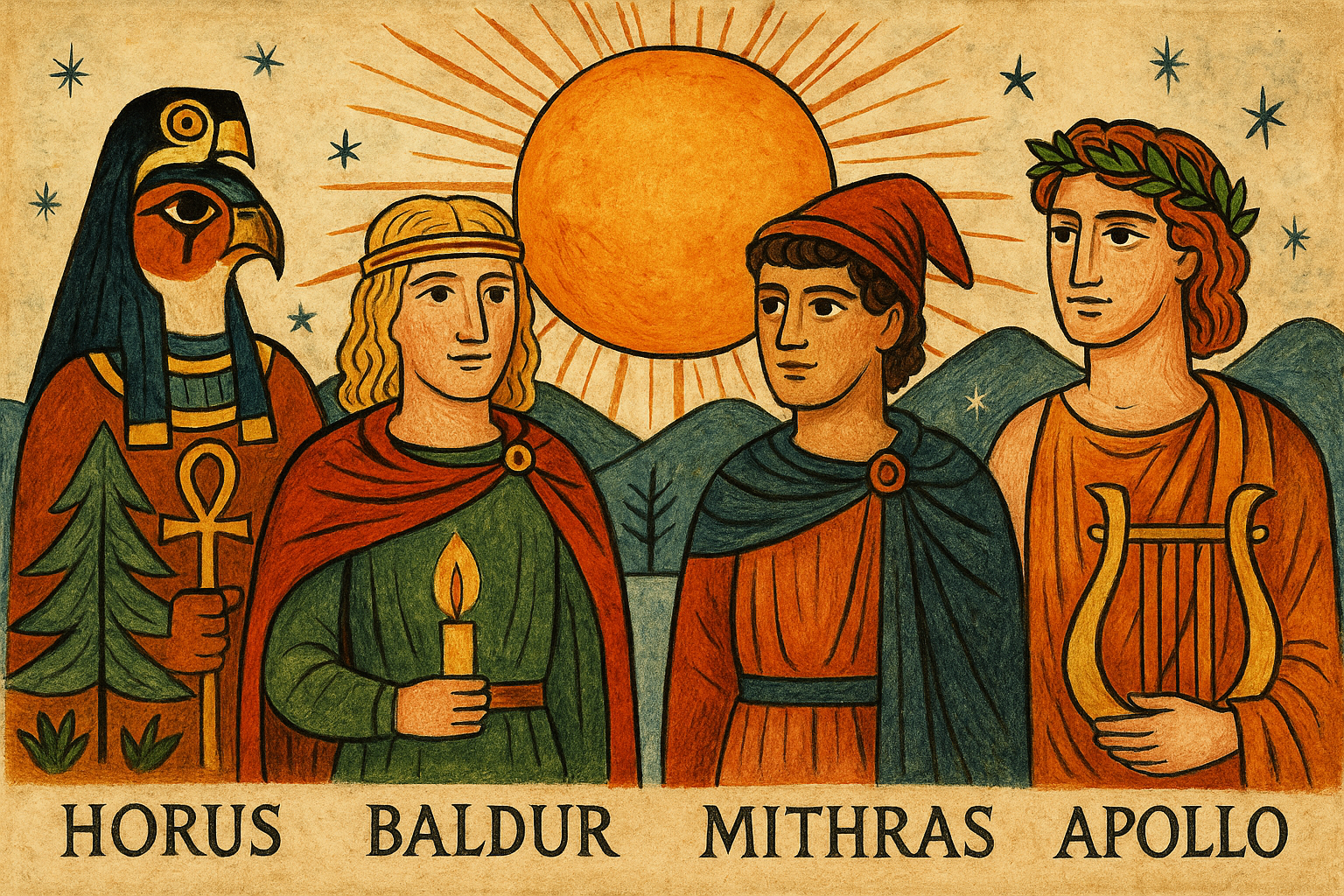
Across the ancient world the returning sun inspired stories about divine children who arrived at the edge of winter. Their births weren’t simple celebrations — they were cosmological events meant to reassure people that warmth, growth and life would rise again.
Up north, in Norse mythology, the beloved Baldur shone so brightly he seemed made of early morning light. His death plunged the world into grief, but prophecies promised he would return after the final long winter, bringing renewal with him.
Along the Nile, in Ancient Egyptian mythology, Isis gave birth to Horus, a child linked to rising waters and the rebirth of the land. His survival against darkness became a symbol of resilience as the sun regained strength.
In the Mediterranean world, worshippers honored Mithras, the unconquered sun, whose birth signaled triumph over the darkest days of the year. Roman calendars placed his festival near the solstice when the first notch of returning daylight felt like victory.
Even Apollo, ever-youthful and radiant, was imagined returning from his winter journey to bring clarity and warmth back to the world. His reappearance echoed the same relief the sky delivered: The light had turned.
These stories weren’t copies of one another, but they shared a heartbeat. Each culture told its own version of the same truth the solstice revealed — darkness recedes, light returns and the world begins again.
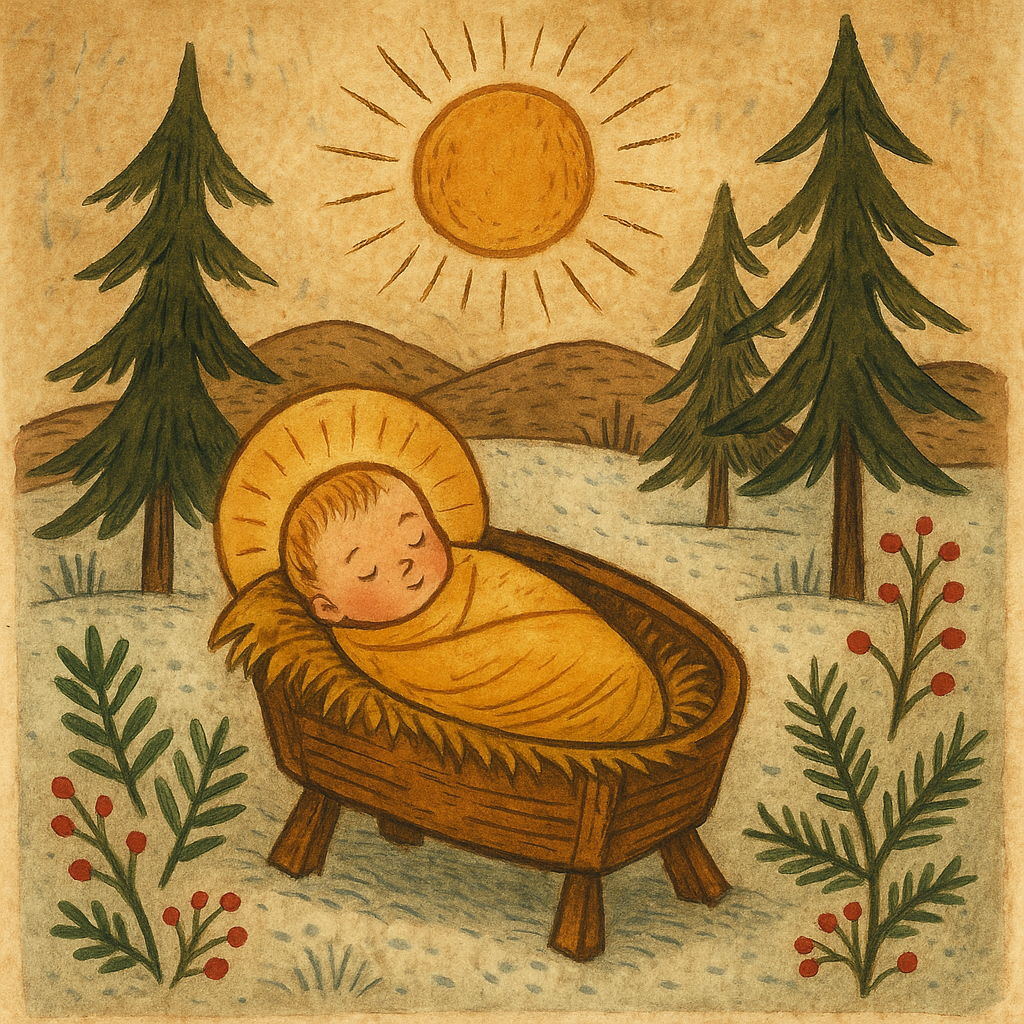
The Christ Child and the Winter Solstice Shift
When early Christian leaders tried to establish a date for Jesus’ birth they didn’t choose one based on evidence. The Bible doesn’t give a season, let alone a day. Instead they looked around at the midwinter festivals that already drew huge crowds: Saturnalia in Rome, the solstice rites of the sol invictus (the unconquered sun), and the northern Yule traditions that celebrated the birth or return of divine light.
By the 4th century, the Church placed the Nativity on December 25, right beside these older celebrations. The timing wasn’t accidental. It allowed new converts to keep familiar midwinter customs while shifting the focus to a different holy child whose arrival also promised hope in the dark.
The symbolism lined up almost too well. A child of light born at the moment the sun begins to strengthen again fit neatly into the larger pattern people already understood. Over time those threads wove together: evergreens, candles, gift giving, even the idea of a miraculous birth when the world felt at its coldest.
In that sense, the Christ child became part of the same long tradition, another figure carrying the message that the darkness wouldn’t last.
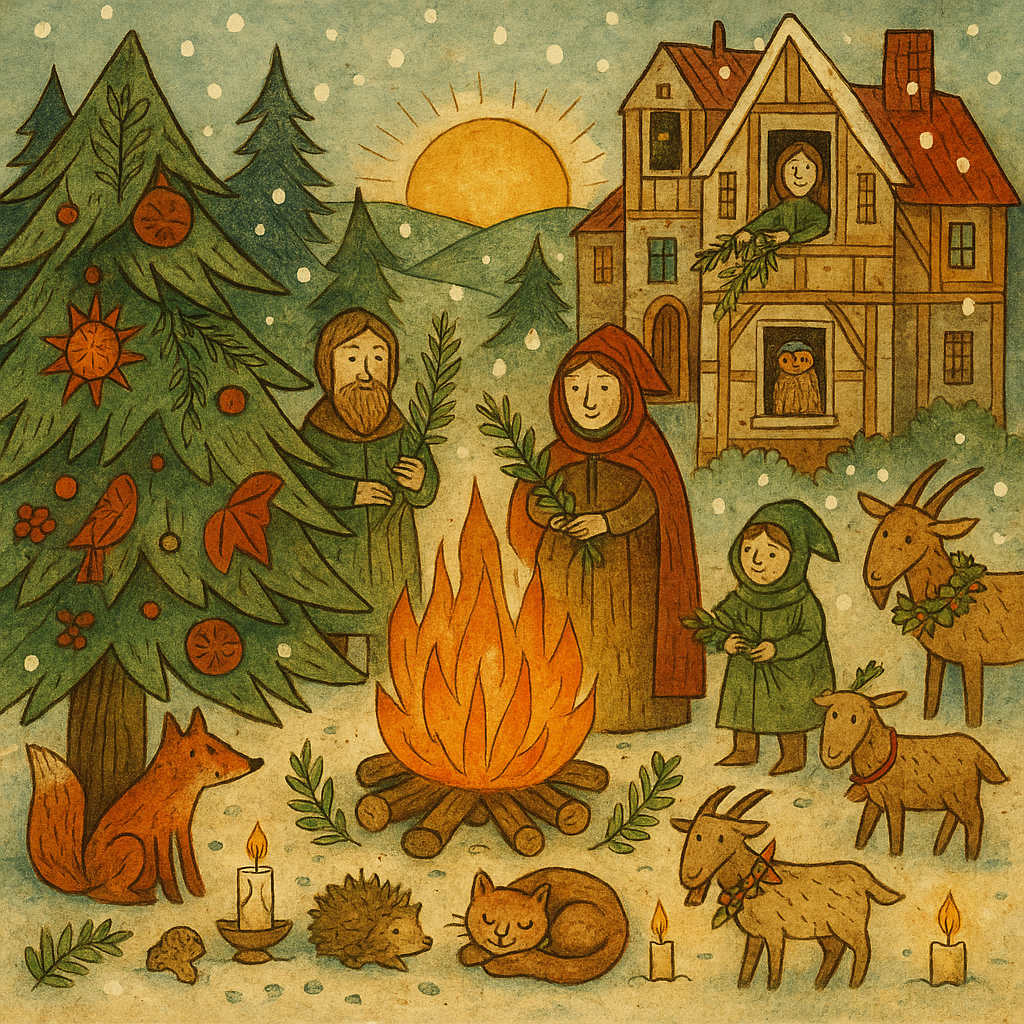
Fire and Evergreen: Yule Symbols That Refused to Die
When daylight wavered ancient communities turned to two symbols that never failed them: flame and evergreen. Both held their own stubborn kind of life, and both became anchors during the solstice when everything else felt fragile.
Fire mattered first. A single spark could warm a room, cook a meal or push back a night that seemed far too long. Solstice fires blazed across Northern Europe, and households saved embers from one year to light the next, carrying continuity through the cold. Candles flickered in windows not as decoration but as small suns, each one a promise that brightness would return.
Evergreens told a different story. While other trees surrendered their leaves, firs and pines stood unchanged, alive even in deep winter. People brought branches indoors to remind themselves that vitality could survive the freeze. Over time the practice grew into wreaths, boughs and eventually full trees decorated with symbols of protection and hope.
Together flame and evergreen formed a kind of winter vocabulary — living light and living green. They reassured people that nature was not finished, that renewal was already stirring, and that the season of returning warmth was on its way.
A Modern Rebirth at Yule: Inviting the Sun Back In
The solstice still carries that quiet threshold feeling, even if our winters come with central heating and streetlights. There’s a sense that the world pauses for a moment, holds its breath and waits for the slow return of something we can’t quite name. Yule rituals tap into that pause, using light and intention to mark the turning.
One simple practice begins before sunrise. Sit in the dim room, light a single candle and let its glow be the stand-in for the first spark of returning daylight. Breathe with it and think about what you want to coax back into your own life — confidence, momentum, joy, clarity, anything that feels like dawn.
If you keep evergreen in your home, hold a sprig or stand before your tree for a moment. That green resilience has been a solstice symbol for centuries. Let it remind you that growth often starts long before you can see it.
When the sun rises — even behind clouds — say a small rhyme to seal the moment:
“From darkest night the light is born,
I welcome back the rising morn.”
It’s simple, but that’s the point. Yule marks the return of light in the sky and in us, a slow brightening that starts with a spark.
Yule Lore: Why We Keep Telling the Same Story
Every winter the world tilts into darkness, and every winter we wait for the moment it begins to turn back toward light. Ancient people explained that shift through stories of radiant children, brave returns and gods who refused to stay in the shadows. We still repeat those stories because the instinct behind them hasn’t changed.
The solstice reassures us that endings are rarely final, that light slips back even when it feels gone, and that renewal doesn’t need fanfare. It just needs time. That’s the heart of Yule — a promise written across the sky and retold every year when the night reaches its deepest point and then begins to lift. –Wally