Do you know your ba from your ka? What’s a vizier? How about a cartouche? Our handy glossary of Ancient Egyptian terms will have you speaking like a pharaoh in no time.
The terms we use to describe the religion, history and artifacts of Ancient Egypt are a strange mishmash of words that have French, Greek, English, Arabic — and yes, sometimes even Egyptian — origins.
Talk Like an Egyptian
As you read more about the fascinating and complex world of Ancient Egypt, it helps to familiarize yourself with the terms that come up the most often. It’s probably a good idea to bookmark this page for easy reference — especially if you’re considering a visit. 🤗
ankh: The hieroglyphic symbol for life, similar to a cross but with a loop in place of the upper arm. It was especially popular in jewellery and on temple carvings, where it was held in the hands of deities or being given by them to the pharaoh, to represent their power to sustain life and to revive human souls in the afterlife.
atef: The atef crown was made up of the White Crown of Upper Egypt with red ostrich feathers on either side. It was worn by the god of the underworld, Osiris.
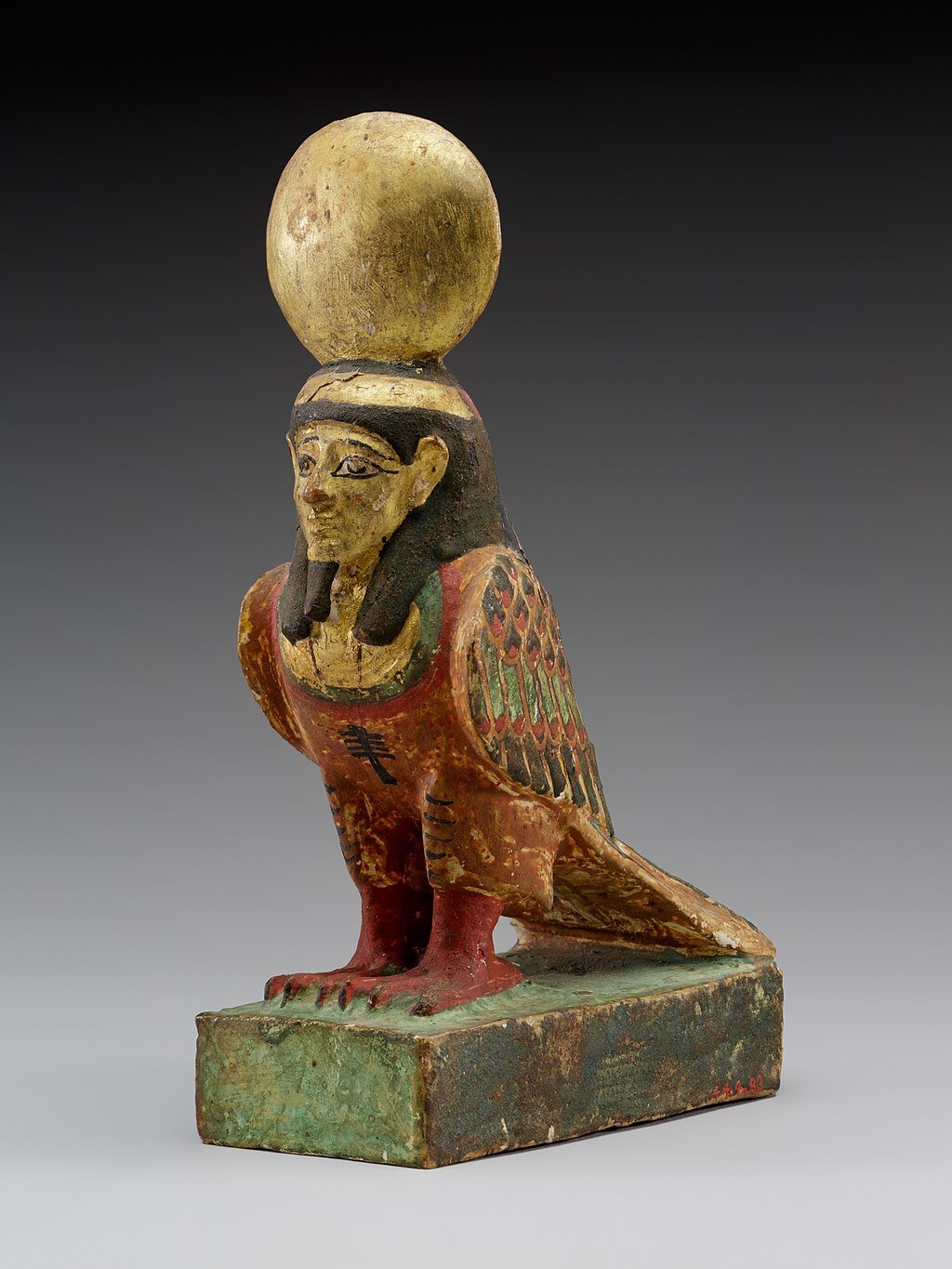
ba: The ba is, essentially, the concept of the soul. Depicted as a bird with a human head, it could leave a person’s tomb to fly about.
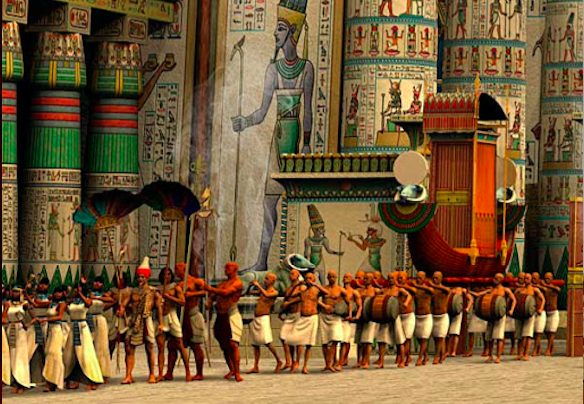
barque: These thin boats that curve up at either end were the transports of the gods, especially during festival processions. In temple sanctuaries, models of barques held statues of a deity. When a pharaoh died, a barque would transport them on their way to becoming a god.
Book of the Dead: This is the modern name ascribed to a collection of 200 hymns, rituals and spells that allowed the deceased to travel safely through the underworld and enter the afterlife. Ancient Egyptians knew it as the Spells for Going Forth by Day.
canopic jars: Four containers used to store the preserved internal organs of the deceased (the lungs, stomach, liver and intestines) extracted during the mummification process. Each jar was topped with the head of one of the god Horus’ sons.
cartouche: The oval frame that surrounds the name of a king, queen or god in inscriptions.
Coffin Texts: Collected during the First Intermediate Period, around 2134-2040 BCE, these 1,185 incantations and other forms of religious writing were inscribed on coffins to help the deceased navigate the afterlife, providing maps of the underworld and the best way to avoid dangers on one’s way to paradise.
deshret (or Red Crown): The crown, with a square base that curved upward into a point and had a coil spiraling out in front, was worn by the rulers of Lower Egypt.
djed: A representation of the spine, it symbolized stability. A djed amulet was often placed in coffins, where the backbone of the deceased would lay, to ensure eternal life. During a Sed festival, the pharaoh, with the help of priests, would raise a djed column.
Duat: The underworld, home of the gods Osiris, Anubis and Ma’at, as well as many grotesque monsters. The sun deity Ra travels through the Duat every night, where he battles the serpent Apep, or Apophis. This is where a deceased person’s soul travels for judgment.
Eye of Horus (aka udjat eye or wedjat eye): A falcon’s eye that acts as a protective talisman and symbolizes rebirth after death. Its origins lie in a myth where the evil god Set plucks out one of his nephew Horus’ eyes.
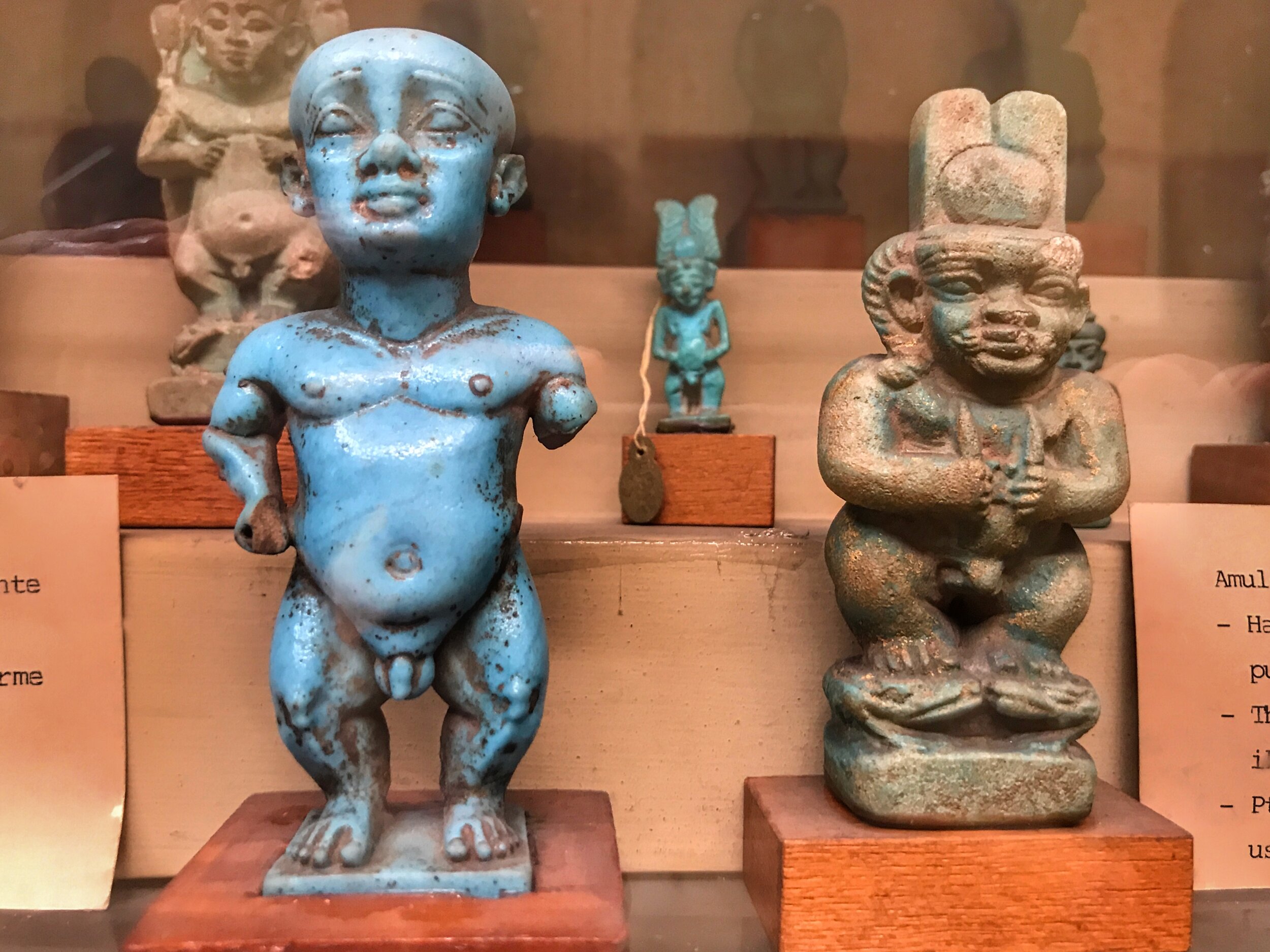
faience: A powdered quartz paste that ranges in color from turquoise to teal. Modeled and sometimes fired, it was commonly used for jewelry, pottery and sculptures.
hedjet (or White Crown): The crown of Upper Egypt, it’s often irreverently (but accurately) described as looking like a bowling pin.
hieroglyphs: Think of them as the emojis of their day. Often mistakenly called hieroglyphics, they make up the system of pictorial writing used in Ancient Egypt. Though they sometimes represented the actual objects they depicted, hieroglyphs usually stood for particular sounds.
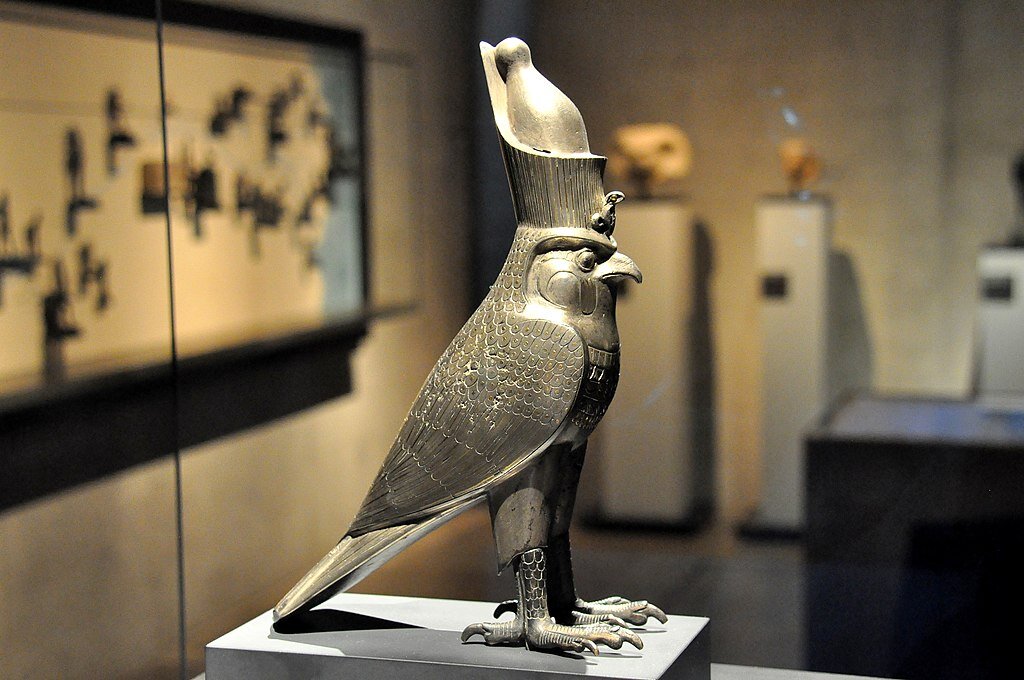
Horus name: Beginning in the Predynastic Period, pharaohs would take on an additional name, cementing their relationship with the falcon-headed god Horus. The pharaoh oversaw their entire country and, like the bird of prey, could strike at enemies below.
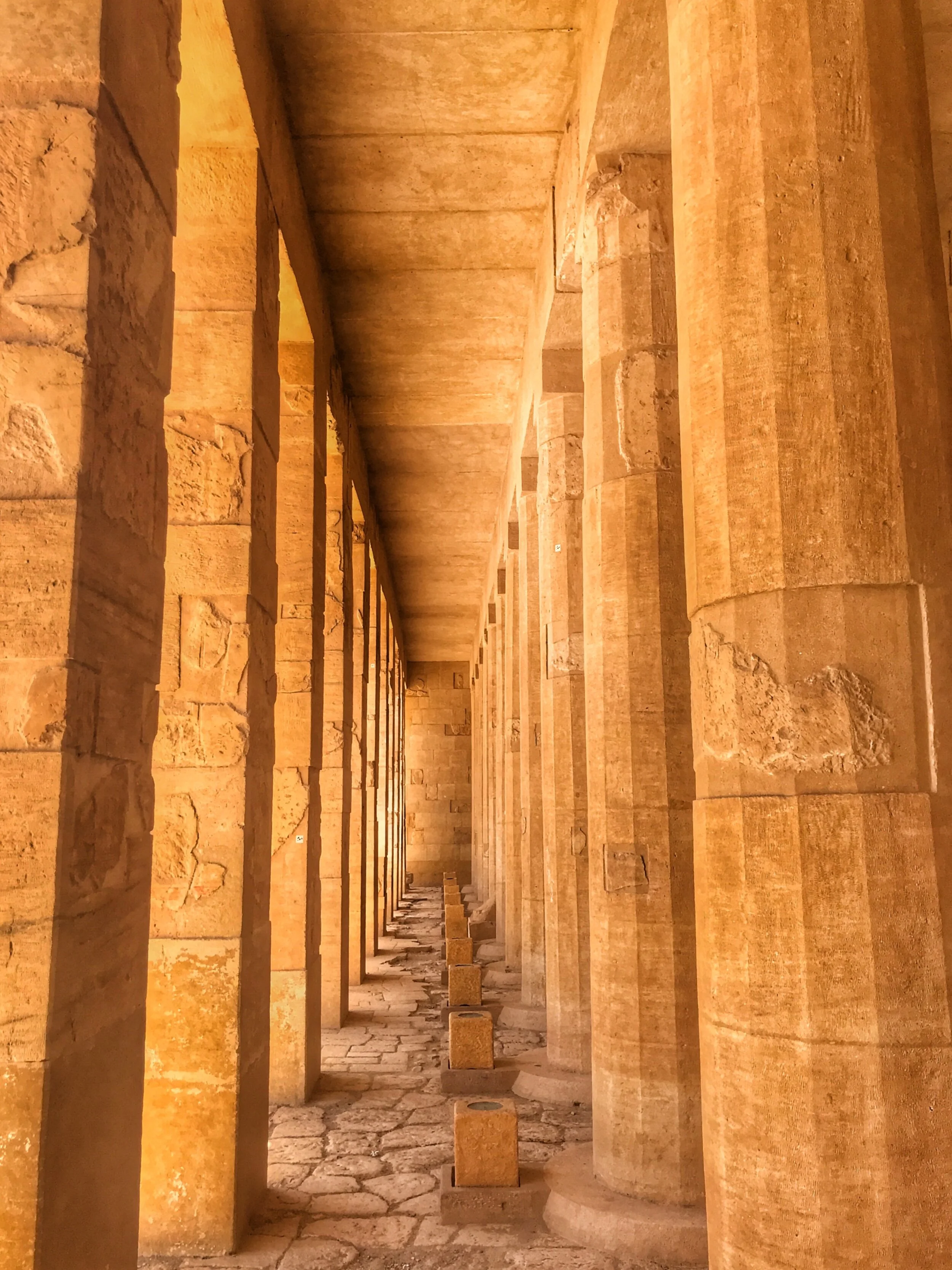
hypostyle hall: The reception area of a temple. Originally, most would have had a roof over rows of densely packed columns with capitals depicting palms, papyri or lotuses to represent the lush island of creation.
ka: The best way to describe this is as a soul — it’s someone’s other self, what makes them unique. It’s with a person throughout their life, but upon death the ka and the body become separate. The body has to be preserved, and the ka nourished, or it will starve and cease to exist. It’s represented as a human with upraised arms — or just the arms raised at a 90-degree angle.
khepresh (or Blue Crown): Often worn by pharaohs when going into war, the khepresh was a blue headpiece with a uraeus on the brow.
kohl: Black powder made from galena ore (the chief source of lead) mixed with oil and used as an eyeliner by women and men.
Lower Egypt: The Ancient Egyptian worldview was upside-down compared to ours. Lower Egypt was the northern half of Egypt, so called because the Nile flows north before entering the Mediterranean Sea. Its capital was Memphis.
ma’at (aka maat): The principle of balance and cosmic order, personified by a goddess of the same name. It was a pharaoh’s duty to rule according to ma’at.
mammisi: A birth house, where a woman would go to deliver a child and recover for two weeks or so. These chapels were often situated in front of a temple and were said to be where a god had been born.
mastaba: A type of tomb first created in the Old Kingdom. From the Arabic word for “bench,” they were rectangular and flat-roofed, with a substructure belowground. As time went on, architects stacked stories atop them, leading to step pyramids and, eventually, the triangular pyramids like those at Giza.
nemes: A striped head covering worn by pharoahs. It covered the brow and skull, hung down on the side to rest on the shoulders, and was drawn together in the back in a sort of ponytail. King Tut was a fan.
Opening of the Mouth: A ceremony held at the tomb, where the mouth of a mummy was symbolically opened so the dead could use their senses in the afterlife.
Opet: A festival held during the inundation, or flooding of the Nile. The statue of the chief god Amun would travel upon a barque from his sanctuary at Karnak to Luxor Temple.
papyrus: The writing surface used by Egyptian scribes. Derived from the pith of the stalks of papyrus, which grew along the banks of the Nile, the plant was also used to make boats, sandals, baskets and rope.
pectoral: An elaborate necklace that covered much of the chest.
pharaoh: The supreme ruler of Ancient Egypt. He or she (there are a few times when a woman took the throne, like the remarkable Hatshepsut) was considered a god.
pschent (or the Double Crown): A combination of the deshret and hedjet crowns, it showed that the pharaoh controlled both Lower and Upper Egypt.
pylon: A massive gateway leading into a temple. Some held rooms, like the one for the harem at Medinet Habu.
Pyramid Texts: The earliest religious texts of Ancient Egypt. These spells, religious beliefs and myths were inscribed on the walls of Fifth and Sixth Dynasty pyramids (2465-2150 BCE). They were used to magically transform the deceased into the god of the afterlife, Osiris. Composed of 2,217 spells grouped into 714 “utterances,” they gave way to the Coffin Texts.
rekhyt: A stylized lapwing bird with wings spread and human arms raised in adoration, representing the general populace or the pharaoh's subjects. When depicted on the walls of ancient temples, it signified that the public was allowed in that area.
sarcophagus: A large stone container that held a mummy's coffin. Its name comes from the Greek sarkophagos, meaning “flesh-eater.”
Sed: A festival of rejuvenation that renewed the powers of a pharaoh, it was usually — but not always — held in their 30th year of rule.
senet: A game played in Ancient Egypt. No one knows the rules, but they think it was a bit like chess. Pieces were usually fashioned from animal bone or clay.
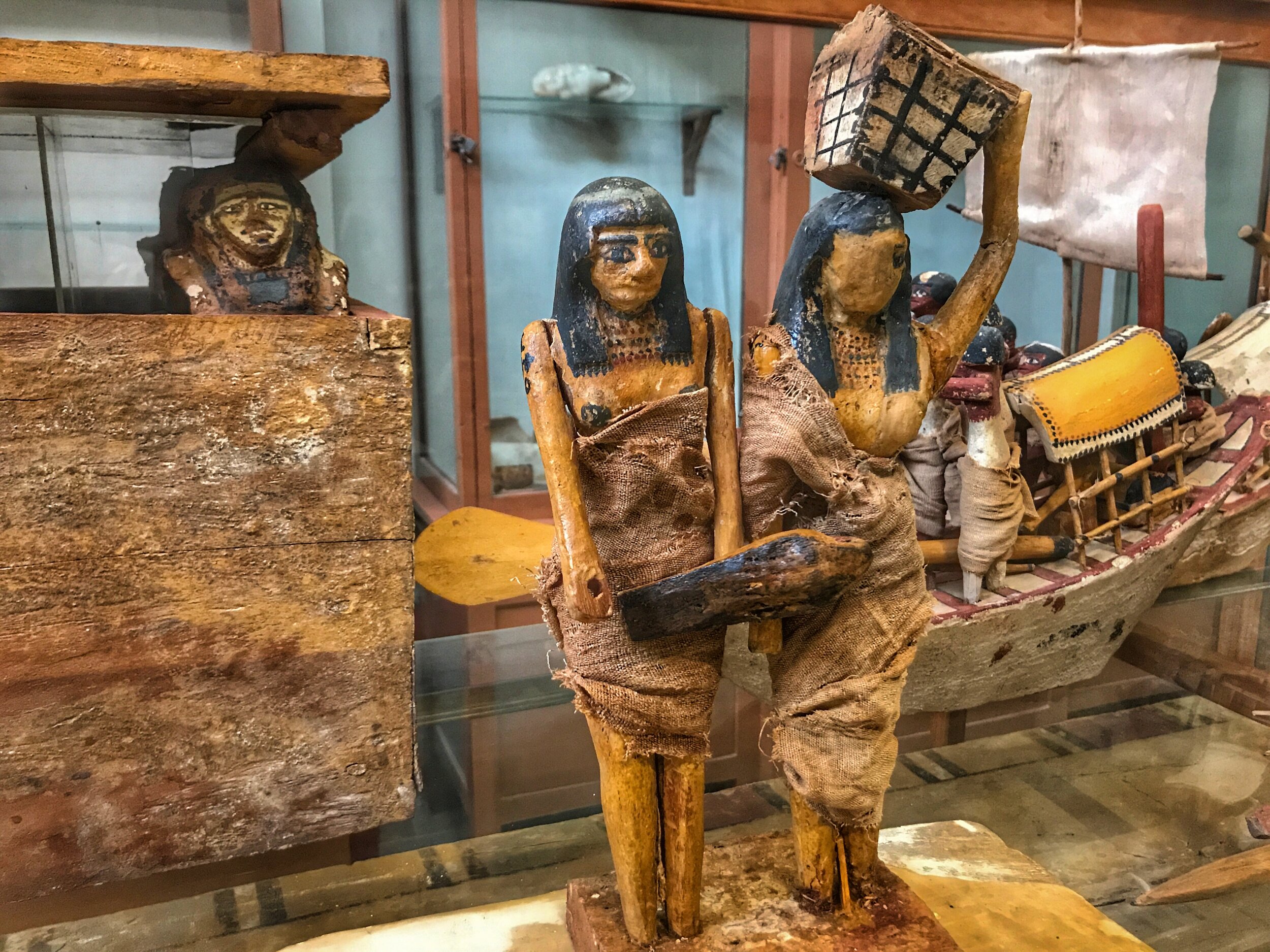
shabti (also shawabti or ushabti): A small mummy statuette of a servant placed in tombs that could be magically brought to life to perform tasks for the deceased in the afterlife.
sistrum: A sacred rattle made of a wood, metal or clay frame set loosely with crossbars strung with small metal discs. It was shaken during ritual dances for the goddess Hathor and later Isis.
sphinx: A mythological beast with the body of a lion that usually had the head of a pharaoh or god. The famous one sits outside Cairo at Giza.
stele (also stela): An upright slab of stone that served as a monument, inscribed with religious or historical text.
Upper Egypt: The southern half of the kingdom of Ancient Egypt. It’s called Upper Egypt because the Nile River flows northward, from Upper to Lower Egypt. Its capital was Thebes.
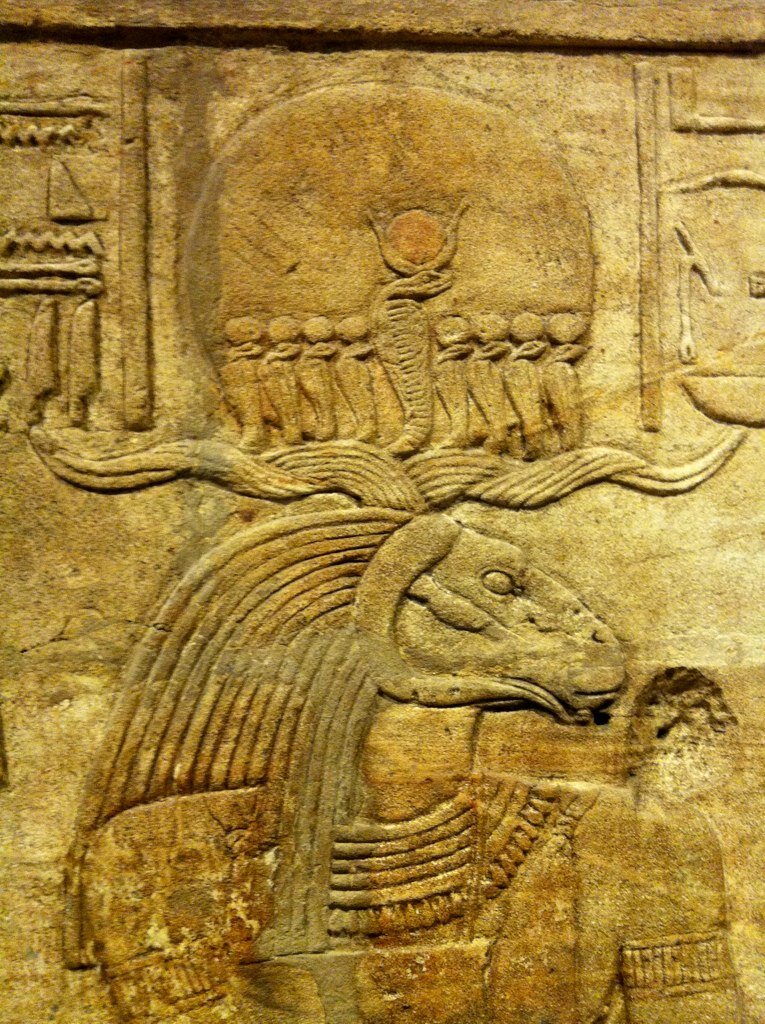
uraeus: A rearing cobra in a threatening pose that represented divine authority, worn as a crown or head ornament by Ancient Egyptian divinities and rulers. It showed that the pharaoh had the protection of the goddess Wadjet, the patroness of Lower Egypt.
vizier: The second in command after the pharaoh. The role held many responsibilities, including administration of the government, security, judgement and the safety of the empire.
was scepter: A staff that’s often forked at the bottom and topped with the head of a creature, possibly the Bennu bird, a mythological heron who wears the atef crown. Carried by gods and pharaohs, the was scepter stood for power and dominion. –Wally