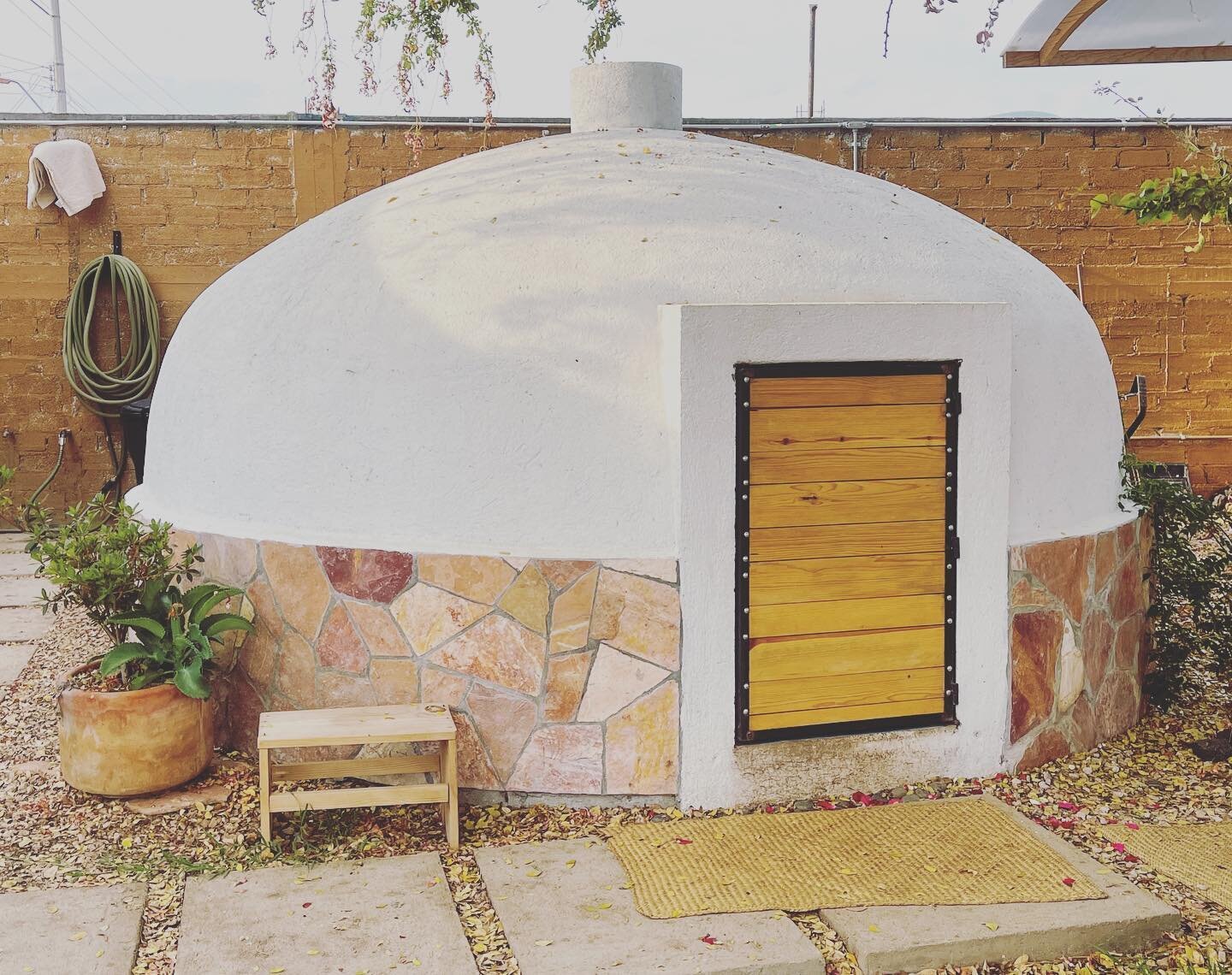
This Luxor temple depicts the victory over the Sea Peoples and includes carvings of severed penises. It’s also the site of the murderous Harem Conspiracy.
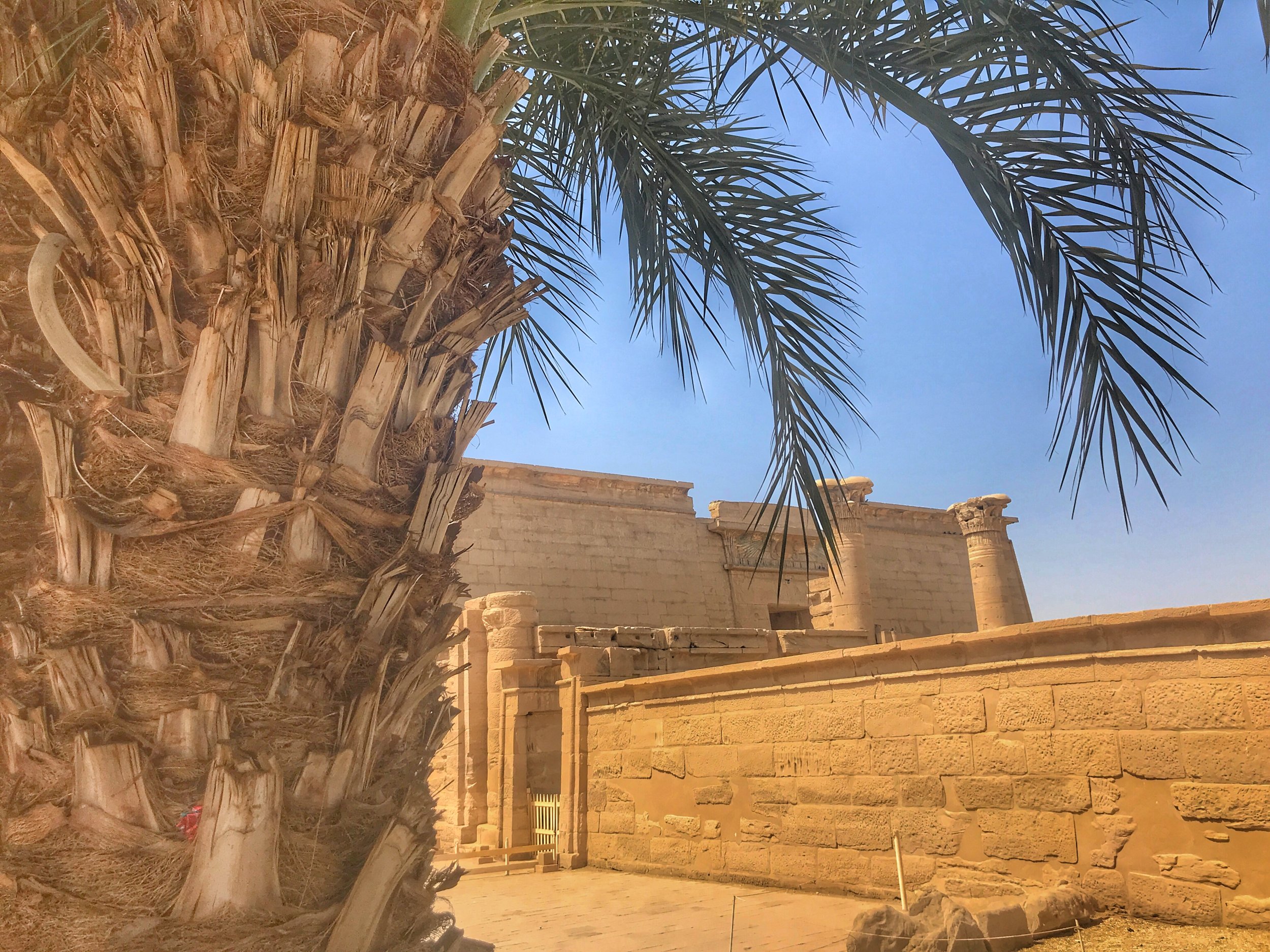
When in Luxor, be sure to visit Medinet Habu, an often-overlooked temple
The temple wasn’t even on our itinerary, but it ended up being one of our favorites. We had some extra time after a morning wandering the cool tombs of the Valley of the Kings and Hatshepsut’s mortuary temple. Rasha, who runs the highly recommended guide service Egypt Sunset Tours, suggested we add on the Tombs of the Nobles and Medinet Habu.
Admission to the temple costs a mere 80 Egyptian pounds (about $4.75), making this the cheapest of all the sites we visited.
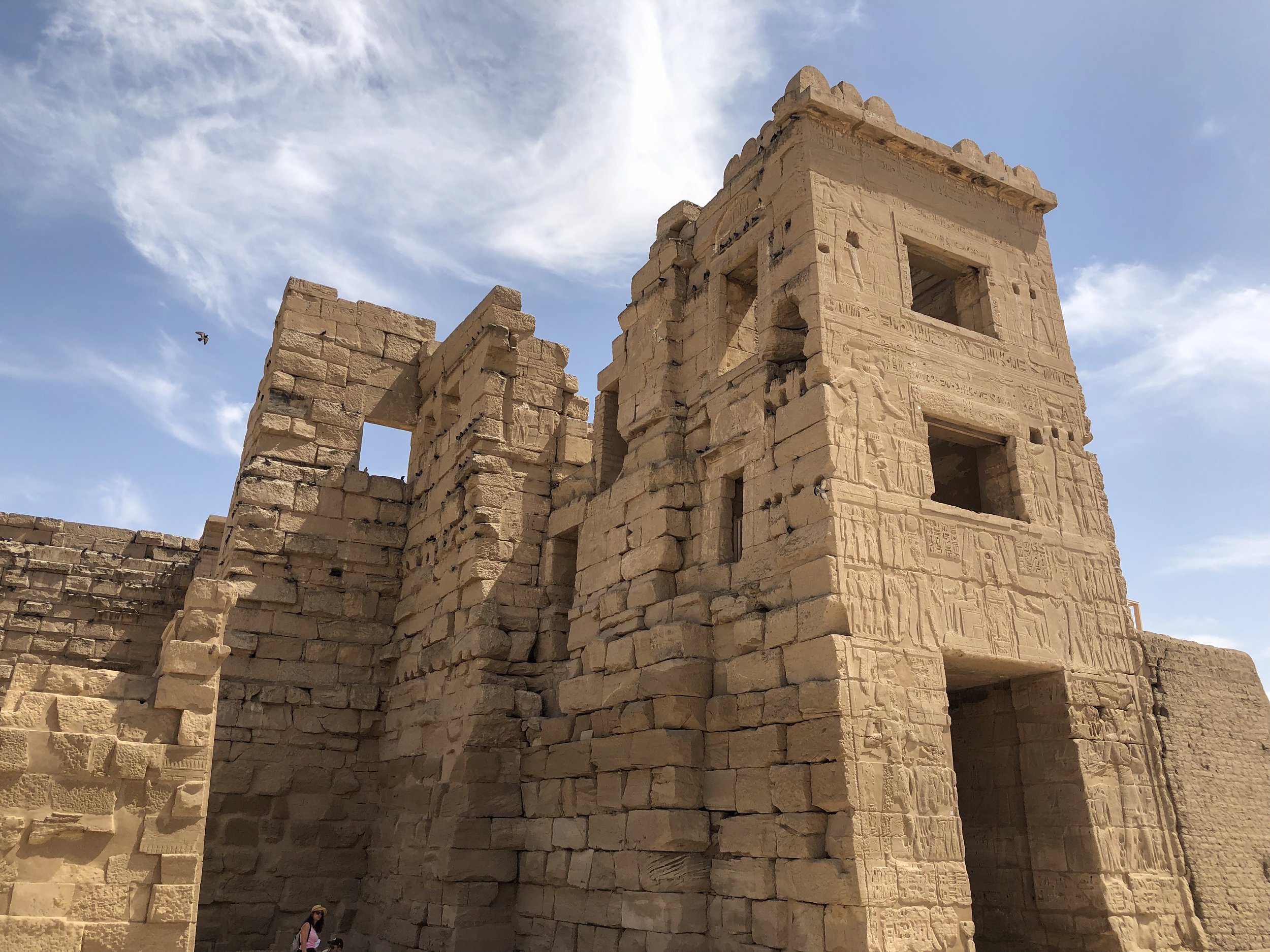
The exterior wall is yet another sign that Medinet Habu was built to resemble a fortress
On one hand, all the temples of Ancient Egypt begin to blur together, their elements similar: a heavy pylon entranceway, staggeringly tall colonnades, small, secret sanctuaries at the back.
But, in truth, each temple has its own distinct personality. Karnak sprawls, much of it in ruins, its piles of rubble evoking Ancient Rome. Dendera has a magical feel, with its turquoise blue ceiling painted with astrological iconography. Luxor’s colonnade is open to the sky, reveling in the light and warmth of the sun.
And Medinet Habu, too, has a unique design; it evokes a feeling of military might not found in other temples. This martial flair is fitting, for Ramesses III built the structure to celebrate the victory of a battle that threatened to end the Egyptian Empire for good.
Duke and Wally loved visiting the temple complex, which was quite deserted
“New evidence revealed that Ramesses III did meet a gruesome end at the hands of his conspirators.
CT scans of his mummy found a deep slash across his throat.”
The bas-reliefs on the pylon gateways depict Ramesses III’s victory over the fierce Sea Peoples
Pirates of the Mediterranean: The Sea Peoples’ Slaughter
They came from the sea, though historians aren’t quite sure of their homelands. They were fierce, ruthless and mighty warriors. All around Ancient Egypt, neighboring empires fell under the Sea Peoples’ barrage. They even conquered the Hittites, Egypt’s sometimes-friends, sometimes-foes.
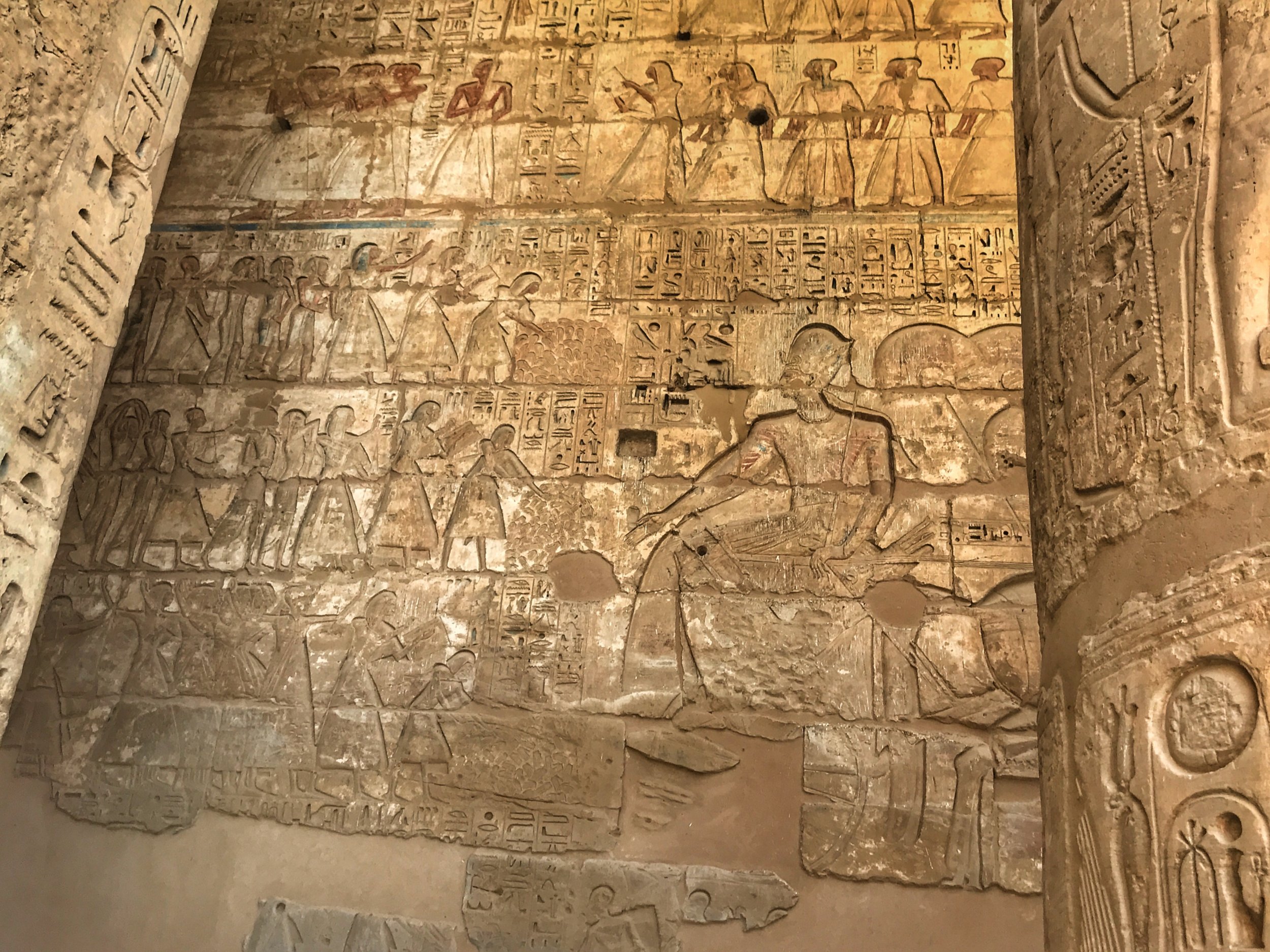
Some of the bas-reliefs were still works in progress
Chariots helped Egypt gain advantages in battle
If you defeat warriors who were undefeated, you brag about it, like Ramesses III did
So when they finally came for Egypt in 1179 BCE, Ramesses III must have been worried. He staged the war on two fronts. One, a land battle at the delta of the Nile, was successful, but its lack of detail belies the probability that losses were severe (and therefore glossed over in the official record).
We know more of the second battle, which went more strongly in Egypt’s favor. This naval skirmish wiped out the Sea Peoples, beginning with a hail of arrows and ending with the capsizing of the Mediterranean ships.
Ramesses III turned his mortuary temple into a war memorial, calling it the Mansion of Millions of Years of King Ramesses, United With Eternity in the Estate of Amun. That’s quite a mouthful, so I’m glad the site now goes by its Arabic name.
The temple is infamous for being the site of the Harem Conspiracy
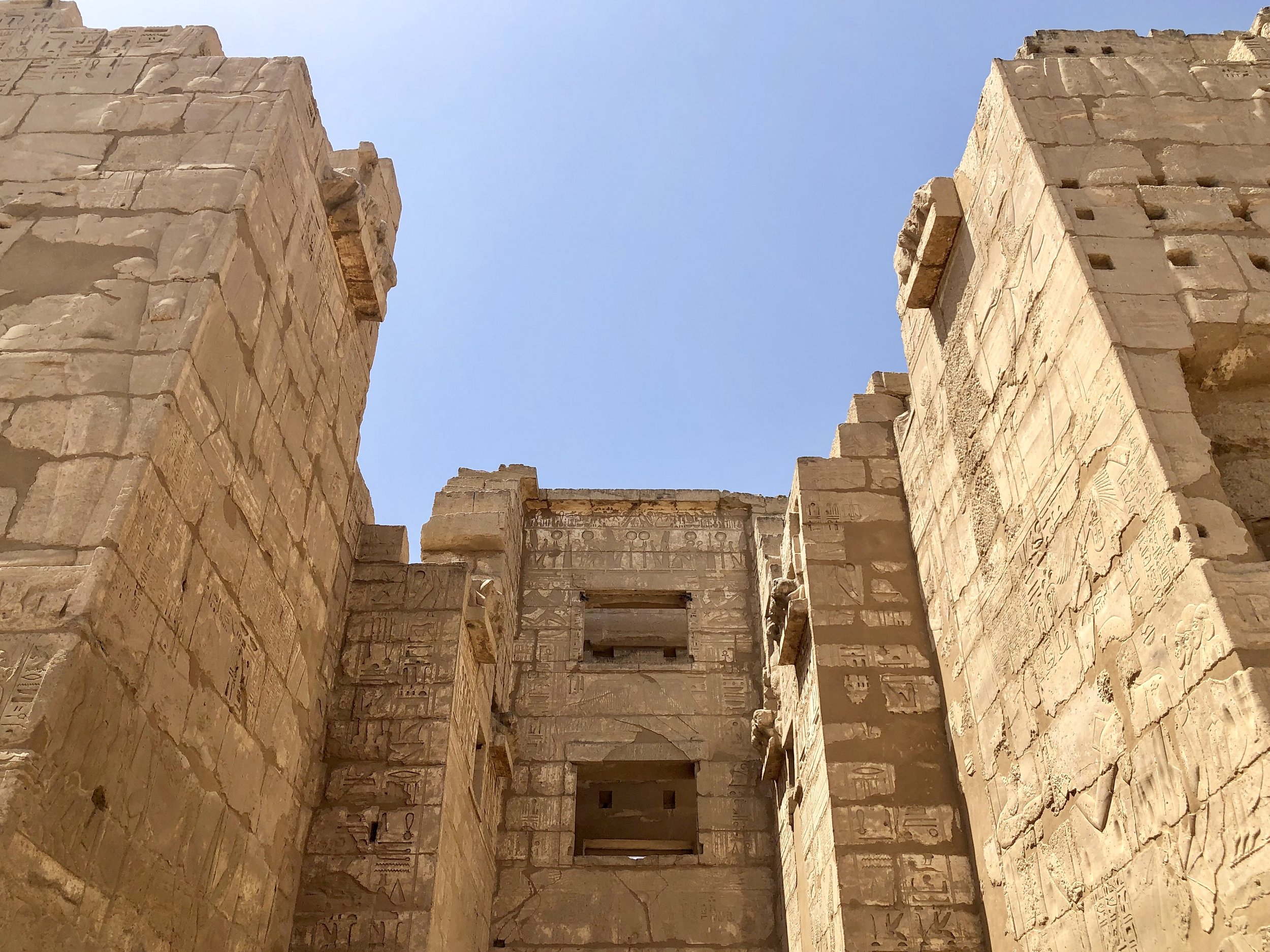
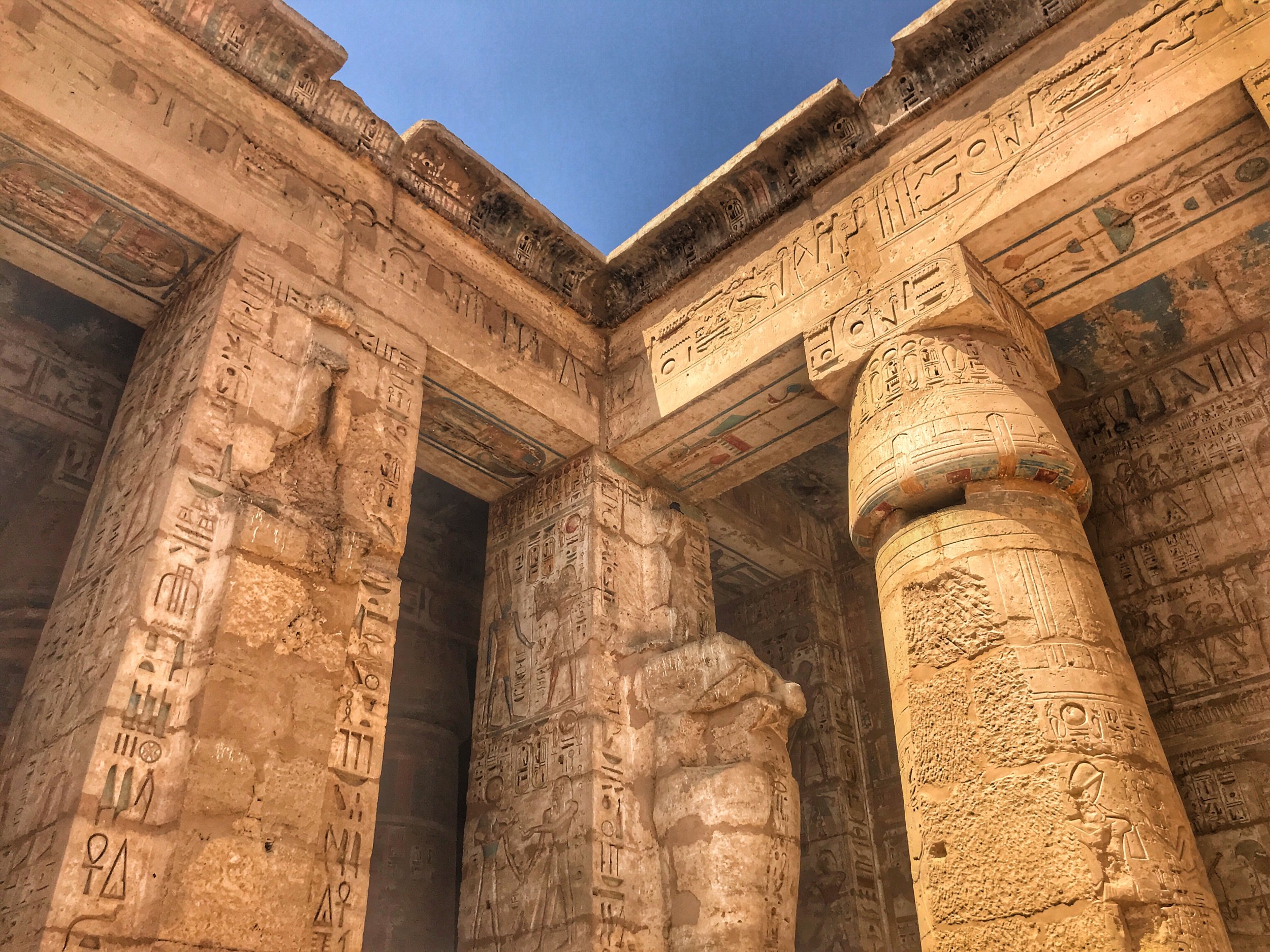
Inside Medinet Habu
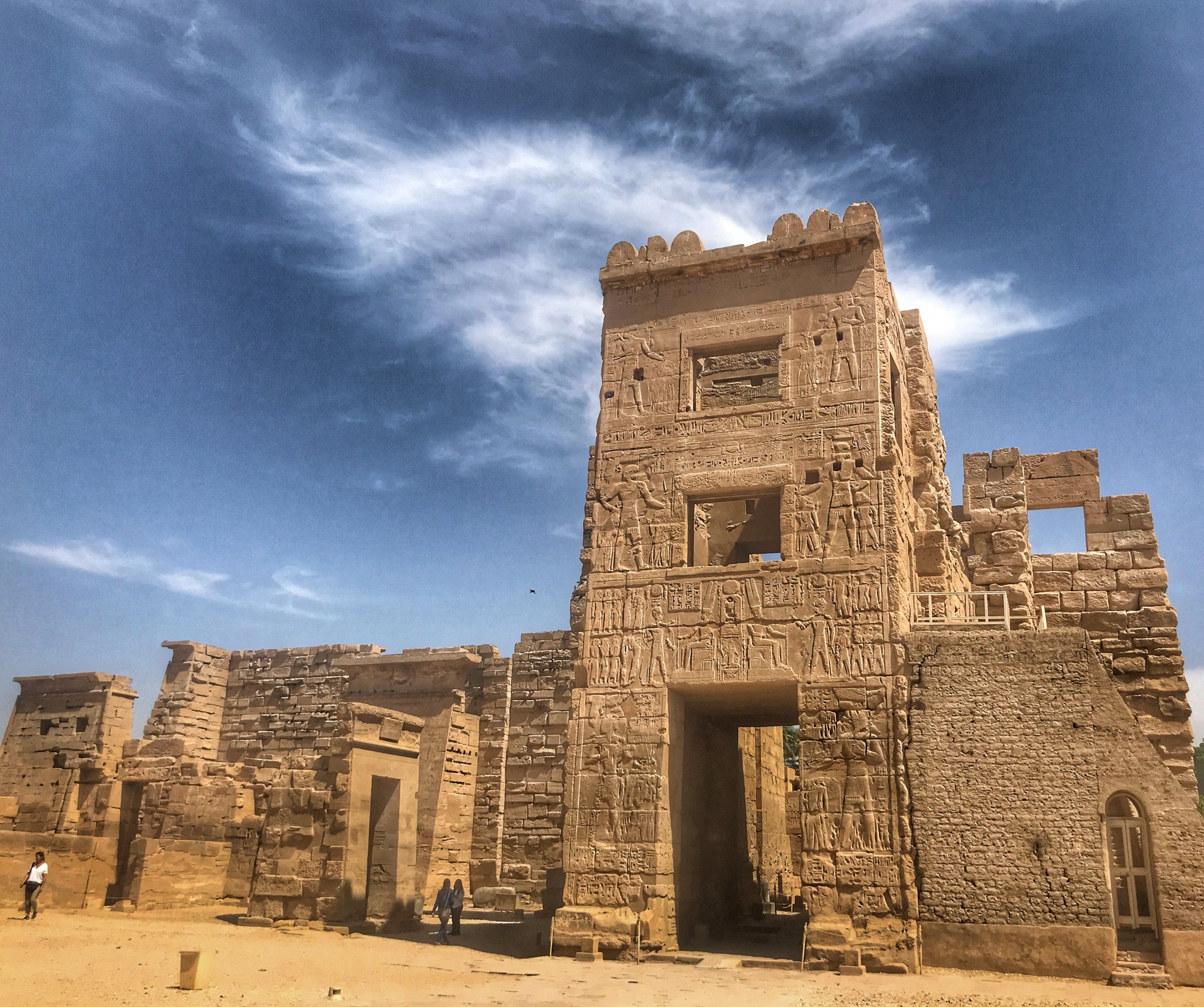
The imposing entrance pylon façade strikes the visitor immediately as severe, a brutal sand-colored monolith. This is the fortified gatehouse Ramesses III built and was modeled on Syrian migdol gates he had encountered on his military campaigns. Adding to the fortress feel was a high mud-brick wall that once enclosed the complex.
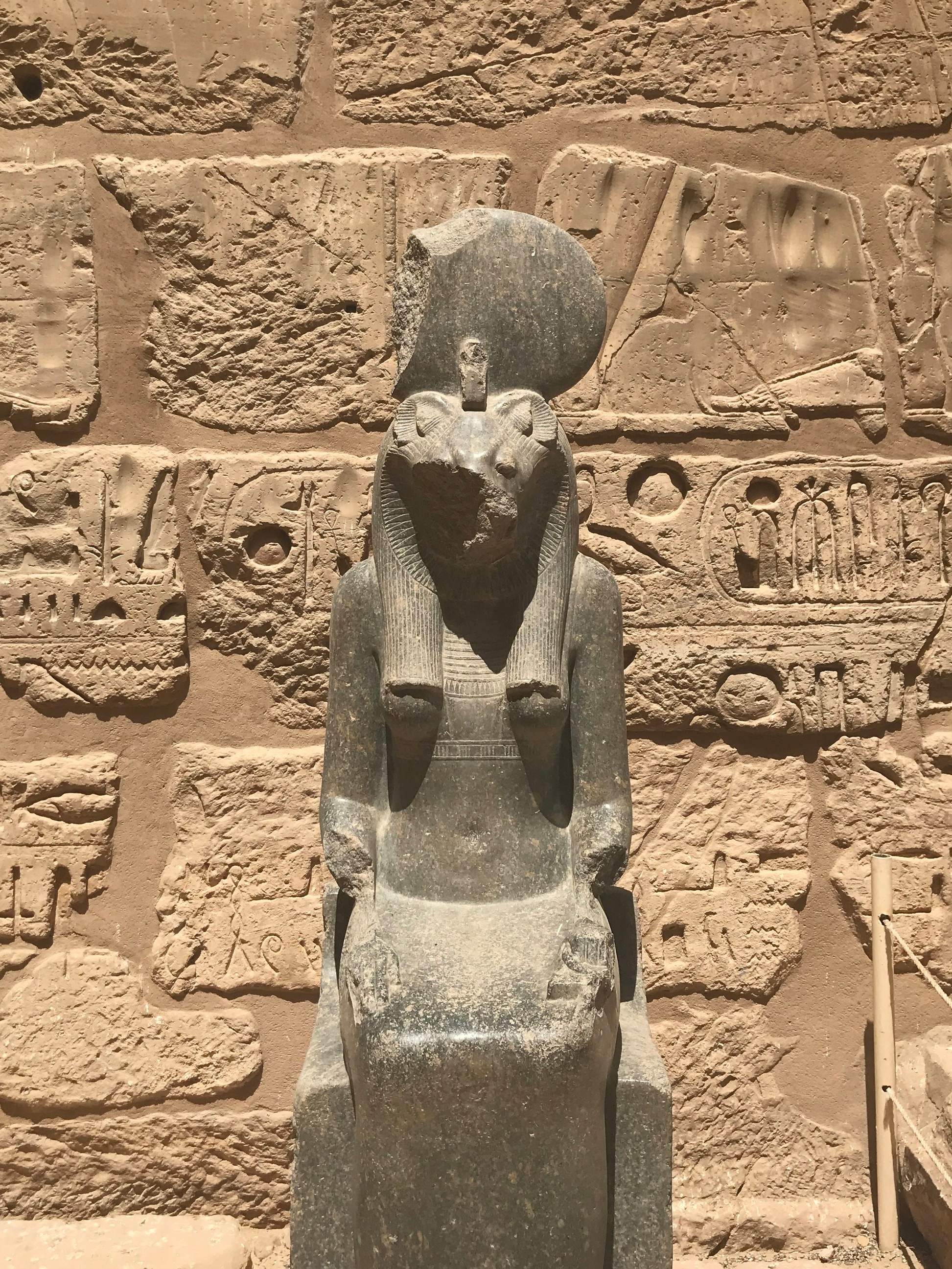
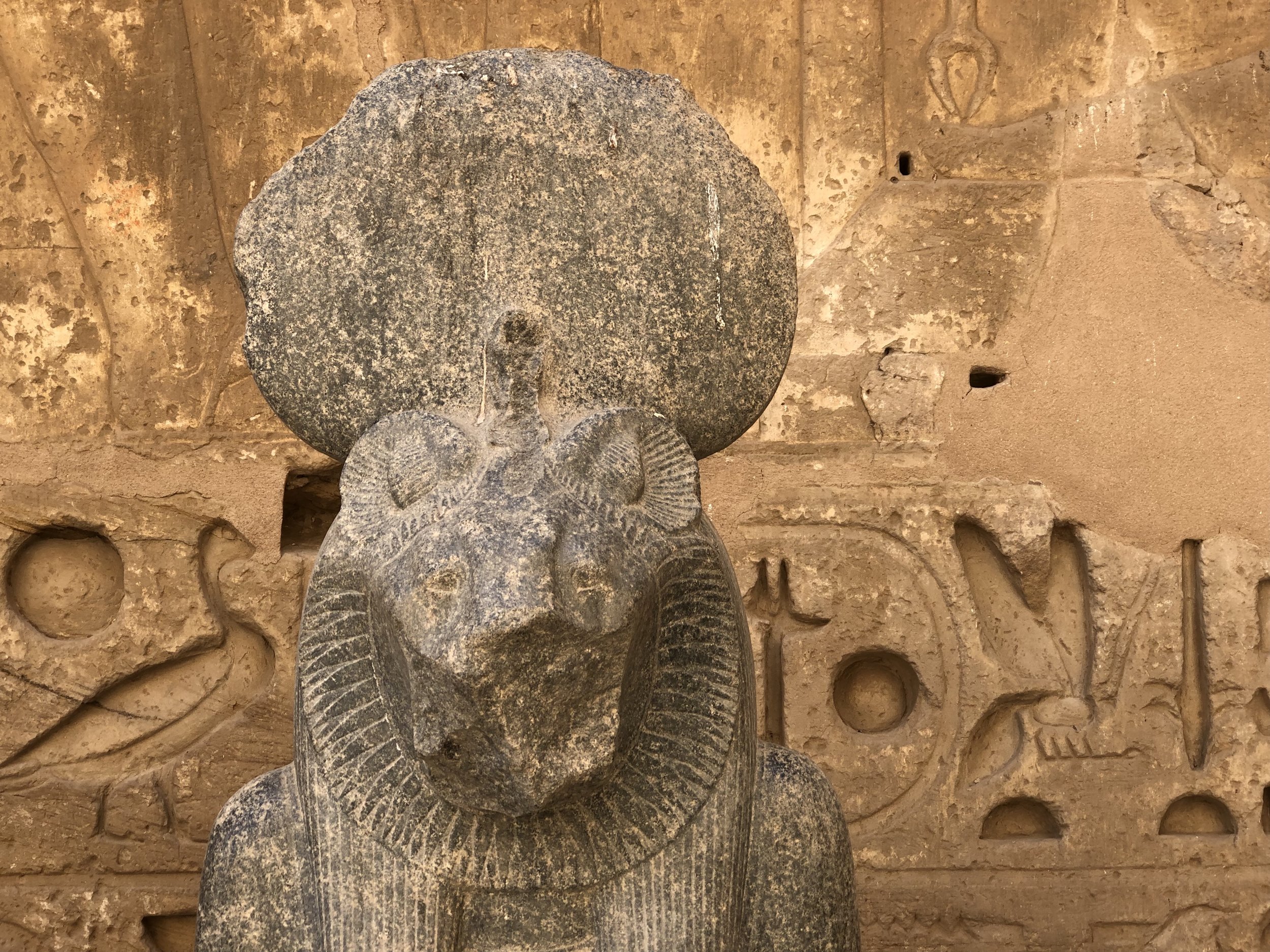
Upon entry, there are decaying statues of Sekhmet, the lioness-headed goddess of war
Aside from towering depictions of pharaohs, you don’t see many statues in temples
What deity did Ramesses choose to feature immediately inside the gate? Why, none other than Sekhmet, the fierce lioness-headed goddess of war.
It was in these rooms at the top of the structure where Ramesses III hung out with his many wives — and where he met his demise
Treason in the Harem
The top floor of the gatehouse was where Ramesses hung out with his harem. The carvings here show Ramesses III in intimate poses with various wives or relaxing in a chair playing board games.
But all wasn’t as idyllic as pictured. “There was something about the claustrophobic atmosphere that fed the bitter jealousies and personal rivalries of the king’s many wives,” writes Toby Wilkinson in The Rise and Fall of Ancient Egypt. “With little to occupy their minds besides weaving and idle pleasures, the more ambitious concubines nurtured resentments, angry at the lowly status of their offspring and wondering how they might improve their own and their children’s fortunes.”
The Second Courtyard later became a Christian church in the 9th century
The statues were preserved because they were covered in mud by the Coptics
In 1155 BCE, one of the pharaoh’s secondary wives, Tiy, plotted to assassinate Ramesses III as well as his heir apparent, Prince Ramesses, and install her son, Pentawere, on the throne. The plot, known as the Harem Conspiracy, grew to include a mutiny in the army and a revolution in the countryside. But as the plan became intricate, more and more people became involved, and eventually someone blabbed.
The conspirators were arrested and tried at a tribunal. Found guilty, they were forced to commit suicide. Those who were involved to a lesser degree were horribly disfigured, their noses and ears hacked off to permanently mark them as convicts.
Not only was this a mortuary temple, it was also Ramesses III’s palace. It was very unusual to combine both of these buildings into one complex
New evidence revealed that Ramesses III did meet a gruesome end at the hands of his conspirators, though. Researchers reexamined his mummy with CT scans and found a bone-deep slash across his throat that would have been fatal.
Medinet Habu is a beautiful structure — and the site of a pharaoh’s assassination
The underside of this gateway shows the winged sun amongst other paintings
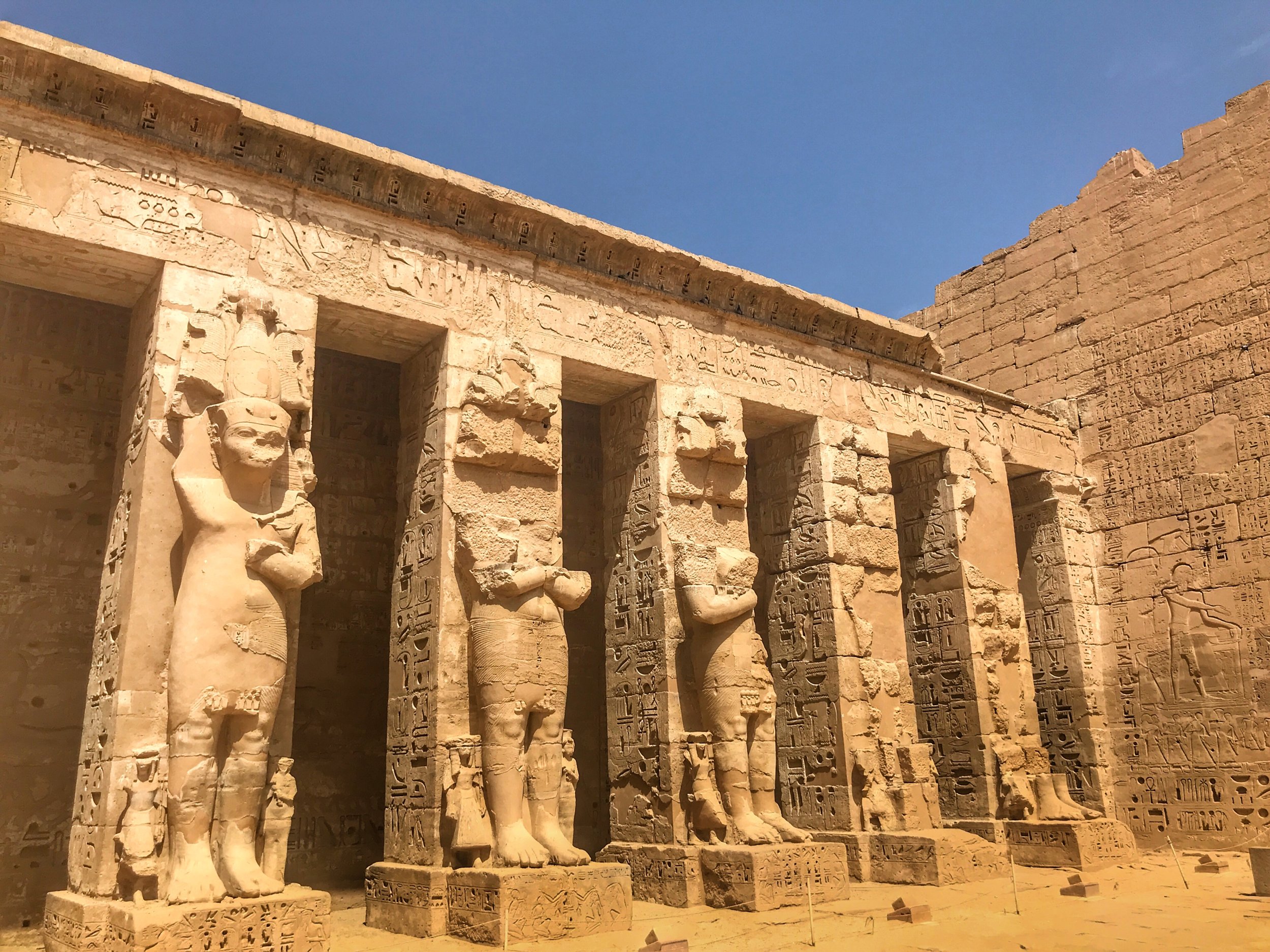
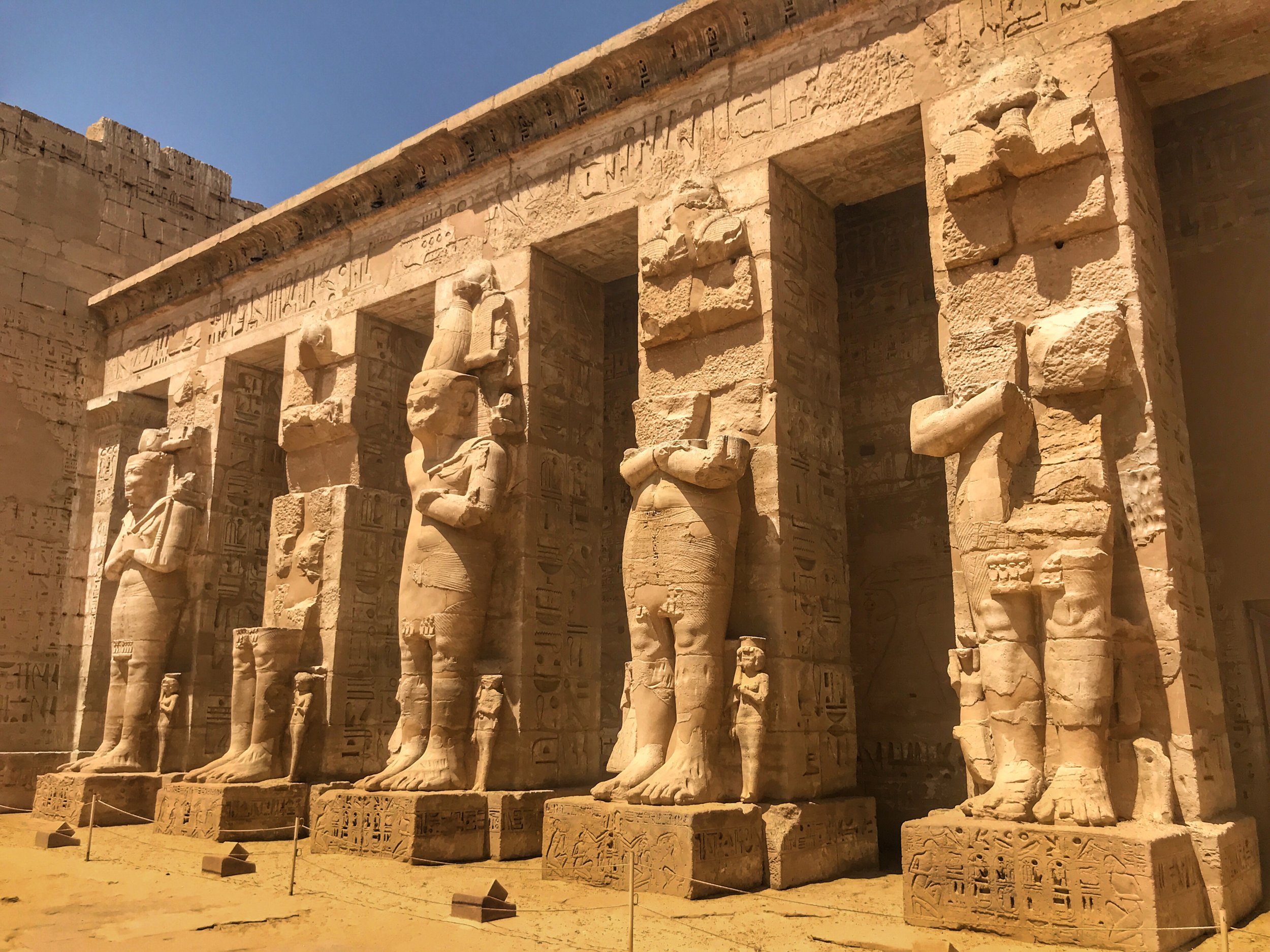
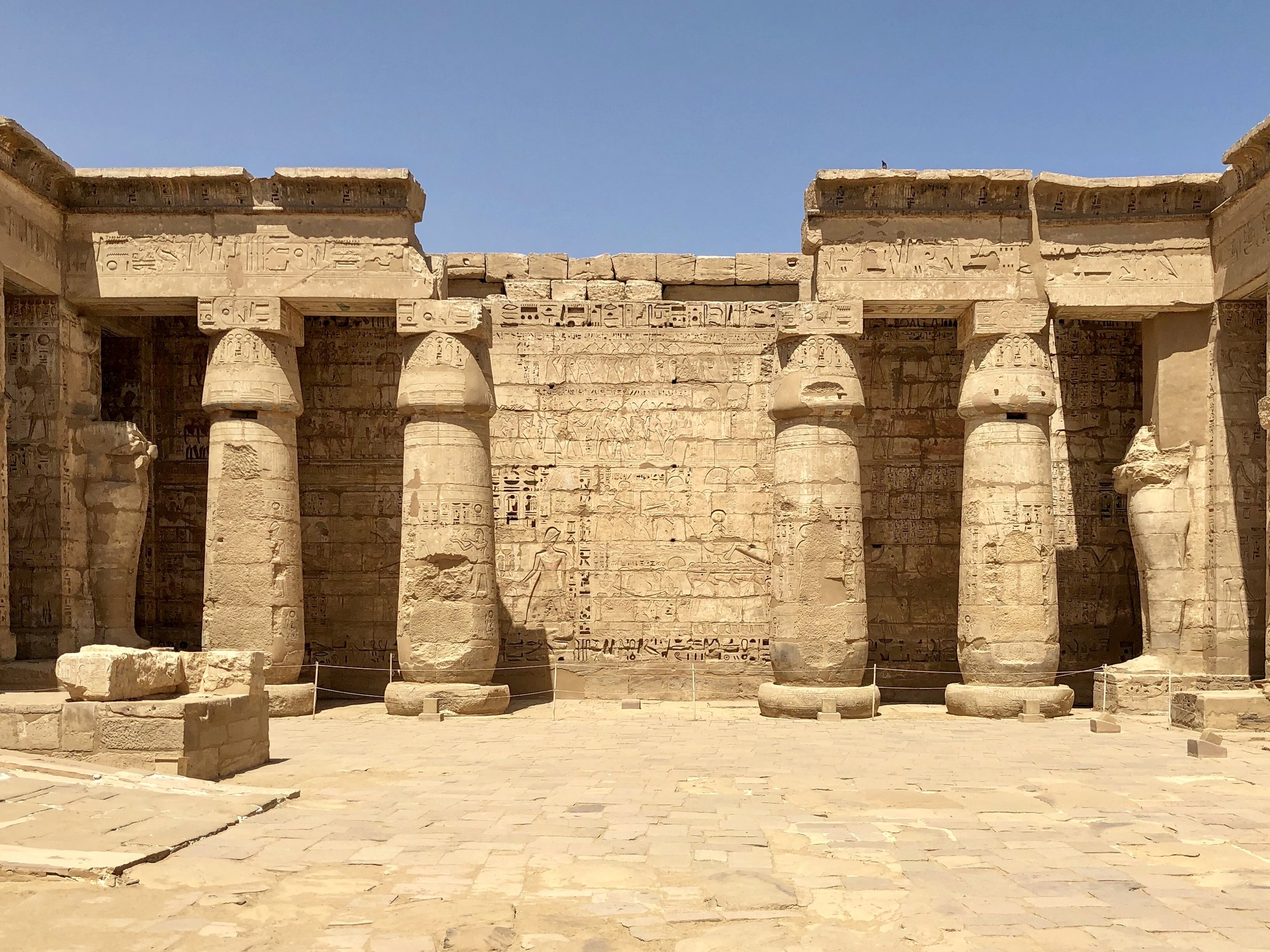
Like many other Ancient Egyptian temples, you proceed through a series of courtyards
From Temple to Amun to Mortuary Temple to Christian Church
The temple within dates to 1490 BCE and was dedicated to Amun, the god of creation and fertility, by Hatshepsut and Thutmose III. It was deemed a magical site, and even today, local farmers are said to believe in the protective powers of Medinet Habu.
Is Duke feeling the magic that Egyptians to this day believe is imbued in this holy site?
Medinet Habu includes a larger version of the Ramesseum. Seems like Ramesses III had to one-up his father
Ramesses III chose this spot for his mortuary temple. It’s essentially a larger-scale version of the Ramesseum, Ramesses II’s mortuary temple — which makes me feel less bad that we skipped visiting that particular temple in favor of this. The pharaoh enclosed the temple within his own, larger complex.
The site functioned as the administrative center of western Thebes, and it was here that the workmen who constructed the royal tombs in the Valley of the Kings went on strike when their payment was late.
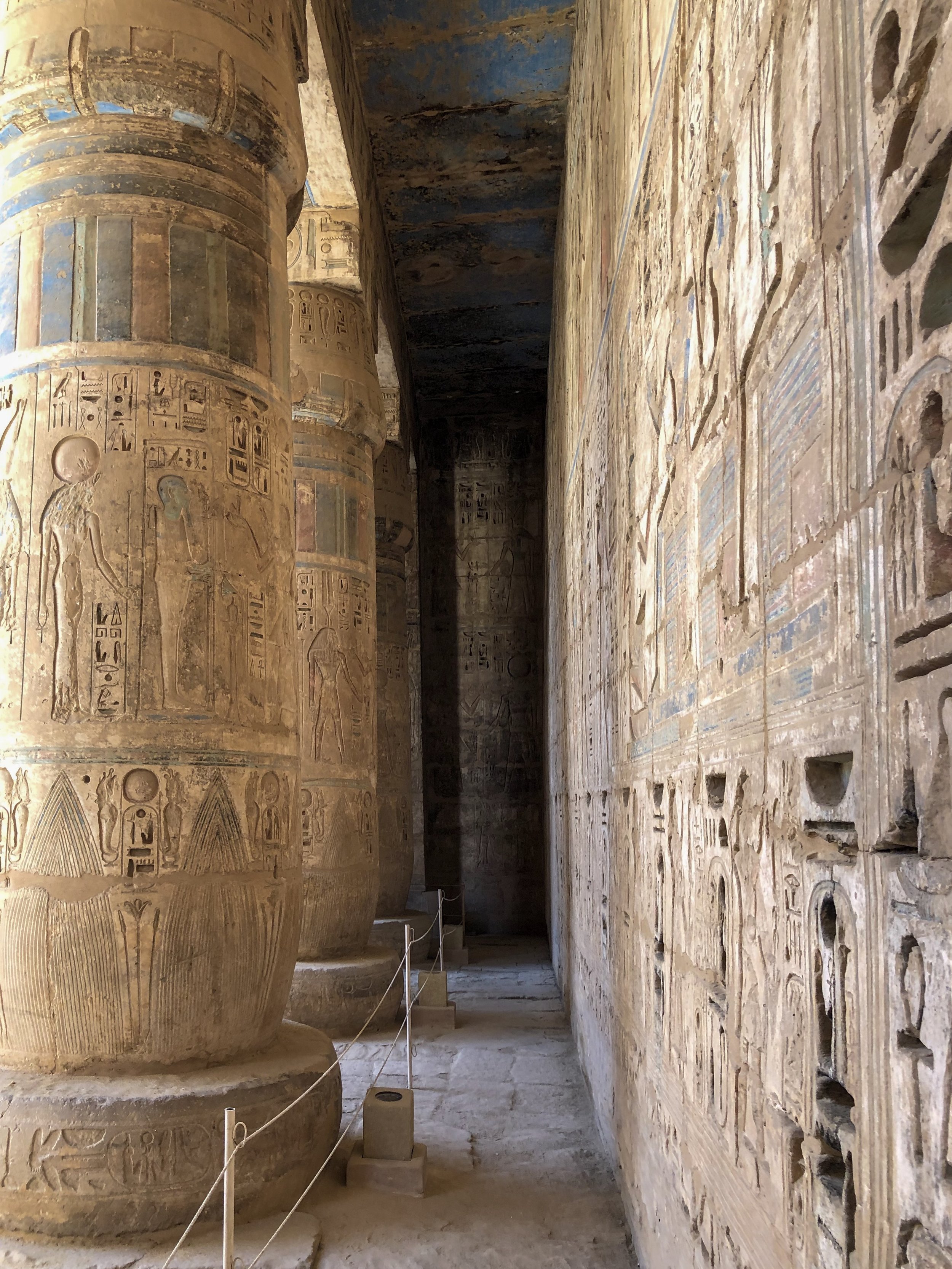
The shaded parts of the colonnade still have blue paint visible
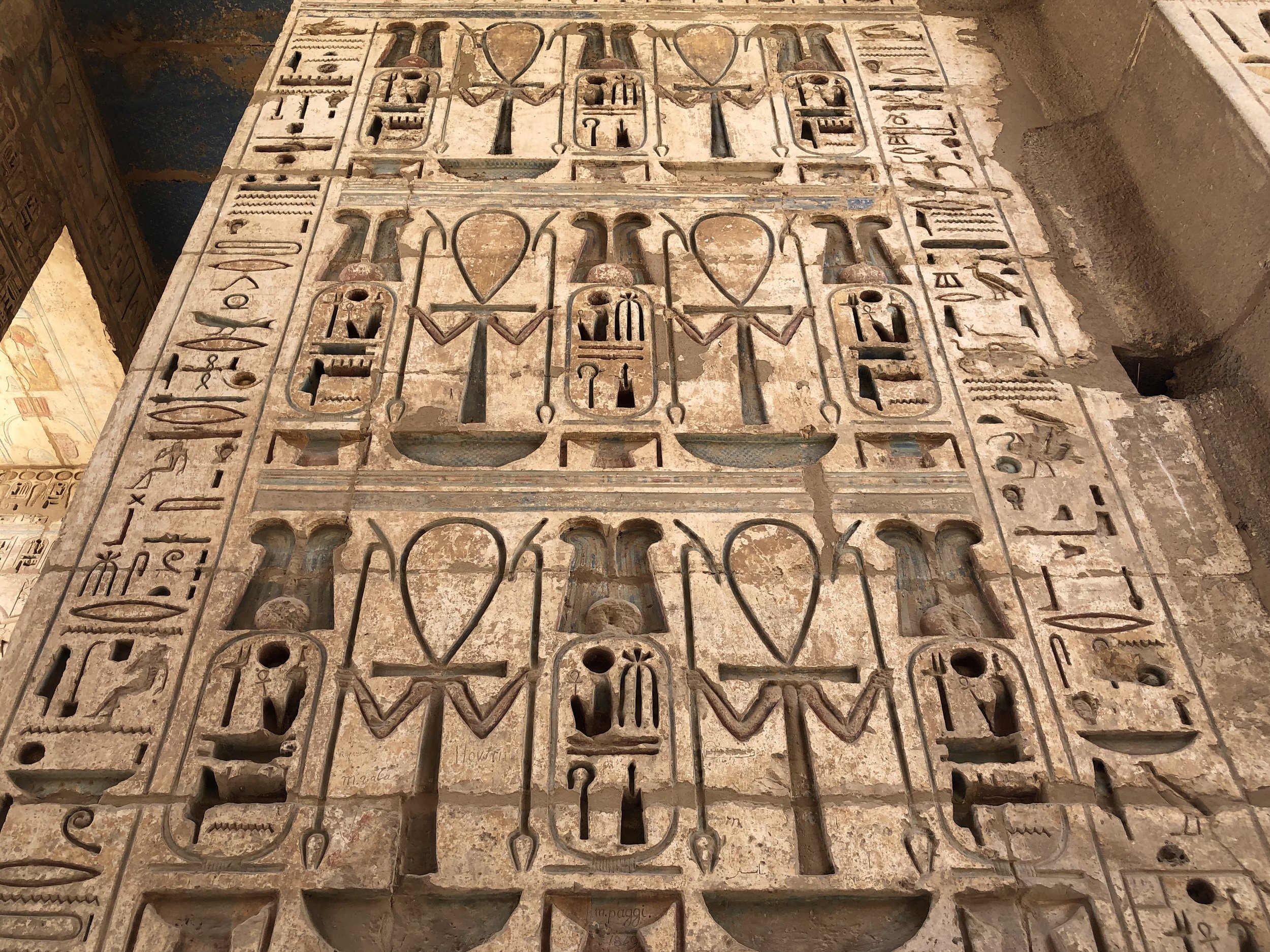
These symbols were ankhs (representing life) with arms holding was scepters (power, dominion)
Shh! Don’t tell anyone, but Wally liked Medinet Habu better than Hatshepsut’s temple
After the Ramesside period, Libyans took control of Egypt, and Medinet Habu gained a dubious claim to fame. The Libyan rulers plundered the tombs of the pharaohs, taking all the riches to the state treasury, and unwrapped the royal mummies in the hunt for hidden jewels. Under the orders of Butehamun, the scribe of the necropolis, in 1066 BCE, the mummies were taken to Medinet Habu for processing and rewrapping before being unceremoniously dumped into the tomb of Amenhotep II.
Hundreds of years after Medinet Habu was built, in the 9th century, Rome’s dominion stretched into Egypt, and the Coptic Christians established the first church in the country. Its ruins remain, off to the right side of the complex. The monk cells behind the church were used for medical experiments, our guide Mamduh told us. Yes, there once was a time when religion and science were seen as compatible.
Look closely: In addition to hands, soldiers are presenting war trophies of chopped-off penises to claim their bounty
Chopped-Off Hands and Penises
In the first courtyard, there’s a window of appearances, where the pharaoh would greet his subjects and reward military commanders. This portico connects the temple to the palace. One of the bas-reliefs on the wall here shows soldiers collecting their bounty by presenting the severed hands of their enemies to the pharaoh. But, Mamduh told us, some of the soldiers tried to double up on their rewards by cutting off both of their victims’ hands. So the king decided to come up with another prize to collect. Gee, what’s portable, and something men only have one of? If you look at the carving, you’ll see that in addition to tossing out hands, the soldiers are also presenting severed penises.
A popular design element in Ancient Egypt was the lotus column, constructed to mimic the plant that symbolized Upper Egypt
Out back is the Great Hypostyle Hall, modeled after Karnak’s — again Ramesses III gained inspiration from his father, Ramesses II
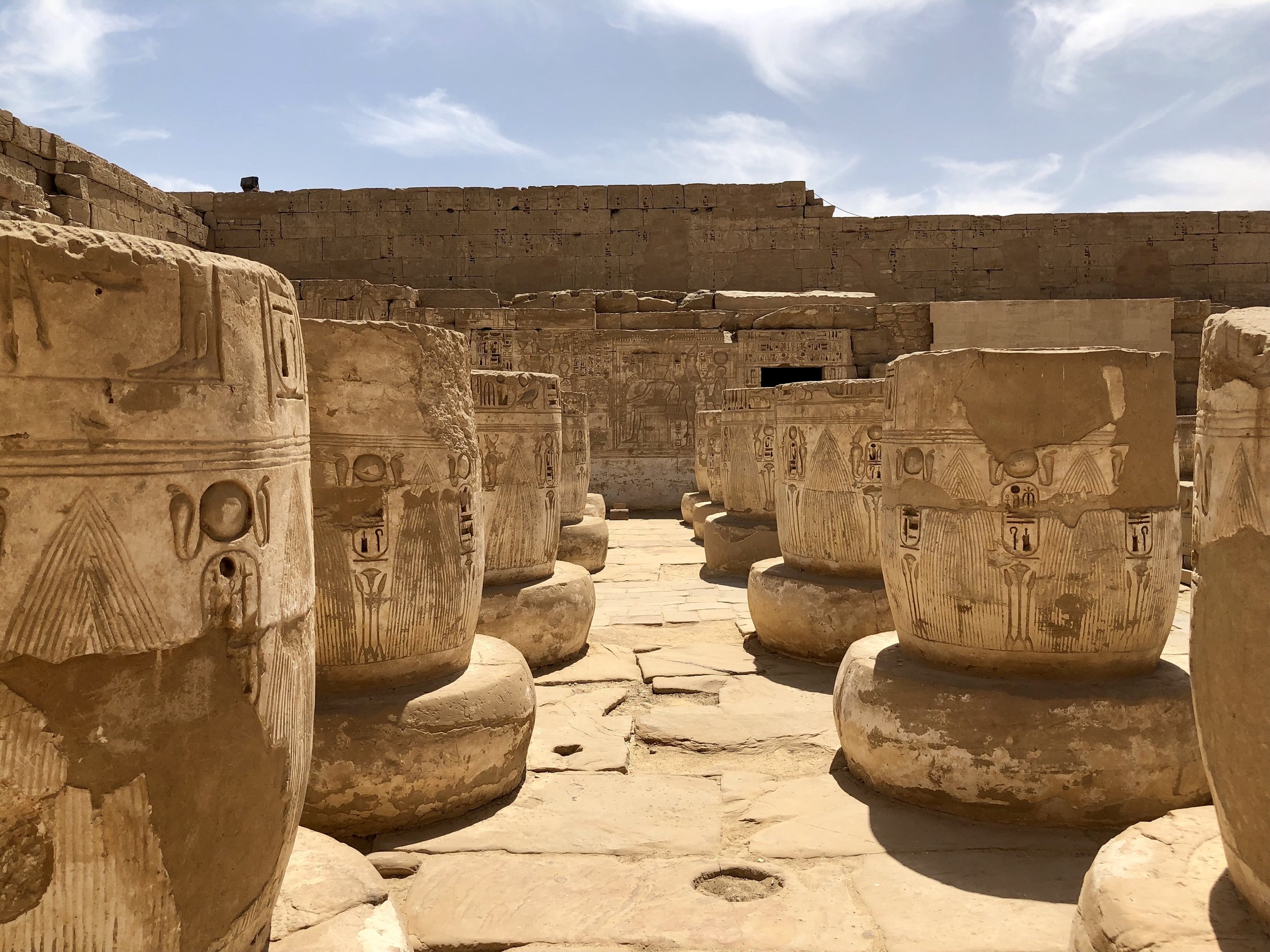
Only the bases remain of most of the columns
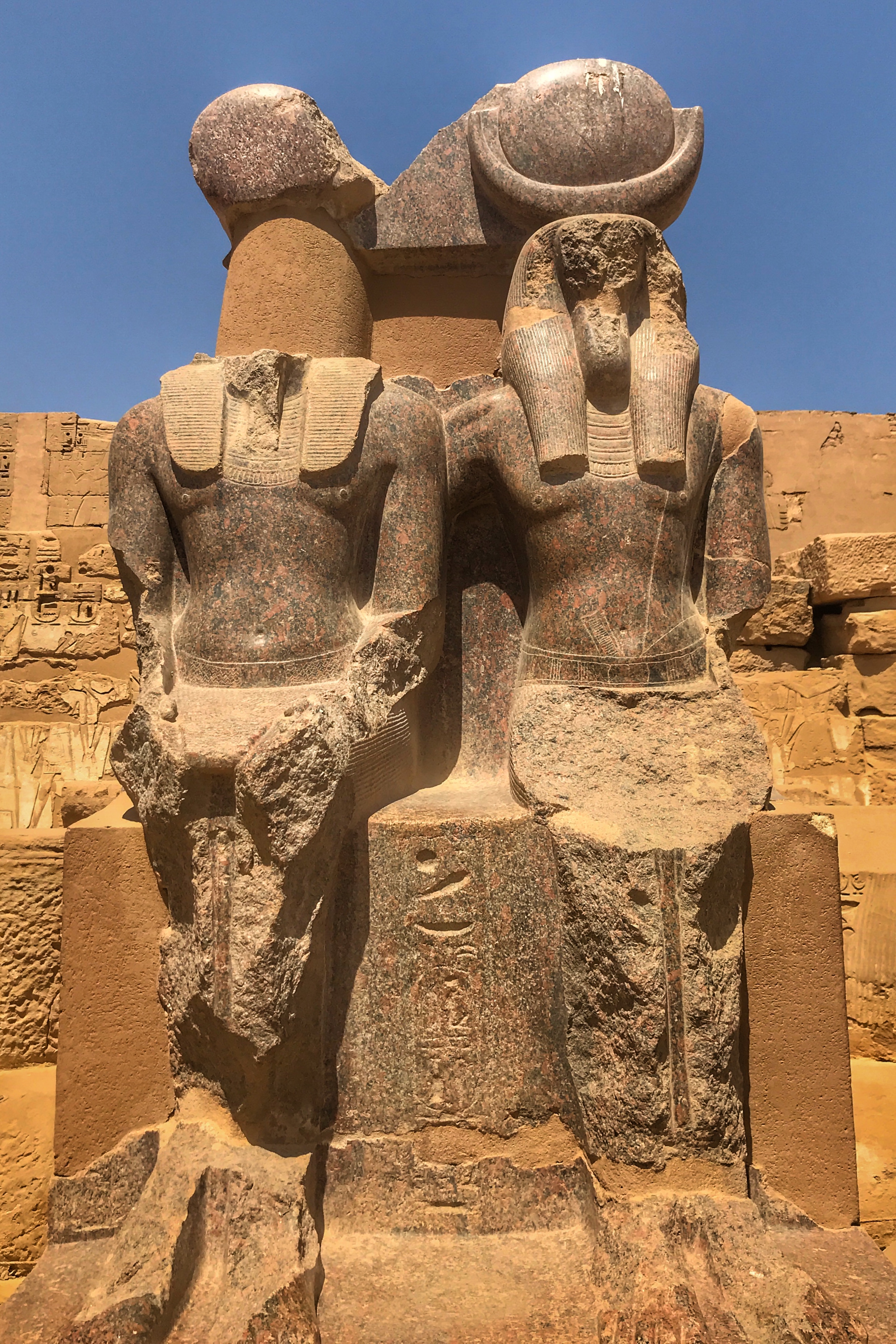
There are four rose granite statues at the very back of the complex. They depict Ramesses III with Maat, the goddess of truth and justice, and Thoth, the god of wisdom
This delightfully grisly scene is just one reason this temple, so rich in history, is well worth visiting. So don’t dick around — add this to your Luxor itinerary. –Wally
The design of Medinet Habu borrows from the military gatehouses Ramesses III encountered in Syria